Name _________________ Test 2 March 7, 2012
advertisement
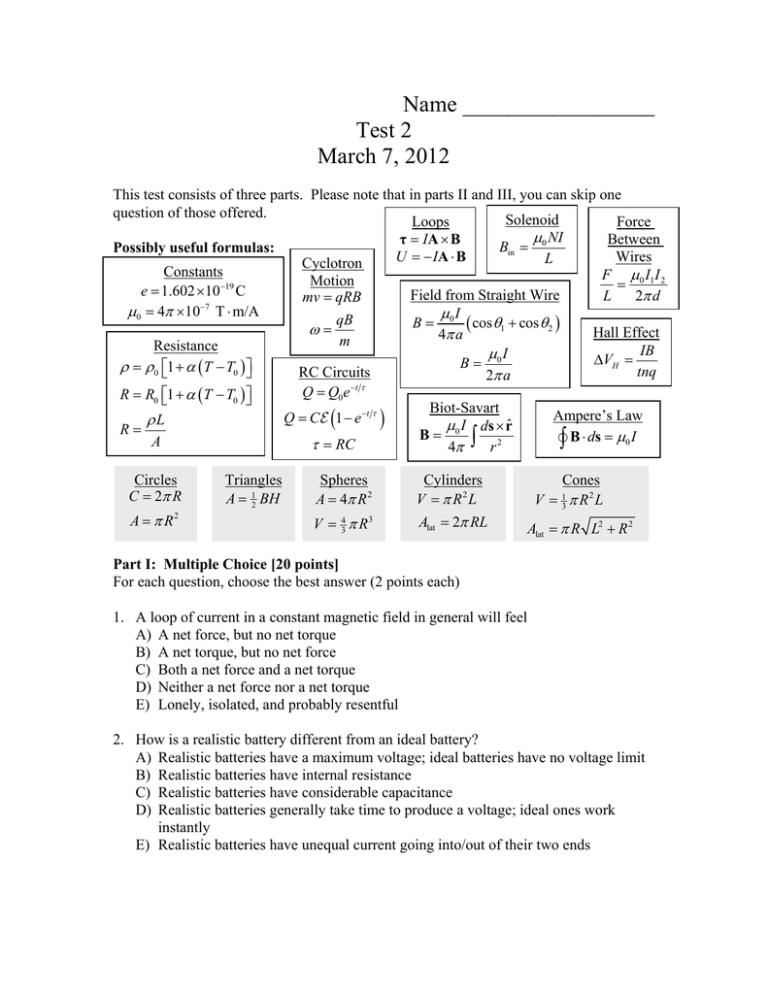
Name _________________ Test 2 March 7, 2012 This test consists of three parts. Please note that in parts II and III, you can skip one question of those offered. Solenoid Loops Force 0 NI τ IA B Between Bin Possibly useful formulas: U IA B Wires L Cyclotron Constants 0 I1 I 2 F Motion 19 e 1.602 10 C Field from Straight Wire L 2 d mv qRB 7 0 4 10 T m/A I qB B 0 cos 1 cos 2 Hall Effect 4 a m Resistance IB 0 I V B H 0 1 T T0 tnq RC Circuits 2 a t Q Q0 e R R0 1 T T0 Biot-Savart Ampere’s Law Q C 1 e t L 0 I ds rˆ R B A B ds 0 I RC 4 r 2 Circles C 2 R A R2 Triangles A 12 BH Spheres A 4 R 2 V 43 R 3 Cylinders V R2 L Alat 2 RL Cones V R2 L 1 3 Alat R L2 R 2 Part I: Multiple Choice [20 points] For each question, choose the best answer (2 points each) 1. A loop of current in a constant magnetic field in general will feel A) A net force, but no net torque B) A net torque, but no net force C) Both a net force and a net torque D) Neither a net force nor a net torque E) Lonely, isolated, and probably resentful 2. How is a realistic battery different from an ideal battery? A) Realistic batteries have a maximum voltage; ideal batteries have no voltage limit B) Realistic batteries have internal resistance C) Realistic batteries have considerable capacitance D) Realistic batteries generally take time to produce a voltage; ideal ones work instantly E) Realistic batteries have unequal current going into/out of their two ends 3. If I am trying to remove 6 C of charge from some object, and I do so with a current of 2 A, how long will it take me to remove the charge? A) 24 s B) 12 s C) 3 s D) 1/3 s E) 1/12 s 4. Which of the following is one of Kirchoff’s rules? A) The total voltage going into a vertex must be zero B) The total current around a loop must be zero C) The total voltage differences across all components in any circuit is zero D) The total current flowing through a capacitor must be zero E) The total voltage differences around a loop is zero 5. In the Hall effect, a current flows through a conductor while a magnetic field is present, and a voltage difference appears across the conductor. Which direction is this voltage difference? A) Parallel to both the current and the magnetic field B) Parallel to the current and perpendicular to the magnetic field C) Parallel to the magnetic field and perpendicular to the current D) Perpendicular to both the current and the magnetic field E) Neither perpendicular nor parallel to the current or the magnetic field 6. In a velocity selector, there are charged particles in a region of a magnetic field. How come the particles move in a straight line, despite the magnetic field? A) The particles are moving parallel to the magnetic field, so no force B) The particles are moving anti-parallel to the magnetic field, so no force C) The particles move so slowly that the magnetic force is negligible D) The particles attract electrons that cancel the charge, so no force E) There is an electric field that exactly balances the magnetic field 7. In which of the following cases is there not a right hand rule? A) Working out the forces from magnetic fields B) Working out the magnetic field inside a loop or solenoid C) Finding the magnetic field from an infinite wire D) Finding electric forces E) Actually, there is a right-hand rule for each of these 8. The formulas for loops have the vector A describing the loop. What is this A? A) A vector whose magnitude is the area and whose direction is perpendicular to the plane of the loop B) A vector whose magnitude is the area and whose direction is parallel to the plane of the loop C) A vector showing the current flowing in the loop, measured in amps, and oriented along the loop D) A vector showing the current flowing in the loop, measured in amps, and oriented perpendicular to the loop E) A vector measuring the current density inside the loop of wire 9. When you put two identical resistors in parallel, the resistance is _________, if you put them in series, the resistance is ___________ A) Decreased, increased B) Increased, decreased C) Decreased, decreased D) Increased, increased E) None of the above 10. A wire with current I going to the right passes through a sphere of radius r. If we calculate the total magnetic flux passing out of the sphere, the result will be A) Positive B) Negative C) Zero D) Insufficient Information E) Can I still drop this class? Part II: Short answer [20 points] Choose two of the following questions and give a short answer (1-3 sentences) or brief sketch (10 points each). - + 11. You have no idea what that curly thing is in this circuit diagram, so you decide to add an ammeter and a voltmeter to the circuit to see what the voltage across it and the current in it are. Add them at appropriate places to the sketch. 12. Ampere’s Law states B ds I . 0 What is the meaning of that funny symbol on the integral? What should be included in the current I? 13. Suppose I have current flowing through an imperfect conductor, and the charge carriers are electrons. Explain how the direction of the electric field, the drift velocity of the electrons, and the current will be related. Part III: Calculation: [60 points] ` Choose three of the following four questions and perform the indicated calculations (20 points each) – 30 k 60k 14. Consider the circuit at right. The capacitor is initially uncharged (a) What is the effective resistance of the two resistors? + 12 V 40 F (b) What is the time constant for this circuit? (c) How much charge has accumulated on the capacitor 0.6 s after the switch is closed? 15. A resistor is going to be made in the shape I of a cylinder with length L = 1.00 cm and unknown radius r. It will be made from carbon, which has a resistivity of 3.5 105 m at T0 20C , and a coefficient of resistance of 5.0 104 / C . (a) At T0 20C , it is supposed to have a resistance of exactly R = 470 . What should be the radius r of the resistor? (b) The resistance is measured on an especially cold day and found to have risen to 480 . What is the temperature? 4.00 cm 16. A solenoid is in the shape of a cylinder 3.00 m in length and 2.00 cm in radius. The solenoid has 800 turns per centimeter, carries a current of I = 0.25 A, and it is wrapped counter-clockwise as viewed from above. (a) What is the magnetic field and the direction of the field inside the solenoid? 3.00 m (b) A proton (mass m 1.672 1027 kg is placed in the solenoid and observed to move in a circular orbit. Which direction does it circle? What is the maximum velocity the proton can be given and still stay within the confines of the solenoid? (c) How long does it take to go in each circle? 5.00 A 1 cm 4 cm 17. A straight infinite wire is carrying a current of 5.00 A to the right. A square loop of side a = 4.00 cm is carrying a clockwise current of 1.00 A and is located a distance 1.00 cm from the infinite wire. (a) Find a formula for the magnetic field due to the infinite wire. Find the direction and the magnitude at the top and bottom of the loop. 1.00 A (b) Find the force and the direction of the force on the top and bottom of the loop due to the magnetic field from the wire. Find the total force. Will there be any forces from the other two sides of the loop? Will they contribute to the total force?