Name _________________ Test 1 - February 10, 2014

Name _________________
Test 1 - February 10, 2014
This test consists of three parts. Please note that in parts II and III, you can skip one question of those offered.
Possibly useful formulas:
Charge on
Surface of
Parallel
Plate
k
e e
Constants
1.602 10
19
C
9 2
8.988 10 N m /C
2
0
8.854 10
12 2
C /N/m
4
0 k e
1
2
Conductor
E
0 n
Metric Prefixes m = 10
–3
,
= 10
–6 n = 10 –9 , p = 10 –12
Capacitor
C
A
d
0
Cylinders
2
V R L
A lat
Part I: Multiple Choice [20 points]
For each question, choose the best answer (2 points each)
2
RL
Energy in a
U
Capacitor
1
2
C
2 u
1
2
Spheres
A
4
R
2
V
0
E
2
4
3
R
3
1. Suppose there is a region where there is an electric field pointing to the right. What will happen to an electric dipole if you place it in this field?
A) It will accelerate to the right
B) It will accelerate to the left
C) It will feel a torque, or twisting force, that tries to get the positive end of the dipole to the right
D) It will feel a torque, or twisting force, that tries to get the negative end of the dipole to the right
E) None of the above
2. Which of the following units is appropriate for measuring electric field?
A) V (only)
B) F (only)
C) N/C (only)
D) V/m (only)
E) N/C or V/m
3. A cube of edge a has charge 24 nC in its exact center, and six additional charges, each of magnitude a –2 nC spaced a distance a away from each face of the cube, so that these additional charges are outside the cube. What is the total electric flux out of the cube?
A) 24 nC/
0
B) nC/
0
C) –12 nC/
0
D) 4
0
E) 2 nC/
0
4. The charge of an electron, in terms of the fundamental charge e , is
A) + e B) C) 0 D) –2 e E) None of the above
τ
Dipoles p E
U
Triangles
A
1
2
BH
C
Circles
2
R
A
R
2
5. If a capacitor is a rectangular parallel plate capacitor of length L , width W , and separation D between the plates, with a material with dielectric constant
between the plates, which of the following would not be a way to double the capacitance?
A) Double
B) Double L
C) Double W
D) Double D
E) Actually, all of these would be a way to double the capacitance
6. For the simple circuit sketched at right, what can we say about the potential?
A) Point A has a potential of 12.0 V
B) Point B has a potential of 12.0 V
C) Point A has a potential 12.0 V higher than point B
A
B
12.0 V
D) Point B has a potential 12.0 V higher than point A
E) None of the above
7. In the presence of electric fields, what happens to charges in an insulator?
A) They can move freely over long distances
B) They can move, but only a very small distance
C) There are charges, but they can’t move at all
D) Insulators do not contain charges
E) It is impossible to have electric fields in an insulator
8. A plane of fixed area A is free to swing around at various angles compared to a background electric field. If we wanted to make the electric flux through the plane as negative as possible, which direction will the normal to the surface n point?
A) Parallel to the electric field (pointing to the right) n B) Perpendicular to the electric field, and pointing up
C) Perpendicular to the electric field, and pointing down
D) Anti-parallel to the electric field (pointing to the left)
E) None of the above
9. What does it mean when we say the electric field is a vector, while the electric potential is a scalar?
A) The electric field has a direction, the electric potential does not
B) The electric potential has a direction, the electric field does not
C) The electric field can produce forces, the electric potential can not
D) The electric potential can produce energies, the electric field can not
E) I have no idea; please mark this one wrong
10. A negatively charged particle in a region of electric fields will be moving towards
A) Wherever there’s free chocolate
B) Regions of strong electric field
C) Regions of weak electric field
D) Regions of most negative electric potential
E) Regions with most positive electric potential
E
Part II: Short answer [20 points] brief sketch (10 points each).
11. Sketched at right are the electric potential lines around a pair of charges
A and B , with the corresponding voltage
+4 kV
0 kV
–4 kV
+6 kV
A
–6 kV
B marked in. Which of these charges is positive or negative, and which of these charges has a larger magnitude (hint – the potential half way in between is 0)?
+5 kV
+3 kV
+2 kV
+1 kV
–1 kV
–5 kV
–2 kV
–3 kV
12. Using the same diagram as for question 11, sketch in the electric field lines, clearly marking the direction of these lines. Sketch at least six lines, and make sure at least some of them go in or near the middle of the diagram. I recommend simply writing over the previous diagram.
13. For the Superbowl, you have purchased a conducting piece of metal roughly in the shape of a football, as sketched at right. If you put charge on it, where will the electric field just outside the football going to be the largest? Where on the surface will the surface charge density be the largest?
Part III: Calculation: [60 points]
Choose indicated calculations (20 points each)
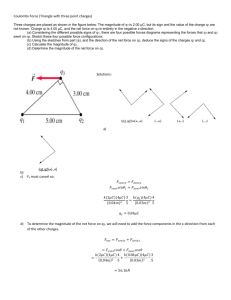
14. Point charges are arranged at the corners of a 30-60-90 triangle with hypotenuse 12.0 cm, with +20.0
C at the 60
angle and –60.0
C at the 30
angle, as illustrated at right. A third, unknown charge q is then placed at the right angle.
(a) Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the right angle from the other two charges
(b) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force on the charge q = -30.00
nC.
60
+20.0
C
–60.0
C
30
90
q
15. A point charge of magnitude q = +2.00 pC lies at the exact center of a hollow conducting sphere of inner radius r = 2.00 cm and outer radius r = 4.00 cm. The conducting sphere itself has a net charge Q = –12.00 pC.
(a) Find the electric field
E
at the following distances from the center: r = 1.00 cm, r =
3.00 cm, and r = 5.00 cm.
(b) Find the surface charge density
, if any, on the interior surface of the sphere, and on the exterior surface of the sphere point charge q
2 cm 4 cm conductor, charge Q hollow space
16. The potential in a certain region of space is given by
V
Axy
where
6
5.20 10 V/m
2
(a) Find all three components of the electric field, E x
, E y
, and E z
, as functions of x and y .
(b) A particle of mass m = 3.00 g and charge q = 2.60
C is initially at rest at position
, ,
. Find the initial acceleration of this charge.
(c) The particle shortly thereafter finds itself at
, ,
.
How much did its potential energy change?
17. Three capacitors, initially uncharged, are connected through two switches and S
1
S
2 to an 18.0 V battery, as sketched at right
(a) Assume first that switch S
2
is open.
When switch S
1
is closed, how much
18.0 V
3.0
F
9.0
F charge flows out of the battery, and what is the total energy in the
18.0
F system of capacitors?
(b) Now, suppose instead that switch S
2
is closed. When switch S
1
is closed, how much charge flows out of the battery, and what is the total energy in the system of capacitors?