TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER TITLE PAGE
advertisement

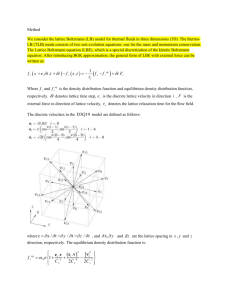
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 2 TITLE PAGE DECLARATION ii DEDICATION iv ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS vi ABSTRACT vii ABSTRAK viii TABLE OF CONTENT ix LIST OF TABLES xii LIST OF FIGURES xiii LIST OF SYMBOLES xv INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 Background of the study 1 1.2 Statement of problem 4 1.3 Objectives 4 1.4 Scope of the study 5 LITERATURE REVIEW 6 2.1 How to simulate a fluid by CFD methods 6 2.2 Kinetic Theory 9 2.3 Lattice Boltzmann method 2.3.1 History 10 2.3.2 The Boltzmann equation 2.3.3 Distribution Function 11 2.3.4 14 Boltzmann Distribution 2.3.5 The BGKW Approximation 2.3.6 Two Dimensional Structure in LBM 10 12 15 17 2 2.3.6.1 D2Q5 and D2Q4 Arrangements 2.3.6.2 D2Q9 Arrangement 17 18 2.3.7 Boundary Condition 2.3.8 Advantages of Lattice Boltzmann Method 19 20 2.4 NanoFluids 2.4.1 History 21 21 2.4.2 Model description 22 2.4.2.1 Single phase 22 2.4.2.2 Two-phase model 23 2.4.3 Thermal conductivities of nanofluids 2.4.4 Application of nanofluids 24 26 2.4.4.1 Heat Transfer Applications 26 2.4.4.2 Automotive Applications 27 2.4.4.3 Electronic Applications (Cooling Microchips) 2.4.4.4 Biomedical Applications 2.5 3 4 4 REFRENCES Lattice Boltzmann model for nanofluids of 30 30 31 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 40 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Algorithm of Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM) 40 3.3 42 Flow Chart for LBM algorithm 40 3.4 Geometry 43 ANALYSIS, FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION 44 4.1 44 Introduction 4.2 Grid Dependency Test 44 4.3 Effect of volume fraction 46 4.4 Effect of Rayleigh number 53 CONCLUSIONS 55 57 3 61 APPENDIX LIST OF TABLES 4 TABLE NO. 1.1 TITLE Development from the Boltzmann equation to the PAGE 16 lattice Boltzmann 1.2 Various viscosity models for nanofluids 33 1.3 Various thermal conductivity models for nanofluids 34 4.1 Grid size for Rayleigh numbers 45 LIST OF FIGURES 5 FIGURE NO. TITLE PAGE 2.1 Fraction of molecules in different speeds 13 2.2 Lattice arrangements for 2D problems, D2Q4 and D2Q5 18 2.3 Lattice arrangements for 2D problems, D2Q9 18 2.4 Bounce back scheme one 19 2.5 Bounce back scheme two 20 3.1 Geometry of this study 43 4.1 Grid dependency test for different Rayleigh numbers 45 4.2 Changing nusselt average with volume fraction for CuO 46 nanoparticles 4.3 Changing nusselt average with volume fraction for Al2O3 47 nanoparticles 4.4 Streamlines of CuO nanoparticles in phi=5% for a)Ra=103 48 b)Ra=104 c)Ra=105 4.5 Effect of volume fraction on streamlines of Al2O3 nanofluid 49 with aspect ratio 1.0 for Rayleigh of a)103 b)104 c)105 4.6 Isotherms of different volume fraction of a)CuO b)Al2O3 nanofluid in Ra=10 4.7 50 3 Isotherms of different volume fraction of a)CuO b)Al2O3 50 nanofluid in Ra=104 4.8 Effect of volume fraction on locale Nusselt number across 51 heated wall 4.9 Variation of y-component of velocity at the horizontal 52 centerline at a)Ra=104 & b)Ra=105 for Al2O3 4.10 Changing of Nusselt number by increasing Rayleigh number 53 4.11 Comparison of isotherms by changing Rayleigh number for 54 CuO, =5% for all the aspect ratios a)103 b)104 c)105 6 LIST OF SYMBOLES 7 cp - Specific heat capacity (J/kg K) C - Lattice streaming speed (m/s) Ar - Aspect ratio fi - Density distribution function fieq - Equilibrium distribution function gi - Energy distribution function gieq - Equilibrium distribution function lx - Length of channel ly - Height of channel k - Thermal conductivity (W/m K) Nu - Nusselt number=−(knf/kf)×(∂θ/∂Y) Nuave - Average Nusselt number=∫Nu⋅dx Pr - Prandtl number=υ/α Ra - Rayleigh number T - Temperature (K) u - Velocity in x direction v - Velocity in y direction H - Enclosure height W - Enclosure weight BGK - Bhatnagar-Gross-Krook CFD - Computational Fluid Dynamics D2Q9 - Three FEM - FDM - Finite Difference Method FVM - Finite Volume Method LB - Lattice Boltzmann Abbreviayions Dimensions nineteen Boltzmann method Finite Element Method velocities lattice 8 LBE - Lattice Boltzmann Equation LBM - Lattice Boltzmann Method LGA - Lattice Gas Approach PDE - Partial Differential Equations MRT - Multi-Relaxation Time SRT - Single Relaxation Time Greek symbols α - Thermal diffusivity (m2/s) ε - Internal energy (J/kg) ϕ - Particle volume fraction μ - Dynamic viscosity (kg/m s) ρ - Density (kg/m3) τ - Relaxation time for fi τc - Relaxation time for gi υ - Kinematic viscosity (m2/s) avg - average C - Cold F - Fluid H - Hot nf - Nanofluid subscripts