Area: Strategy: Appropriate Grade Level:
advertisement

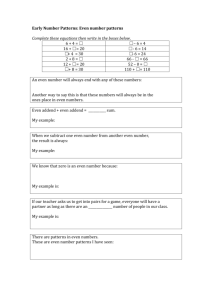
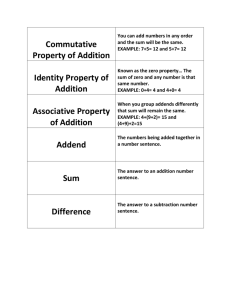
Mathematics Area: Addition Strategy: Counting Appropriate Grade Level: K – 2 Procedures/Steps: Count all – Student counts all of the numbers in the problem one unit at a time. Count on – Student starts with the first number in the problem and counts on the number of units the second number specifies. Maximum addend – First, student determines the smaller number in the problem. Second, the student starts with the smaller number and counts on the number of units the larger number specifies. Minimum addend – First, student determines the larger number in the problem. Second, the student starts with the larger number and counts on the number of units the smaller number specifies. Name of Strategy Count-All Count-On Maximum Addend Minimum Addend Task Count all numbers in the problem one unit at a time. Count on from the first number in the problem. Count on from the smaller number in the problem. Count on from the Larger number in the problem. Example 3+5, start from 1 and count up to 8 one unit at a time. 2+3, start at 2 and add 3 more units, counting one by one. 6+4, start at 4 and add 6 more units, counting one by one. 4+8, start at 8 and add 4 more units, counting one by one. Comments and/or tips: All of the counting strategies should be used for simple addition problems that are of the type A+B=__. The minimum addend counting strategy is the most frequently used out of the four. It is also considered to be the most efficient counting strategy for students in grades k – 2. All of the counting strategies should be taught as an alternative to the “drill and practice” approach. Source: Tournaki, N. (2003). The Differential Effects of Teaching Addition Through Strategy Instruction Versus Drill and Practice to Students With and Without Learning Disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 36(5), 449-458.