• Mahasiswa dapat menghitung pemecahan masalah/kasus model PL dengan menggunakan metode grafik..
advertisement

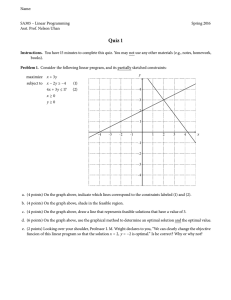
Learning Outcomes • Mahasiswa dapat menghitung pemecahan masalah/kasus model PL dengan menggunakan metode grafik.. Outline Materi: • Contoh-contoh pemecahan kasus PL dengan menggunakan metode grafik.. Contoh-contoh Kasus Optimal Solution y Example 1: 4 Maximize x+y Subject to: x + 2 y 2 x3 3 Feasible Region 2 y4 x0 y0 1 0 These LP animations were created by Keely Crowston. x 0 1 2 3 Contoh-contoh Kasus y Example 2: 4 Minimize ** Multiple Optimal Solutions! x-y Subject to: 1/3 x + y 4 -2 x + 2 y 4 3 2 Feasible Region x3 x0 y0 1 0 0 1 2 3 x Contoh-contoh Kasus y Example 3: 40 Minimize x + 1/3 y Subject to: x + y 20 -2 x + 5 y 150 30 Feasible Region 20 x5 x 0 y 0 10 x Optimal Solution 0 0 10 20 30 40 Do We Notice Anything From These 3 Examples? Extreme point y y y 4 4 40 3 3 30 2 2 20 1 1 10 0 0 1 2 3 x 0 0 1 2 3 x 0 x 0 10 20 30 40 A Fundamental Point y y y 4 4 40 3 3 30 2 2 20 1 1 10 0 0 1 2 3 x 0 0 1 2 3 x 0 x 0 10 20 30 If an optimal solution exists, there is always a corner point optimal solution! 40 Graphing 2-Dimensional LPs Second Corner pt. Example 1: Optimal Solution y 4 Maximize x+y Subject to: x + 2 y 2 x3 3 Feasible Region 2 y4 x 0 y 0 1 Initial 0 Corner pt. x 0 1 2 3 And We Can Extend this to Higher Dimensions Linear Programs in higher dimensions minimize subject to z= 7x1 + x2 + 5x3 x1 - x2 + 3x3 >= 10 5x1 + 2x2 - x1, x2, x3 x3 >= 6 0 What happens at (1,2,3)? What does it tell us about z* = optimal value of z? The Dual maximize subject to z’ = 10y1 + 6y2 y1 + 5y2 <= 7 -y1 + 2y2 <= 1 3y1 – y1, y2 y2 <= 5 0 What is the dual of a dual? Every feasible solution of the dual gives a lower bound on z* The Primal minimize z= subject to 7x1 + x2 + 5x3 x1 - x2 + 3x3 >= 10 5x1 + 2x2 - x1, x2, x3 x3 >= 6 0 Every feasible solution of the primal is an upper bound on the solution to the dual. LP Geometry • Forms a n dimensional polyhedron • Is convex : If z1 and z2 are two feasible solutions then λz1+ (1- λ)z2 is also feasible. • Extreme points can not be written as a convex combination of two feasible points. Barrier Algorithms Simplex solution path Barrier central path o Predictor o Corrector Optimum Interior Point Methods y objective LP optimum feasible solutions x Linear Program y objective optimum of LP relaxation IP optimum feasible solutions = rounding down optimum of LP relaxation x Integer Program