OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Lecture 13: COMP 175: Computer Graphics April 12, 2016
advertisement

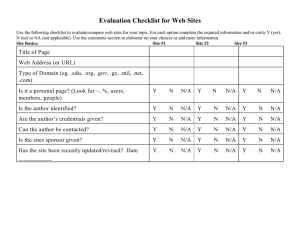
COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Lecture 13: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) COMP 175: Computer Graphics April 12, 2016 Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 1/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Motivation Last week, we discussed the many of the new “tricks” in Graphics require low-level access to the Graphics pipeline For example, using textures, which is a pain in regular OpenGL. Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 2/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Graphics History Software Rendering Fixed-Function Immediate Mode (What we have used) Programmable Pipeline (~2001) Old-fashioned way (Use ray casting) GL Shading Language (What we will learn) CUDA/OpenCL (GPGPU) (~2008) General Purpose GPU Programming Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 3/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ray Casting (Software Rendering) Wolfenstein Quake 1 Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 4/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Fixed-Function Quake 3 Half-Life Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 5/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Programmable Pipeline (Shaders) Doom 3 Far Cry Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 6/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS GPGPU General Purpose Graphics Processing Unit Utilize graphics card for computation Do work other than graphics Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 7/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Old Fixed-Function Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 8/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Programmable Pipeline Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 9/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS 10 4/15/2014 Accessing Programmable Pipeline Introducing Shaders! Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 10/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS CPU + GPU CPU: Typical C++ code GPU: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) CPU passes data to GPU Some processing happens on the CPU: Get mouse movement Load and parse data from disk Some processing happens on the GPU: Transform point from Object to World space Solve lighting equation Render Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 11/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Types of Shaders Most common: Vertex Fragment (Pixel) Newer: Geometry Tessellation Compute Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 12/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Two Things to Learn: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Syntax Sequence and processes Communication between CPU and GPU Vertex Shader Pixel Shader What type of information can be passed How to pass information Note that you also need to know how to load a shader program, but that’s “magic incantation” that (mostly) stays the same every time. Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 13/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 14/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Interfacing with the GPU Modern OpenGL Mobile/Web Programming Direct3D Compute Languages Stream, OpenCL, CUDA Future Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 15/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Client/Server Architecture Think of like a network Client = the CPU Server = the GPU The less they talk, the better Less waiting for memory to transfer Bandwidth is almost always the bottleneck Send data over once, and have it ready to go Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 16/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Optimizations Available Vertex Array Display Lists Vertex Buffer Objects Pixel Buffers Frame Buffer Objects Michael Shah Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 17/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Immediate Mode Every ‘gl’ command is being sent to the GPU every iteration. Very inefficient Think of it like having an interpreter versus a compiler for C++ Michael Shah Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 18/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Vertex Array No more glBegin/glEnd Store Vertices, indices, normals, colors, texture coordinates in an array Minimizes OpenGL calls on Client (CPU) Data still being passed from Client to Server every frame A little better because it’s all at once Stylistically, much cleaner code as well Michael Shah Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 19/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS 20 4/22/2014 Display List Compiled geometry Send it to the Server(GPU) once, and it is stored in memory on Server Geometry cannot be updated, without deleting display list. someGeometryDisplayList = glGenLists(1); glNewList(someGeometryDisplayList,GL_COMPILE); drawShape(); glEndList(); Michael Shah Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 20/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS 21 4/22/2014 Vertex Buffer Object (VBO) Improves upon Vertex Array We can store data on the Server (GPU) Just like display lists! We get a pointer into the Server (GPU) so that we can update it! As good as display lists! Because we have a pointer to the data, multiple clients can access data. Multiple instances of a program can access data Michael Shah Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 21/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Modifiers to Variables Uniform/Varying/Attribute Uniform – Read only data passed into vertex/fragment shaders Attributes – Input value which change every vertex. Read only – Used only in vertex shader Depending on GLSL version: GLSL <3.0: Varying – Pass data from vertex to fragment shader. GLSL >=3.0: in / out – in is the variable being passed in, out is the variable being passed out Read-only in fragment shader. Read/Write in Vertex Shader Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 22/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS OpenGL Shading Language Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 23/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS GLSL C-Like Language Made for GPU Architecture Because GPU’s are different than CPU’s Still Cross Platform Debugging – Still as difficult Domain Specific Language Compiled at runtime Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 24/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS GLSL Primitives float, int, bool Example: float f = 10.0; or float f = float(10); (Casting not allowed, choose your type wisely!) Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 25/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS GLSL Types Vector: vec2, vec3, vec4 Overloaded to take in each type Example: vec4 temp= vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) Matrix: mat2, mat3, mat4 Example: glModelViewMatrix is a mat4 type Access first column with: mat[0] Access second column with: mat[1] Example: mat[1] = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0); Access individual element: mat[2][1]; Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 26/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Some more examples Pass in vec3 into a vec4 vec3 color = vec3(1.0,0.5,0.25) vec4 temp = vec4(color, 1.0) Get components of vector color.x = 1.0; or color[0] = 1.0 color.y = 1.0; or color[1] = 1.0; Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 27/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Swizzling [1] Swizzling is the ability to rearrange a vectors components vec2 pos = temp.xy; // retrieve x and y component, or any of xyzw vec2 pos = temp.yz; vec4 = color.agbr; // opposite of rgba Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 28/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS More GLSL Keywords [1][2] Note that some of these default keywords might not be there depending on GLSL version number (for example: gl_ModelViewMatrix isn’t there any more) Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 29/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Write a Simple Shader Basic Vertex and Fragment Shader Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 30/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Writing a Shader Writing a shader, compiling a shader, and loading a shader Compile at runtime So we do not need to recompile entire source, if we only modify shader. Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 31/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 32/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Simple Vertex Shader Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 33/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Simple Fragment Shader Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 34/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS The cpp file Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 35/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Drawing with immediate mode for now Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 36/XX COMP 175 | COMPUTER GRAPHICS Final Image Remco Chang 13 – GLSL 37/XX