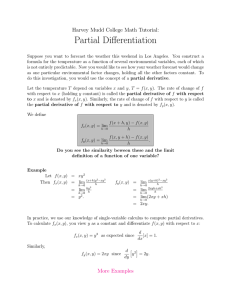
Derivatives of General Exponential Functions (y=b
advertisement
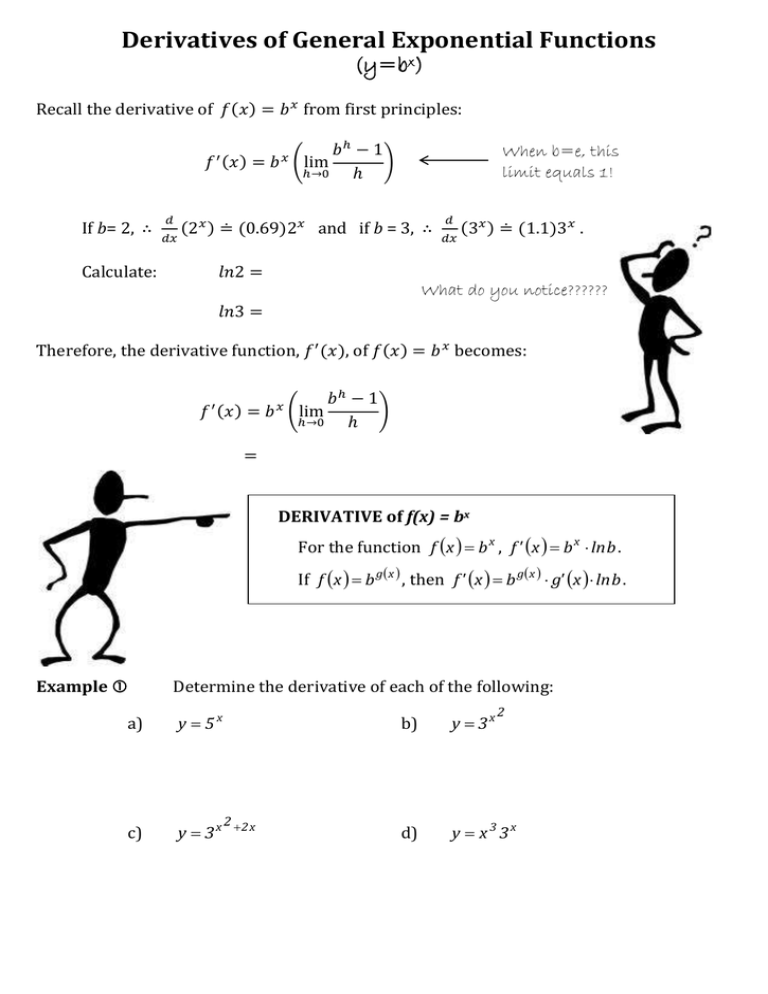
Derivatives of General Exponential Functions (y=bx) Recall the derivative of 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑏 𝑥 from first principles: 𝑓 If b= 2, ∴ 𝑑 𝑑𝑥 ′ (𝑥) 𝑏ℎ − 1 = 𝑏 (lim ) ℎ→0 ℎ When b=e, this limit equals 1! 𝑥 (2𝑥 ) ≐ (0.69)2𝑥 and if b = 3, ∴ Calculate: 𝑙𝑛2 = 𝑑 𝑑𝑥 (3𝑥 ) ≐ (1.1)3𝑥 . What do you notice?????? 𝑙𝑛3 = Therefore, the derivative function, 𝑓 ′ (𝑥), of 𝑓(𝑥) = 𝑏 𝑥 becomes: 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) 𝑏ℎ − 1 = 𝑏 (lim ) ℎ→0 ℎ 𝑥 = DERIVATIVE of f(x) = bx For the function f x b x , f ' x b x ln b . If f x b g x , then f ' x b g x g' x ln b . Example Determine the derivative of each of the following: a) y 5x c) y 3x 2 2 x 2 b) y 3x d) y x3 3x Example Determine the equation of the tangent to f x 2 3 x at x = 2. Example Determine the critical points of f ( x ) 10 2 x e x . Example A certain radioactive substance decays exponentially over time. The amount of a sample of the substance that remains, P, after t years is given by 𝑃(𝑡) = 100(1.23)−5𝑡 , where P is expressed as a percent. 2 a) Determine the rate of change of the function, 𝑃 ′ (𝑡). b) Determine the rate of decay when 50% of the original sample has decayed. Homework: p.240 #1–6, 8