LESSON 3 – THE TANGENT RATIO STEPS FOR LABELING TRIANGLES
advertisement

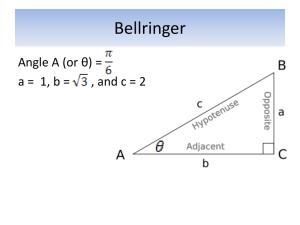
LESSON 3 – THE TANGENT RATIO TRIGONOMETRY – the study of the properties of triangles and triangle measures TRIGONOMETRIC RATIO – ratio of the lengths of two sides in a right triangle STEPS FOR LABELING TRIANGLES 1. Label the hypotenuse first 2. Highlight the angle you know or the one you want to know 3. Label the adjacent and opposite side according to that angle Example ① Label the hypotenuse, opposite and adjacents sides in ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶. a) From ∠𝐶 b) From ∠𝐴 𝐴 𝐵 𝐴 𝐶 𝐶 𝐵 Why do we need to know how to label triangles? THE PRIMARY TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS 𝑆𝑂𝐻 𝐶𝐴𝐻 𝑇𝑂𝐴 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑎𝑑𝑗 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 = ℎ𝑦𝑝 𝑡𝑎𝑛𝜃 = 𝑎𝑑𝑗 𝜃 is called ‘theta’ and is an angle in degrees 𝑜𝑝𝑝, 𝑎𝑑𝑗, and 𝑡𝑎𝑛 are side lengths The ratios relate the sides of a right angled triangle to an acute angle in the triangle Used to determine angles within a triangle or side lengths Example ② Determine the tangent ratio for ∠𝐶 in each of the following: a) 𝐴 b) 10 𝑐𝑚 𝐶 𝑊 𝐶 12 𝑐𝑚 𝑇 𝑜𝑝𝑝 𝑂 Example ③ Calculator Work – Calculate each of the following, to four decimal places. a) 𝑡𝑎𝑛 43° b) 𝑡𝑎𝑛 78° G1 – Press 𝑡𝑎𝑛 then the angle. G2 – Press the angle then 𝑡𝑎𝑛 Example ④ Calculator Work – Calculate ∠𝐴, to the nearest degree. a) 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐴 = 0.8391 b) 𝑡𝑎𝑛 𝐴 = 1.7352 G1 – Press 2nd , 𝑡𝑎𝑛 , then the angle. G2 – enter the angle then 2nd 𝑡𝑎𝑛 Example ⑤ Determine the measure of the acute angles, to the nearest degree. 𝑋 a) b) 𝐷 1 𝑚 𝐸 3 cm 𝑍 7 cm 10 𝑚 𝑌 𝐹 Example ⑥ Determine the length of the unknown side, to the nearest tenth. a) b) 𝑁 𝐵 50° 𝑥 𝑥 42° 𝑂 7m 𝐶 𝑀 18 cm Example ⑦ Solve the following triangle (determine all sides and all angles) 𝑇 52° 2.5 𝑐𝑚 𝑈 𝑉 𝐴