Pertemuan 1 PERTIMBANGAN DAN PROSEDUR UMUM DESAIN Matakuliah
advertisement

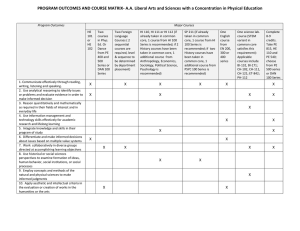
Matakuliah Tahun Versi : D0472/PERANCANGAN ELEMEN MESIN : 2005 : Pertemuan 1 PERTIMBANGAN DAN PROSEDUR UMUM DESAIN 1 Learning Outcomes Pada akhir pertemuan ini, diharapkan mahasiswa akan mampu : – mengidentifikasikan pertimbangan dan prosedur yang harus diambil dalam proses desain 2 Outline Materi • • • • • • • Pendahuluan Pertimbangan Umum Desain Prosedur Umum dalam Desain Besaran dan Sifat Material Pembebanan dan Tegangan Material Selection Safety Factor 3 Pendahuluan How design depend on viewpoint of the individual who define the problems [George E. Dieter, 1991] 4 5 PERTIMBANGAN UMUM DALAM DISAIN • Type of load and stressed • Motion of the parts • Selection of materials • Form and size of the parts • Gesekan dan pelumasan • Use of standard parts • Safety of operation • Workshop facilities • Number of part to be manufactured • Cost • Assembling 6 PROSEDUR UMUM DALAM DISAIN • Make a complete statement of the problem • Select mechanism which will gived the desired motion • Find the forces acting on each member • Select the materials best suited for each member • Find the size of each member • Modify the size to agree with manufacture facilities. • Draw the detailed drawing of each component 7 PEMILIHAN MATERIAL Classification of Engineering Materials ??? 8 9 PEMILIHAN MATERIAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS • • • • • • Physical ? Electrical ? Mechanical ? Thermal ? Chemical ? Fabrication ? 10 PEMILIHAN MATERIAL The most important properties • • • • • • Tensile strength Shear strength Modulus (elasticity, shear) Elongation Yield strength Hardness 11 PEMILIHAN MATERIAL Faktor yang dipertimbangkan : • • • • • • • • • Performance Safety Risk Environmental impact Aesthetics Machineability Cost Recyclability BEBAN 12 BEBAN DAN TEGANGAN •BEBAN (LOAD) •TEGANGAN (STRESS) •REGANGAN (ELONGATION) •TEGANGAN TARIK (TENSILE STRESS) •TEGANGAN TEKAN (COMPRESSIVE STRESS) •TEGANGAN GESER (SHEAR STRESS) Shear Force : A good example of shear force is seen with a simple scissors. The two handles put force in different directions on the pin that holds the two parts together. The force applied to the pin is called shear force. •MODULUS YOUNG •TEGANGAN DUKUNG (BEARING STRESS) •TEGANGAN TEKUK (BENDING STRESS) 13 A Static Load : A good example of this is a person seen on the left. He is holding a stack of books on his back but he is not moving. The force downwards is STATIC. A Dynamic Load : A good example of a dynamic load is the person on the right. He is carrying a weight of books but walking. The force is moving or DYNAMIC. Tension : The rope is in “tension” as the two people pull on it. This stretching puts the rope in tension. Compression : The weight lifter finds that his body is compressed by the weights he is holding above his head. 14 SAFETY FACTOR It is defined, in general, as the ratio of the maximum stress to the working stress, mathematically, FS Max stress Working or design stress In case of ductile materials, the factor of safety is based upon the yield stress. In case of brittle is based on ultimate stress. The selection of proper FS to be used in designing machine components depends upon a number of consideration, such as: the materials, mode of manufacture, types of stress, general service conditions and shape of the parts. 15 DESAIN CONSIDERATION 16 17 18 PENUTUP • Pertimbangan dan prosedur dalam perancangan suatu elemen spesifik untuk elemen tersebut. • Pertimbangan dan pemilihan prosedur merupakan kunci perancangan. 19