Propaganda in World War One 6/21/2016
advertisement

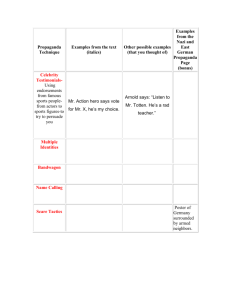
Propaganda in World War One 6/21/2016 What is Propaganda? • Propaganda is a specific type of message presentation aimed at serving an agenda. • The spreading of ideas to promote a certain cause or to damage an opponents cause. • Can take the form of books, posters, pamphlets, songs, movies, newspaper articles or radio addresses. • Propaganda was used to recruit troops, vilify enemies, and create support for the economy. Why do we use Propaganda? • Each of the nations that participated in World War One from 1914-18 used propaganda posters. • They used posters to: – justify their involvement to their own populace – As a means of recruiting men – A way to raise money and resources to sustain the military campaign. – To urge conservation Why Posters? • Television had not yet been invented • Not everyone owned or had access to a radio • Posters were the most effective means of getting a message across Government Support • Quite often propaganda is connected with negative emotions • During the Great War the governments needed money for the war effort so they focused their efforts on posters aimed at raising money from citizens for the war effort Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Name Calling: links a person, or idea, to a negative symbol. • Examples: commie, fascist, yuppie Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Card Stacking: is a propaganda technique that seeks to manipulate audience perception of an issue by emphasizing one side and repressing another. • Examples: a snack food is loaded with sugar (and calories), the commercial may boast that the product is low in fat, which implies that it is also low in calories. Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Band Wagon: makes the appeal that “everyone else is doing it, and so should you.” • Examples: an ad states that “everyone is rushing down to their Ford dealer” Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Testimonial: a public figure or a celebrity promotes or endorses a product, a policy, or a political candidate. • Examples: an athlete appears on the Wheaties box; an actor speaks at a political rally Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Plain Folks: Propagandists use this approach to convince the audience that the spokesperson is from humble origins, someone they can trust and who has their interests at heart. • Examples: an ordinary father talking about the war. Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Transfer: a device by which the propagandist links the authority or prestige of something well respected and revered, such as church or nation, to something he would have us accept. • Example: a political activist closes her speech with a prayer Seven Tricks of Propaganda • Glittering Generality: Vague, sweeping statements and slogans using virtue words; the opposite of name calling, i.e., links a person, or idea, to a positive symbol. • Examples: democracy, patriotism, family Analysis: Purpose: Target Audience: Techniques Used: Analysis: Purpose: Target Audience: Techniques Used: Analysis: Purpose: Target Audience: Techniques Used: