The Cold War.ppt
advertisement

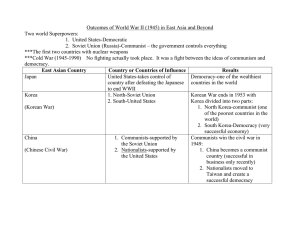
1945 – 1991 The Cold War Difference in Ideologies Capitalism Property Ownership Social Objectives Economic Objective Political System Communism Truman vs. Eisenhower “Containment” [George Kennan] 1. Marshall Plan 2. Truman Doctrine 3. Berlin Airlift 4. NATO 5. NSC #68 6. Korean War “Brinksmanship” [John Foster Dulles] 1. Mutual security agreements. 2. Massive retaliation. 3. M. A. D. 4. “Domino Theory” 5. CIA & covert operations 6. Eisenhower Doctrine 7. “$ Diplomacy” – Part II Foreign Policy “Hot Spots” EUROPE: 1. 1955 Warsaw Pact created. 2. 1956 Hungarian Revolution. 3. 1958 Berlin Crisis. 4. 1959 Nixon-Khrushchev “Kitchen Debate.” 5. 1960 U-2 Spy Incident Foreign Policy “Hot Spots” Middle East: 1. 1953 CIA sponsored coup in Iran P. M. Mohammed Mossadegh nationalization of the Anglo-Iranian Oil Co. 2. 1956 Suez Crisis. 3. 1958 Civil War in Lebanon Foreign Policy “Hot Spots” Latin America: 1. 1948 O. A. S. [Organization of American States] was created during Truman’s administration. 2. 1954 CIA covert ops. in Guatemala. 3. 1950s Puerto Rican independence movement. 4. 1959 Castro’s Communist Revolution in Cuba. 5. 1961 Bay of Pigs invasion Foreign Policy “Hot Spots” Far East: 1. 1953 end of the Korean War. 2. 1954 French depart Indo-China. Geneva Accords 3. 1964 China explodes its first atomic bomb [during LBJ’s administration]. The Cold War begins… USSR and other Communist ally states oppose the USA and endure conflicts across the globe. The Korean War 1950 Bay of Pigs 1961 Cuban Missile Crisis 1962 The Vietnam War 1965 The JFK Assassination November 22, 1963 JFK is assassinated Lyndon Johnson takes over as President Leading Causes of the Korean War Stalin encouraged the spread of communism as long as it did not result in a war with America. He soon realized that nuclear war might be a possibility and wanted to avoid that and beat the USA using more indirect means. The Creation of Eastern Bloc occurred at the end of WWII as most of Europe was divided into democratic or Communist spheres The Domino Effect - Truman believed that if Korea fell to communism, Japan (a major trading partner) would follow. The Truman Doctrine stated that the USA would lend aid to any country not wishing to be suppressed by the political ideals (communism) of any other country. The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was the large- scale American program to aid Europe where the United States gave monetary support to help rebuild European economies after the end of World War II in order to prevent the spread of Soviet communism April 1950 the American National Security Council issued a report recommending direct involvement (a proxy war) against communism. Stalin saw that the Korean War Was a chance for a war by proxy. Kim II Sung visited Stalin to persuade him that he could conquer South Korea. This map is from an American magazine from 1950. This shows how much the US feared communism in the far east. The United Nations now had to formulate a plan. Sixteen member states would provide troops under a United Nations Joint Command. It would fight with the South Korean army. This United Nations force was dominated by America even to the extent of being commanded by an American general – Douglas MacArthur On September 15th 1950, United Nations troops landed at Inchon. The landing was a huge success and the United Nations effectively cut the North Korean army in half and pushed them out of South Korea. Note: MacArthur was later fired by Truman for getting the Chinese involved in the war. United Nations Korean War [1950-1953] Kim Il-Sung Syngman Rhee “Domino Theory” Soviet Union Soviets sold Chinese military equipment, including artillery and MIG fighter planes. The USSR also provided advisers and military hardware to the North Koreans. Soviet pilots flew MIGs against US planes. However, Stalin was unwilling to become involved with the United States in a war over Korea. United States The US provided the majority of the UN military forces which drove the North Koreans out of South Korea and still stand guard along the border. The US moved their troops into South Korea quickly. The US and the Soviets agreed to divide Korea temporarily to avoid long term decisions regarding Korea's future. Although the United States took the lead in the Korean action, it did so under the order of the United Nations. Results There was an armistice signed by North Korea, China, and the UN but not by South Korea. The armistice was NOT a peace treaty, just a temporary cessation of hostilities. Modern Korea Korea is still split up into North Korea (communist) and South Korea (noncommunist) The border between the two countries has remained one of the most heavilyarmed stretches of land on Earth Winners? Losers? After three years, July 27, 1953- ceasefire stopped the fighting Although there was no declared winner, South Korea never succumbed to a communist rule. The Cold War at Home - HUAC The Red Scare allowed for many people in America to be suspected of being communists. Joseph McCarthy pun many Americans on trial under suspicion of being communists. Many called this a witch hunt, similar to the events of the Salem witch hunt.