Document 14471484
advertisement

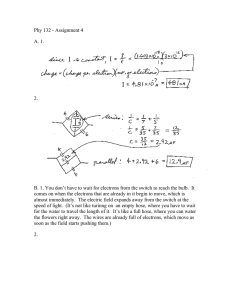
OSSLT Practice: Hydro-­‐Electricity – a Renewable Resource Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Using the natural flow of water from waterfalls and rivers to generate power has existed for thousands of years. It began as simple wheels attached to buildings such as grain mills or saw mills. The water came through and turned the wheel which, in turn, powered the machinery in the buildings. These simple machines meant to utilize the power of moving water eventually evolved into hydro-­‐electric power plants. In these power plants, water is directed through a smaller channel and runs past turbines which are forced to turn by the moving water. The movement of these turbines generates usable electricity. A drawing of a hydro-­‐electric power plant is shown below to demonstrate how one works.. ____ One of the major benefits of hydro-­‐electric power is the fact that it is a renewable resource. In order for a resource to be considered renewable, it must be a natural resource that is always replenished and will never run out. The use of water for electricity is considered a renewable resource because the flow of the water over a waterfall or through a river is part of the water cycle which will continue perpetually. Hydro-­‐electric power is also friendly to the environment because it does not pollute the air or the water. A detractor for hydro-­‐electric power is that it usually entails disturbing the natural aquatic ecosystem. Watersheds and fish migratory patterns are disrupted as the water is redirected from its natural flow. 1. What makes water a renewable resource for energy? a. It flows naturally. b. It does not pollute. c. It never runs out. d. It does not disturb the natural ecosystem. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 2. What does the word “detractor” mean in paragraph 4? a. divert b. disadvantage c. distraction d. farm vehicle 3. Why is the water channelled through smaller channels when turning the turbines? a. to increase the velocity of the water b. to filter the water c. to increase the volume of water d. to decrease the velocity of the water 4. Why does the source of the water need to come from a river or a waterfall and not a lake? a. There is too much water in the lake. b. The water must be moving. c. The water is cleaner. d. The water is colder. 5. Based on the phrase “One of the major benefits of hydro-­‐electric power” from the second paragraph of the selection, what can you reasonably conclude? a. Hydro-­‐electric power has more than one major benefit. b. Hydro-­‐electric power has some minor benefits. c. all of the above d. none of the above 6. What is meant by the words “in turn” used in paragraph 1? a. The wheel must wait in line for its turn. b. The machinery is turning. c. There is a specific sequence to the events. d. The water is turning as it comes through the mill. 7. What does a hydro-­‐electric plant produce? a. clean water b. fuel c. waterfalls d. electricity 8. Why does hydro-­‐electric power alter natural aquatic ecosystems? a. The natural flow of water is re-­‐routed. b. It spurs increased recreation on the water. c. It encourages development along the shoreline. d. It increases the number of non-­‐native species. OSSLT Practice: A Shocking Experience! ____ 9. ____ 10. ____ 11. ____ 12. You walk across a carpet floor in your stocking feet. You stop to shake hands with a friend and receive an unpleasant surprise. You and your friend get shocked. You take a wool hat off your head, and your hair immediately stands up on end. What is this? Why does it happen? It is static electricity. You see, all matter is composed of atoms. Every object has a charge that depends on the number of protons (positively charged particles) and electrons (negatively charged particles) the object has. A neutral object has an equal number of protons and electrons. A negatively charged object has more electrons than protons. A positively charged object has fewer electrons than protons. When two neutral objects are rubbed together, electrons can be transferred from one object to the other. Both objects become charged. As you walk across the carpet, you receive extra electrons and become negatively charged. When you make contact with the other person, your friend acts as a ground, and the extra electrons rush to ground. During the discharge of electrons from your hand, your friend feels the shock, and the electrons return to balance in your hand. The hair stands on end after the removal of the hat because of static electricity. The hat gains electrons and becomes negatively charged, and the hair loses electrons and becomes positively charged. Each hair becomes positively charged, which creates static electricity. The positive charges on the individual hairs react in such a way because the like charges on the hair repel each other. What is the purpose of the first paragraph? a. introduce new facts b. test the reader c. engage the reader d. analyze new ideas What produces the shocking experience alluded to in the title? a. electric current b. static electricity c. ground d. a big surprise Which of the following makes an atom negatively charged? a. equal number of protons and electrons b. more protons than electrons c. more electrons then protons d. more neutrons then electrons or protons What is the meaning of “composed” in the first sentence of paragraph 2? a. calm b. made up of c. cool d. written ____ 13. When a static shock occurs, what are the atoms in the object seeking? a. a discharge b. to repel c. to attract d. balance ____ 14. Why does hair with static electricity stand on end? a. unlike charges repel b. like charges repel c. like charges attract d. unlike charges attract ____ 15. How does rubbing two objects together affect the charges of the two objects? a. It creates friction. b. It shocks both objects. c. Electrons and protons are transferred, creating a positive or negative charge. d. It does not affect the charges. ____ 16. What is the purpose for paragraphs 3 and 4? a. They answer the questions in paragraph 1. b. They present new facts. c. They present supporting facts. d. They provide a conclusion. Check the class web page tonight for the solutions! Electricity OSSLT Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: C 2. ANS: B 3. ANS: A 4. ANS: B 5. ANS: B 6. ANS: C 7. ANS: D 8. ANS: A 9. ANS: C 10. ANS: B 11. ANS: C 12. ANS: B 13. ANS: D 14. ANS: B 15. ANS: C 16. ANS: A PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1 PTS: 1