Circulatory System
advertisement

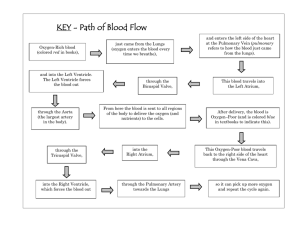
Circulatory System http://www.google.ca/imgres?imgurl=http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/1097.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/imagepages/1097.htm&usg=_ _sxVbmmUP7xtLo3hBoinkdL534Uk=&h=320&w=400&sz=18&hl=en&start=2&um=1&itbs=1&tbnid=cAYwU2vQEnw4M:&tbnh=99&tbnw=124&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dheart%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26sa%3DN%26rls%3Dcom.microsoft:*%26tbs%3Disch:1 The Heart • ___________ between the ___________ above the ___________ • Surrounded by pericardium – Protective membrane • Consists of 4 chambers 1. ___________ 2. ___________ 3. ___________ 4. ___________ 1+2 = Upper chambers 3+4 = Lower Chambers http://www.bami.us/Images/Cardiac/HeartNIAAA.gif Heart con’t • ________ receive the blood from the lungs and body cells and then pump it to the ____________ • Ventricles are ____________ and pump the blood out of the heart to the lung and body cells How Blood Travels • Starts off _____________ and in the _____ atrium • Receives ___________ blood from all body cells • Atrium _________, passing blood through the tricuspid valve into a relaxed right ventricle • Right ventricle contracts and the blood then goes through the semi-lunar valve into the ______________, which carries the blood to the lungs • Place of gas exchange – Carbon dioxide out – Oxygen in How blood travels con’t • ___________ blood returns from the lung by the _______________ and enter the left atrium • The ______atrium contracts and sends blood through the bicuspid valve into the _______ventricle • The left ventricle contracts and the blood passes through the semilunar valve and into the ________ which carries blood to all parts of the body except the lungs • The blood returns to the right atrium by the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava – Superior = upper body parts – Inferior = lower body plus abdomen • Left side of heart oxygenated blood (thicker wall) • Right side of heart deoxygenated blood (thinner wall) http://www.health.com/health/static/hw/media/medical/hw/h9991260_001.jpg http://www.preventing-a-heart-attack.com/images/heart-blood-flow.gif Heart Nourishment • Above the aortic semilunar valve is the opening of a vessel that carries blood to nourish the heart muscle • Coronary (heart) circulation – System of vessels that supply heart muscle • Systemic circulation • Blood flow to the upper and lower body and back to the heart • Pulmonary circulation • blood flow between the lungs and the heart Heart Rate • Group of specialized cardiac muscle cells called the ______________ – Located in the wall of the right atrium – Generate _________________ causing the muscle to contract • Nerves connect brain and pacemaker – One nerve increase in heart rate – Different nerve decrease in heart rate – As cells need more energy, there’s an increase in heart rate Circulation and Blood • Your circulatory system contains _____ of blood • Carries – ____________ to cells – __________ away from cells – ____________________ from cells in one part of the body to another – Help the body ________ against invading organisms • Definition • Blood travels in repeating loops Blood Components • • • • ______ of blood is fluid (plasma) ______ is blood cells Mostly RBC (red blood cells) ______are WBC (white blood cells) http://www.jonbarron.org/content/images/blood_components.gif Blood Components con’t Plasma • Contains – proteins – glucose – vitamins – minerals – dissolved gasses – waste products from metabolism Blood Components con’t RBC (Erythrocytes) • • • • _______ nucleus when mature 4.5- 5.5 billion RBC in each 1mL of blood Primary function is to _____________ Red in color because of _____________ http://stearn.ca/blog/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/red-blood-cells.bmp Blood Components con’t RBC (Erythrocytes) • How RBC carry oxygen 1. Pick up oxygen as blood is passed through the lungs 2. Oxygen and hemoglobin join to form oxyhemoglobin (bright red color) 3. As blood passes around the body, oxyhemoglobin breaks down and releases oxygen to the body cells 4. Without oxygen blood is dull red. Once cycle is complete, blood is pumped back to the lungs for more oxygen. http://www.clarian.org/ADAM/doc/graphics/images/en/19510.jpg Blood Components con’t RBC (Erythrocytes) • Anemia – Shortage of hemoglobin in the blood – Casues • Few RBC • Lack of hemoglobin • Lack of iron Blood Components con’t RBC (Erythrocytes) Blood types - carry proteins that determine blood types - 4 different blood types - A, B, AB, O Aggulation when different blood types mix they form clumps - clumping of cells clogs up circulation and without treatment, major tissue damage and even death may result Blood Components con’t RBC (Erythrocytes) Blood Type Antigen Present in RBC Antibodies present in plasma A A Anti – B B B Anit – A AB Universal Acceptor A and B None O Universal Donor none Anit – A and Anit - B http://academic.kellogg.edu/herbrandsonc/bio201_mckinley/f21-7a_abo_blood_types_c.jpg Blood Components con’t RBC (Erythrocytes) • Also carry antigens for Rhesus (Rh) factor – Child may be in danger if father is Rh+ and mother is Rhand baby inherits Rh+ from dad – During pregnancy the blood from the mother and baby are separated by the placenta and do not mix • But during child birth, blood cells can pass from embryo to mother – Mom produces antibodies to fight these antigens – During next pregnancy, if baby is Rh+, mom’s antibodies may pass to baby and start to clump the baby’s RBC • RBC are unable to pass through the narrowed channels • Low oxygen levels cause baby to turn blue “Blue Baby” Therefore, all pregnant women with ‘-ve’ blood types need to be given ‘Rogam’ shot http://www.pennmedicine.org/health_info/pregnancy/graphics/images/en/19789.jpg Blood Components con’t WBC • Body’s immune system • 2 types of actions 1. ______________________ (lymphocytes) - destroy germs by making them stick together or dissolving 2. __________________ (macrophages) - pac-man - move towards germs, surround and digest them WBC cancer _________________ - treatment is bone marrow transplant Blood Components con’t Platelets • Fragements of cells formed in the bone marrow • Help _______ bleeding from cuts by producing tiny fibres that form a scab until the new skin grows http://biomed.brown.edu/Courses/BI108/BI108_2005_Groups/10/pictures/web/platelets1.jpg Artery • Transports blood from the _______to the rest of the body • _________ deep within body • Artery wall is very ______ and has _________ fibres – Blood pumped into artery very fast and at a high pressure, so elastic fibres need to stretch http://www.clarian.org/ADAM/doc/graphics/images/en/19194.jpg Vein • Transport blood to the heart from the body • Wall of the vein is made up of the same layers as an artery however, the outer coat and muscle layer is NOT as thick • Function is to collect blood • Very LOW pressure • Valves in the veins stop blood from flowing in the opposite direction http://www.adronline.org/images/evlt/blueVein.gif Heart Disorders • Heart Disease – Leading cause of death in Canada and US • Heart Murmur – When the heart valves do not close properly – Makes a muffled sound – Heart needs to beat faster which may cause fatigue Heart Disorders con’t • Heart Attack – Caused by blocked in coronary circulation – Blockage decreases or stops flow – With no glucose or oxygen to muscle cells of the heart they die – Treatment • Faulty valves can be replaced • By pass surgery • Heart transplant http://www.web-books.com/eLibrary/Medicine/Cardiovascular/Images/HeartAttack.gif Heart Disorders con’t • ____________________ – Artery becomes less elastic • ____________________ – Occurs when deposits of cholesterol build up on the inner wall – Heart has to work harder – Treatment • Angioplasty Arteriosclerosis Heart Disorders con’t • Angina – Chest pain that results from a partial blockage of coronary artery Heart Disorders con’t • Blood Pressure – Force that blood exerts against the wall of a blood vessel – Pressure is highest in arteries when the ventricle contracts – Pressure drops in arterioles when ventricle is relaxed • Systole- contraction of ventricles • Diastole- relaxation phase Normal Blood Pressure is Diastole Systole 120/80 Relaxation Contraction Heart Disorders con’t • Hypertension (High blood pressure) 150/100 - many causes - atherosclerosis (heart works harder) - overwieght - treatment - medication, weight loss, low-salt diets http://www.control-your-bloodpressure.com/images/HighBloodPressure.jpg