Animal Physiology Unit
advertisement

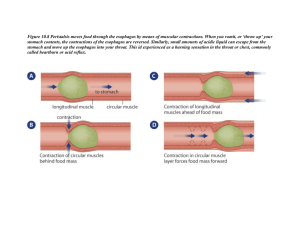
Animal Physiology Unit Organ Systems • _____________is composed of many different sytems with cells being the smallest unit of life. • When cells are similar in shape and size, they work together and form tissues. • four main types of tissues: 1. _________- protection; lines body cavity, organs, etc 2. _________- provides support and holds things together 3. ________ - bundles of cells which contract to create movement 4. ________ - provides communication between all structures • Your body also have various types of organs which carry out different but specific tasks. • These organs have to work together in order to achieve the desired result in something called an organ system. Organ System Major Organs Main Funtion Digestive Esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas Breakdown of food (phys and chem.) Circulatory Heart, blood, vessels Respiratory Lungs, trachea, blood vessels Gas exchange Reproductive Testes, vas deferens, ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, glands Sexual reproduction Excretory Kidneys, bladder, ureter, urethra Removal of wastes Locomotion Bones, muscles Movement of body and body parts Endocrine Pancrease, pituitary gland, adrenal glands Coordination and chemical regulation of body activies Nervous Brain, spinal cord, eyes, ears, nose, tongue, peripheral nerves Response to environment; control of body activities Transport of nutrient, gases and wastes; defence against infection Central Nervous and Endocrine System _____________ • body is constantly changing and so are levels of nutrients, water, etc • homeostasis helps to maintain the bodies stable state – for ex. • Blood = 7.35 pH • Body temp = 37 celcius • Heart rate = ~ 72 bpm (beats per minute) • there is a ______ which determines when a change is drastic and dangerous versus normal and safe – for example, if your body temp drops below 36.2 C then, you will shiver in an attempt to warm up – if your body temp rises about 37.2 C then, you will sweat in an attempt to cool off • diagnosising a patient with a sickness has to do with comparing their symptoms to those of the normal range Component Normal Range Unit Diagnosis Body temperature (outside) 36.2- 37.2 Blood pH 7.35- 7.45 pH Unit Acidosis ( low pH) Alkylosis (high pH) Resting heart rate pulse 50-100 Beats/ min Tachycardia (fast hrt rate) Bradycardia (slow hrt rate Resting breathing rate 16-20 Breaths/ min Hyperventilation (fast breathing rate) Hypoventilation (slow breathing rate) Degrees celcium Fever (high body temp) Hypothermia (low body temp) Digestive System • Ingestion – taking food in, eating • Digestion – Process of reducing food to small molecules so that it can be absorbed by the body – Molecules must be small enough to fit inside the _____ – Digestion takes place in the _________________ which is the tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus – There are two types of digestion • 1. ______________________ – Physical breakdow of food into smaller particles – Inolves chewing (__________) and muscular churning (___________) • 2. ______________________ - Involves chemical breakdown of large molecules into smaller molecules with the use of ________________. Absorption: movement of nutrients into the blood and cells Egestion: elimination of waste or unusable nutrient The Mouth (a.k.a.- the beginning) • Teeth – _______________ • front teeth (chisel shape) • used for biting or cuting food into smaller pieces – _______________ • pointed shape • tear food – _______________ • grinding and chewing food – _______________ • grinding and chewing The Mouth con’t • Saliva – Makes food easier to swallow – 3 pairs of glans (parotid, submandibular, sublingual) – Contains enzyme called ________ which breaks down big sugars into smaller sugars • Tongue – – – – Muscular organ Keeps food where it can be chewed Forces food to the back of the mouth for swallowing Responsible for taste The Mouth- Swallowing • Tongue forces food to back of the mouth called the ___________ • _________ closes the upper part of the pharynx • Epiglottis is a trap-door like structure that prevent food from entering the windpipe • Esophagus – Tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach – Muscular tube – The hollow interior space of the esophagus is called the ___________ – it’ is lined by a layer of cells called mucosa cells – these secrete mucus Step 1: Food is pushed to the back of the mouth by the tongue. Step 2: Tongue raises and pushes food further back. Soft palate lifts to close nasal cavity. Epiglottis starts to close, glottis closed. Step 3: Soft palate closed, epiglottis closed and food slides down esophagus. Step 4: Soft palate opens, epiglottis and glottis open. Peristalsis • Rythmic muscular action that moves food through the entire alimentary canal Stomach • Opening to the stomach is controlled by a ____________ muscle • ‘j’ shaped • ________________ is its major function • 3 kinds of cells line the stomach and secrete – __________ – __________ – Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and water • Enzymes, water and HCl combine to form ________. Stomach con’t • Gastric Juice – Has a pH of 1 (strong acid) – Helps to break up connective tissue, cell membranes as in food, and also kills many harmful bacteria • Enzymes produced by the stomach are mostly ___________ • The principal stomach protease is called _________ – Pepsin breaks down protein Why are stomach cells not destroyed by the gastric juice? • __________ acts as a protective barrier • gastric juice wears at the mucus, thus the stomach must continually renew its protective coating • Occassionally stomach cells are attached by gastric juices and produce ________ – Stress can cause a decrease in production of mucus Lower Alimentary Canal • There are 2 organs that food DOES NOT enter but play an important role in digestion 1. ___________ • 2 functions – Produce regulatory hormones for blood homeostasis – Produe pancreatic juice (BASIC) » Neutralizes stomach contents » Contains digestive enzymes 1. ____________- breakdown protien 2. ____________- breakdown food 3. ____________- breakdown carbohydrates Lower Alimentary Canal con’t 2. Liver - converts extra glucose into glycogen and stores it until it is needed - produces bile; an emulsifier that breaks fat and oil into tiny droplets - bile travels through the ducts to the ______________, where it is stored - bile is released through the common bile duct to the small intestine Small Intestine • Main job is digestion and absorption • lining of the small intestine has small finger-like projections called _________ – increase the surface area so nutrients can pass through the lining cells and enter the circulatory system rapidly – Each villus contains many blood and lymph vessels • Collect nutrient and transports them to locations where they’re needed Small Intestine con’t • Villi are made up of smaller ________ which further improve the absorption • Some substances ingested are composed of small molecules that dissolve readily – ie. ________and ___________- not digested. Simply pass through the stomach wall and are absorbed directly into the blood stream Small intestine con’t • Composed of three parts: 1. Duodenum 2. Jejunum 3. Ileum Small Intestine con’t 1) Duodenum - first ______ of small intestine - bile and pancreatic juice enter here - digestive enzymes produced here - polypeptides amino acids - disaccharides monosaccharides Small Intestine con’t 2) Jejunum - next several meters - many small molecules are absorbed through the villi into blood vessels - most of the chemical digestion is completed here Small Intestine con’t 3) Ileum - last half of small intestine - place of absorption - amino acids and glucose enter the blood stream and go to the liver Large Intestine • Twice as wide as small intestine • Major function is to absorb water and ions • Where the small and large intestine join there is a small structure called the ________ • Humans no function • Rabbits digest cellulose • Appendicitis bacteria enter appendix, grow and secrete toxic waste Rectum - last 20-30 cm of colon - stores feces Anus - way out for feces!!