ME 2560 Statics Vector Components and Vector Addition (2D)
advertisement
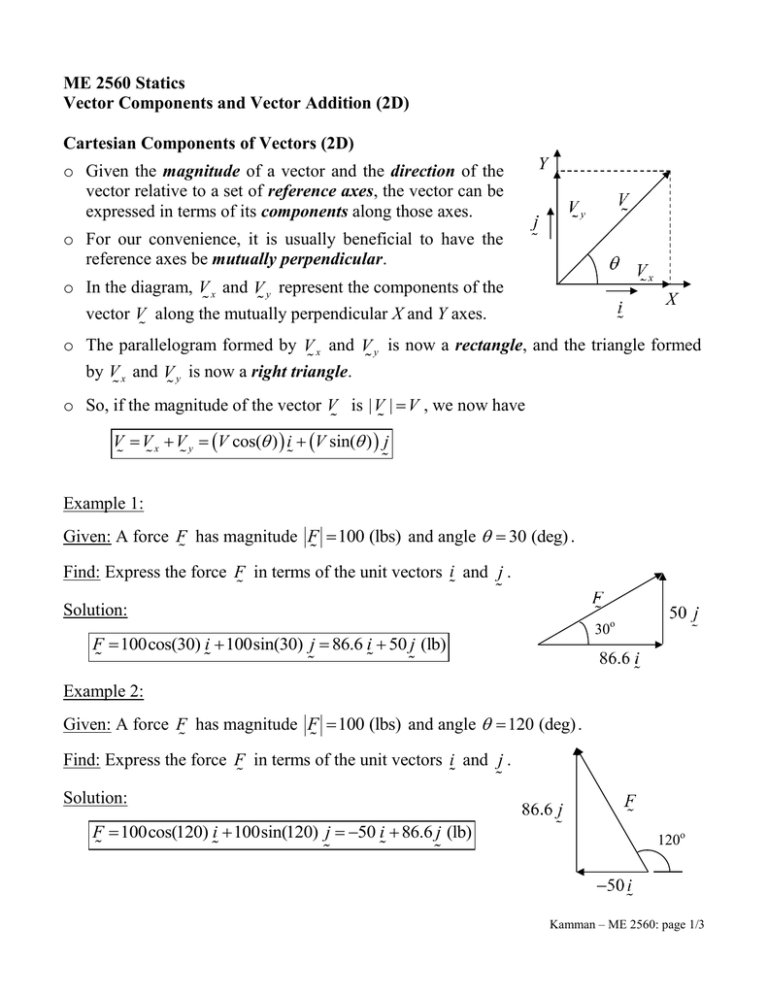
ME 2560 Statics Vector Components and Vector Addition (2D) Cartesian Components of Vectors (2D) o Given the magnitude of a vector and the direction of the vector relative to a set of reference axes, the vector can be expressed in terms of its components along those axes. Y o For our convenience, it is usually beneficial to have the reference axes be mutually perpendicular. o In the diagram, V x and V y represent the components of the vector V along the mutually perpendicular X and Y axes. X o The parallelogram formed by V x and V y is now a rectangle, and the triangle formed by V x and V y is now a right triangle. o So, if the magnitude of the vector V is | V | V , we now have V V x V y V cos( ) i V sin( ) j Example 1: Given: A force F has magnitude F 100 (lbs) and angle 30 (deg) . Find: Express the force F in terms of the unit vectors i and j . Solution: 30o F 100cos(30) i 100sin(30) j 86.6 i 50 j (lb) Example 2: Given: A force F has magnitude F 100 (lbs) and angle 120 (deg) . Find: Express the force F in terms of the unit vectors i and j . Solution: F 100cos(120) i 100sin(120) j 50 i 86.6 j (lb) 120o Kamman – ME 2560: page 1/3 Example 3: Given: A force F 70 i 50 j (lb) . ? Find: The magnitude and direction of F . ? Solution: 35.54 (deg) F 702 502 86.0 (lbs) and tan 1 (50 / 70) 0.6202 (rad) Example 4: Given: A force F 50 i 70 j (lb) . ? Find: The magnitude and direction of F . ? Solution: F (50) 2 702 86.0 (lb) 54.46 180 125.5 (deg) 0.9505 2.191 (rad) tan 1 (70 / 50) Kamman – ME 2560: page 2/3 Vector Addition using Cartesian Components (2D) To add two or more vectors, simply express them in terms of the same unit vectors, and then add like components. Example 5: Given: F1 150 (lbs) , 1 20 (deg) F2 100 (lbs) , 2 60 (deg) Find: a) The total force F acting on the support in terms of the unit vectors shown. b) the magnitude and direction of F . Solution: a) The total force is the vector sum of the two forces. F1 150cos(20) i 150sin(20) j 140.95 i 51.3 j (lb) F2 100cos(60) i 100sin(60) j 50 i 86.6 j (lb) F F1 F2 (140.95 50) i (51.3 86.6) j 90.95 i 137.9 j (lb) b) F 90.952 137.92 165.2 (lb) 56.59 (deg) 0.9877 (rad) tan 1 137.9 / 90.95 Kamman – ME 2560: page 3/3




