PHYS 202-1M Name____________________________ Exam 4
advertisement
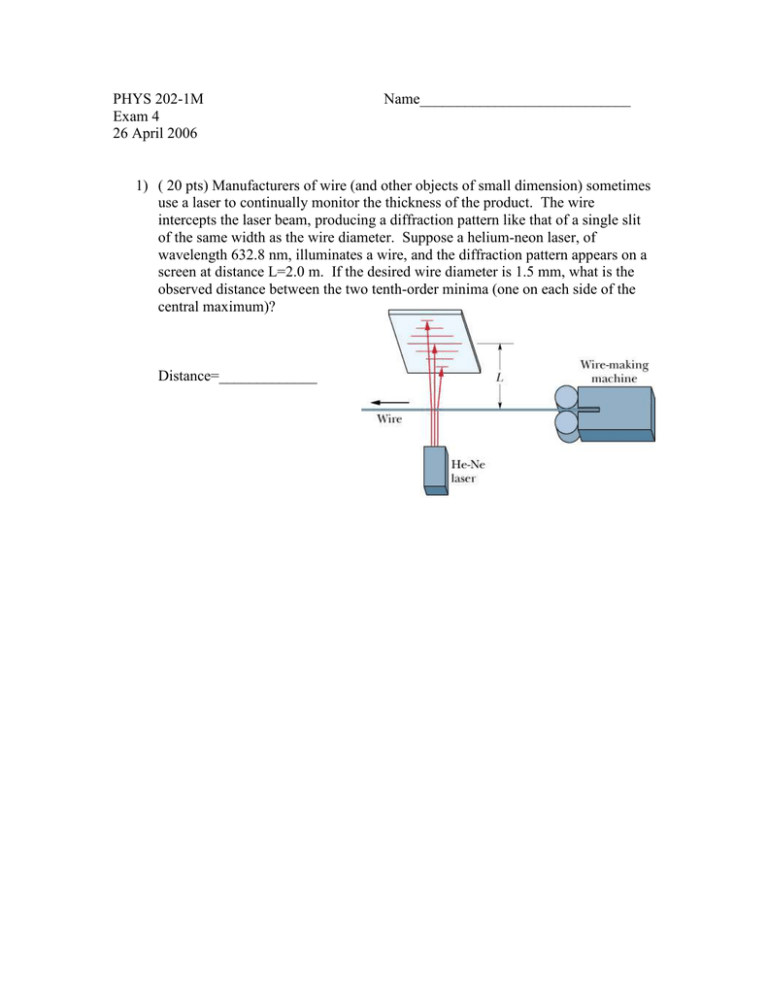
PHYS 202-1M Exam 4 26 April 2006 Name____________________________ 1) ( 20 pts) Manufacturers of wire (and other objects of small dimension) sometimes use a laser to continually monitor the thickness of the product. The wire intercepts the laser beam, producing a diffraction pattern like that of a single slit of the same width as the wire diameter. Suppose a helium-neon laser, of wavelength 632.8 nm, illuminates a wire, and the diffraction pattern appears on a screen at distance L=2.0 m. If the desired wire diameter is 1.5 mm, what is the observed distance between the two tenth-order minima (one on each side of the central maximum)? Distance=_____________ 2) (20 pts) A diffraction grating 20.0 mm wide has 7000 rulings. Light of wavelength 589 nm is incident perpendicularly on the grating. What are the (a) largest, (b) second largest, and (c) third largest values of θ at which maxima appear on a distant viewing screen? a. Largest? ____________ b. Second largest? ____________ c. Third largest? ____________ 3) (15 pts) Two waves of light in air, of wavelength λ=600 nm, are initially in phase. They then travel through plastic layers as shown in this figure, with L1=3.0 µm, L2=2.5 µm, n1=1.2, and n2=1.4. a. What multiple of λ gives their phase difference after they both have emerged from the layers? b. If the waves later arrive at some common point with the same amplitude, is their interference one of the following: i. fully constructive ii. fully destructive iii. intermediate but closer to fully constructive iv. intermediate but closer to fully destructive 4) (20 pts) In a double slit experiment, the distance between slits is 5.0 mm and the slits are 4.0 m from the screen. Two interference patterns can be seen on the screen: one due to light of wavelength 480 nm and the other due to light of wavelength 600 nm. What is the separation on the screen between the third-order (m=3) bright fringes of the two interference patterns? 5) (15 pts) In this figure, two isotropic point sources S1 and S2 emit light in phase at wavelength λ and at the same amplitude. The sources are separated by distance 2d=6λ. They lie on an axis that is parallel to an x-axis, which runs along a viewing screen at distance D=20λ. The origin lies on the perpendicular bisector between the sources. The figure shows two rays reaching point P on the screen, at position xp. a. At what value of xp do the rays have the minimum possible phase difference? b. What multiple of λ gives that phase difference? c. At what value of xp do the rays have the maximum possible phase difference? d. What multiple of λ gives that maximum phase difference? e. What multiple of λ gives the phase difference when xp=6 λ? f. When xp=6 λ, is the resulting intensity at point P maximum, minimum, intermediate but closer to maximum, or intermediate but closer to minimum? 6) (10 pts) If mirror M2 in a Michelson interferometer (in this figure) is moved through 0.34 mm, a shift of 820 bright fringes occurs. What is the wavelength of the light producing the fringe pattern?