Exam 2--PHYS 102--S15
advertisement

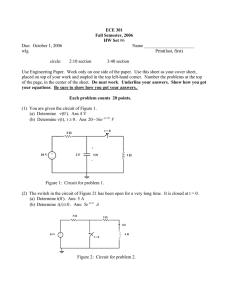
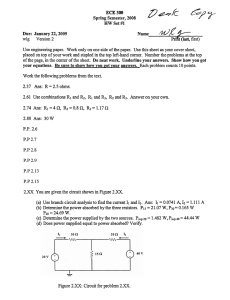
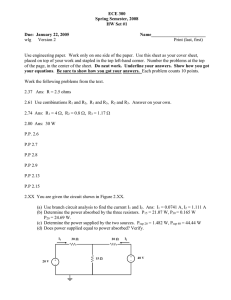
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ Exam 2--PHYS 102--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A parallel-plate capacitor initially has a potential difference of 200 V and is then disconnected from the charging battery. If the distance between the plates is now doubled, what is the new value of the voltage? a. b. c. d. 3. The capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor can be increased by: I. increasing the charge II. decreasing the charge III. increasing the plate separation IV. decreasing the plate separation V. decreasing the plate area a. II & III b. only IV c. I & IV d. II & V 200 V 400 V 100 V 800 V 2. This figure shows a capacitor with plates of area A=0.2 m2 and distance between the plates d=1.2x10-6 m. If an insulator, whose dielectric constant is 5, is placed between the plates, what is the capacitance? a. b. c. d. e. 4. What is the voltage across the 6 µF capacitor? 24 µF 1.5 µF 120 µF 2.7x10-16 F 7.4 µF a. b. c. d. 1 9V 6V 18 V 3V 5. What is the equivalent capacitance of this circuit? 8. Current has these basic SI units: a. volts/meter b. volts/farad c. newtons/second d. tesla*meter e. coulombs/second 9. A 10-ohm resistor has a constant current.If 1200 C of charge flow through it in 4 minutes what is the value of the current? a. b. c. d. a. b. c. d. e. 8 µF 12 µF 15 µF 2 µF 5.0 A 3.0 A 11 A 20 A 15 A 10. Which of these statements, about the use of voltmeters and ammeters, is correct? I. Voltmeters have a large resistance and are connected in parallel. II. Voltmeters have a small resistance and are connected in parallel. III. Ammeters have a large resistance and are connected in series. IV. Ammeters have a large resistance and are connected in parallel. V. Voltmeters have a small resistance and are connected in series. a. I only b. I & III c. III only d. II & IV e. V only 6. For the previous circuit, what is the voltage across the 3µF capacitor? a. 3 V b. 6 V c. 4 V d. 2 V e. 12 V 7. Consider this circuit. What is the energy stored on the topmost 2 µF capacitor (circled here)? 11. A flat iron is marked “120 V,600 W.” In normal use, the current in it is: a. b. c. d. e. a. b. c. d. e. 144 µJ 12 µJ 24 µJ 16 µJ 288 µJ 2 2A 4A 5A 7.2 A 0.2 A 15. A battery has an internal resistance of 0.5 Ω. When it provides a current of 4 A, the potential across the battery is 10 V. What is the ideal electromotive force provided by the battery? 12. A current of 20 A flows through a wire of length 1 m and cross-sectional area 7.85x10 -7 m2. The potential across the wire is 1.4 V. From this table of resistivities, select the material of the wire: Material Copper Silver Gold Tungsten Iron a. b. c. d. e. Resistivity(Ohm-m) 1.7x10-8 1.59x10-8 2.44x10-8 5.5x10-8 10.0x10-8 a. b. c. d. Copper Silver Gold Tungsten Iron 20 V 8V 12 V 14 V 16. Which of these rules for resistors in series is not correct? I. Resistors in series must have the same current. II. Resistors in series must have the same voltage. III. For resistors in series, the total voltage across the resistors is equal to the sum of the voltage across the individual resistors. IV. For resistors in series, the equivalent resistance is equal to the sum of the indiviual resistors a. II only b. II & III c. I & III d. I & IV e. II & IV 13. For a cylindrical resistor made of ohmic material, the resistance does NOT depend on: a. the current b. the radius of the cylinder c. the cross-sectional area d. the resistivity e. the length 14. Which of the following best describes the purpose of resistors? a. turn a circuit on or off. b. act as a timing device within a circuit. c. slow the flow of electricity. d. store electrical energy. 3 17. What is the voltage across R 2 in this circuit: a. b. c. d. 19. Consider this circuit; the first 3 Ω resistor has a voltage of 6 V, as labeled. What is the voltage across the 6 Ω resistor? a. b. c. d. e. 2V 4V 8V 10 V 18. What is the total current, I, for this circuit? 2V 6V 12 V 3V 18 V 20. For the above circuit, what is the equivalent resistance? a. 11 Ω b. 6 Ω c. 2 Ω d. 4 Ω e. 5 Ω 21. Consider this circuit.What is the current through the 1Ω resistor? a. b. c. d. 36 A 9A 2A 54 A a. b. c. d. e. 4 2A 3A 4A 6A 8A 22. Which of these resistors has the smallest current? a. b. c. d. 24. On a circuit breaker, you have a 1200 W heater, a 60 W light bulb, and a 240 W radio. When you add a 180 W blender, the circuit breaker turns off. Assume all the devices operate at 120 V. Which of these is the maximum allowed current for the breaker? a. b. c. d. R1 R2 R3 R5 25. What purpose does the third prong on a three-prong outlet serve? a. b. 23. Which of these statements about a household circuit is true: I. The household circuit is a series circuit. II. All devices in a household circuit operate at the same current. III. As you add more devices to a household circuit, the total current increases. IV. A ground fault circuit interrupt turns off if Iin>Iout for any particular device. a. b. c. d. 10 A 20 A 16 A 13 A No purpose Act as a ground thus providing a safety feature c. An alternative to the European system of electrical outlets d. Allow for more stability in the outlet 26. This is a free question. Please bubble “A” for this question. a. A b. B c. C d. D I & IV III III & IV II & III 5 ID: A Exam 2--PHYS 102--S15 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: B E B D D C A E A A C D A C C A B B A D A B C D B A PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: S15 S15 S15 S15 S15 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: S15 S15 S15 S15 S15 REF: S15 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: S15 S15 S15 S15 S15 S15 S15 S15 1