Document 14404789
advertisement

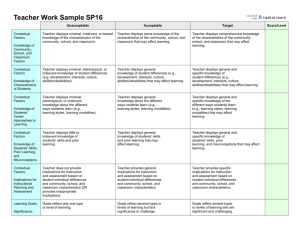
TCHL 540/544/548 Critical Performance – Unit of Study Emphasizing Classroom Management and Collaboration Course Titles: TCHL 540/544/548 – Classroom Instruction Course Sequence Kentucky Advanced Teacher Standard(s) Assessed: Standard 2 – Designs/Plans Instruction, Standard 3 – Creates/Maintains Learning Climate, Standard 4 – Implements/Manages Instruction, Standard 5 – Assesses/Communicates Learning Results, Standard 6 – Implements Technology, Standard 7 – Reflects on & Evaluates Teaching/Learning, Standard 8 – Collaborates with Colleagues/Parents/Others Purpose and Use Statement: This critical performance is an evaluation of Kentucky Advanced Teacher Standards Teacher Standards 1-8. Completion and uploading of this performance into the electronic portfolio is a requirement for a passing grade for TCHL 540, 544, and/or 548. Product: Unit of Study that incorporates best practice with an emphasis on classroom management and collaboration. Task: Develop a Unit of Study with emphasis on Classroom Management and Collaboration that integrates best practice instructional strategies, a student behavior plan, and collaboration project designed to improve student learning. Follow the outline below: Contextual Factors: Identifies relevant school, classroom, and student factors that directly affect the teaching and learning process. Discusses implication of these factors in planning and instruction. Classroom Management Plan: Develops a whole class discipline plan based on student data. Learning Goals: Creates significant, challenging, varied, and appropriate learning goals. Assessment Plan: Designs an assessment plan to monitor student progress toward learning goals. Design for Instruction: Designs instruction for specific learning goals, student characteristics and needs, and learning contexts. Discipline Problem Behavior Inventory and Plan: Uses student data to identify problem behavior and develops an intervention plan based upon the data. Analysis of Student Learning: Uses assessment data to profile student learning and communicate information about student progress and achievement. Reflection and Self Evaluation: Analyzes the relationship between his or her instruction and student learning in order to improve teaching practice. Collaboration: Creates a school and stakeholder partnership plan that is designed to enhance student learning throughout the unit of study. Specifications/Technical Requirements A critical performance is any piece of evidence required by a program and produced by the student that demonstrates the student has met a Standard(s). Critical performances are embedded within courses taught by faculty who evaluate the performance using a rating scale of 1 (low) to 4 (high) based on scoring rubrics developed by faculty within the program. The Electronic Portfolio System can be accessed at http://edtech2.wku.edu/portfolio/. Scoring Guide : Contextual Factors Classroom Management Plan Beginning (1) Displays little, irrelevant, or biased knowledge of the characteristics of the community, school, and classroom. Displays little, stereotypical, or irrelevant knowledge of student differences (e.g. development, interests, culture, abilities/disabilities). Displays little, stereotypical, or irrelevant knowledge about the different ways students learn (e.g., learning styles, learning modalities). Displays little or irrelevant knowledge of students’ skills and prior learning. Does not provide implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics OR provides inappropriate implications. Displays little or no understanding of a proactive classroom management approach based upon the contextual factor data. Displays little or no understanding of the establishment of rules and procedures, interventions, and consequences in a classroom management plan. Developing (2) Displays minimal understanding of the characteristics of the community, school, and classroom that may affect learning. Displays partial understanding of student differences (e.g., development, interests, culture, abilities/disabilities) that may affect learning. Displays partial understanding of the different ways students learn (e.g., learning styles, learning modalities) that may affect learning. Displays limited understanding of students’ skills and prior learning that may affect learning. Implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics are limited. Displays minimal understanding of a proactive classroom management approach based upon the contextual factor data. Displays minimal understanding of the establishment of rules and procedures, interventions, and consequences in a classroom management plan. Proficient (3) Displays an adequate understanding of the characteristics of the community, school, and classroom that may affect learning. Displays general understanding of student differences (e.g., development, interests, culture, abilities/disabilities) that may affect learning. Displays general understanding of the different ways students learn (e.g., learning styles, learning modalities) that may affect learning. Displays general understanding of students’ skills and prior learning that may affect learning. Provides appropriate implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics Displays a general understanding of a proactive classroom management approach based upon the contextual factor data. Displays a general understanding of the establishment of rules and procedures, interventions, and consequences in a classroom management plan. Distinguished (4) Displays a clear understanding of the characteristics of the community, school, and classroom that may affect learning. Displays general & specific understanding of student differences (e.g., development, interests, culture, abilities/disabilities) that may affect learning. Displays general & specific understanding of the different ways students learn (e.g., learning styles, learning modalities) that may affect learning. Displays general & specific understanding of students’ skills and prior learning that may affect learning. Provides specific implications for instruction and assessment based on student individual differences and community, school, and classroom characteristics Displays clear understanding of a proactive classroom management approach based upon the contextual factor data. Displays clear and specific understanding of the establishment of rules and procedures, interventions, and consequences in a classroom management plan. Learning Goals Goals reflect only one type or levels of learning. Goals are not stated clearly and are activities rather than learning outcomes. Goals are not appropriate for the development; prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences; and other student needs. Goals are not aligned with national, state or local standards. Goals reflect several types or levels of learning but lack significance or challenge. Some goals are clearly stated as learning outcomes. Some goals are appropriate for the development; prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences; and other student needs. Some goals are explicitly aligned with national, state or local standards. Assessment Plan Content and methods of assessment lack congruence with learning goals or lack cognitive complexity. The assessments contain no clear criteria for measuring student performance relative to the learning goals. The assessment plan includes only one assessment mode and does not assess students before, during, and after instruction. Assessments are not valid; scoring procedures are absent or inaccurate; items or prompts are poorly written; directions and procedures are confusing to students. Teacher does not adapt assessments to meet the individual needs of students or these assessments are inappropriate. Some of the learning goals are assessed through the assessment plan, but many are not congruent with learning goals in content and cognitive complexity. Assessment criteria have been developed, but they are not clear or are not explicitly linked to the learning goals. The assessment plan includes multiple modes but all are either pencil/paper based (i.e. they are not performance assessments) and/or do not require the integration of knowledge, skills and reasoning ability. Assessments appear to have some validity. Some scoring procedures are explained; some items or prompts are clearly written; some directions and procedures are clear to students. Makes adaptations Goals reflect several types or levels of learning and are significant and somewhat challenging. Most goals are clearly stated as learning outcomes. Most goals are appropriate for the development; prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences; and other student needs. Most goals are explicitly aligned with national, state or local standards. Most of the learning goals are assessed through the assessment plan, but many are not congruent with learning goals in content and cognitive complexity. Assessment criteria have been developed and are somewhat clear and adequately linked to the learning goals. The assessment plan includes multiple modes but and integrates knowledge, skills and reasoning ability adequately. Assessments appear to be somewhat valid. Scoring procedures are explained; most items or prompts are clearly written; most directions and procedures are clear to students. Makes adaptations to assessments that are appropriate to meet the individual needs of most students. Goals reflect several types or levels of learning and are significant and challenging. All goals are clearly stated as learning outcomes. All goals are appropriate for the development; prerequisite knowledge, skills, experiences; and other student needs. All goals are explicitly aligned with national, state or local standards. Each of the learning goals is assessed through the assessment plan; assessments are congruent with the learning goals in content and cognitive complexity. Assessment criteria are clear and are explicitly linked to the learning goals The assessment plan includes multiple assessment modes (including performance assessments, lab reports, research projects, etc.) and assesses student performance throughout the instructional sequence. Assessments appear to be valid; scoring procedures are explained; most items or prompts are clearly written; directions and procedures are clear to students. Makes adaptations to assessments that are appropriate to meet the individual needs of most students. Design for Instruction Few lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. Few learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. Not all learning goals are covered in the design. Teacher’s use of content appears to contain numerous inaccuracies. Content seems to be viewed more as isolated skills and facts rather than as part of a larger conceptual structure. The lessons within the unit are not logically organized organization (e.g., sequenced). Little variety of instruction, activities, assignments, and resources. Heavy reliance on textbook or single resource (e.g., work sheets). Instruction has not been designed with reference to contextual factors and pre-assessment data. Activities and assignments do not appear productive and appropriate for each student. Technology is inappropriately used OR teacher does not use technology, and no (or inappropriate) rationale is provided. to assessments that are appropriate to meet the individual needs of some students. Some lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. Some learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. Some learning goals are covered in the design. Use of content appears to be mostly accurate. Shows some awareness of the big ideas or structure of the discipline. The lessons within the unit have some logical organization and appear to be somewhat useful in moving students toward achieving the learning goals. Some variety in instruction, activities, assignments, or resources but with limited contribution to learning. Little instruction has been designed with reference to contextual factors and pre-assessment data. Few activities and assignments appear productive and appropriate for each student. Teacher uses technology but it does not make a significant contribution to teaching and learning OR teacher provides limited rationale for not Most lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. Most learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. Most learning goals are covered in the design. Use of content appears to be accurate. Shows adequate awareness of the big ideas or structure of the discipline. The lessons within the unit are appropriately organized and most appear to be useful in moving students toward achieving the learning goals. Adequate variety in instruction, activities, assignments, or resources that seem to contribute to learning. Some instruction has been designed with reference to contextual factors and pre-assessment data. Some activities and assignments appear productive and appropriate for each student. Teacher integrates appropriate use of technology that makes an acceptable contribution to teaching and learning OR teacher provides adequate rationale for not using technology. All lessons are explicitly linked to learning goals. All learning activities, assignments and resources are aligned with learning goals. All learning goals are covered in the design. Use of content appears to be accurate and has depth. Focus of the content is congruent with the big ideas or structure of the discipline. All lessons within the unit are logically organized and appear to be useful in moving students toward achieving the learning goals. Significant variety across instruction, activities, assignments, and/or resources. This variety makes a clear contribution to learning. Most instruction has been designed with reference to contextual factors and preassessment data. Most activities and assignments appear productive and appropriate for each student. Teacher integrates creative and appropriate technology that makes a significant contribution to teaching and learning OR provides a strong rationale for not using technology. using technology. Discipline Problem Behavior Inventory and Plan Displays little or no understanding of the student behavior inventory data, the conclusions drawn from the data, and of the prescription of a student intervention plan. Minimal understanding is evident in the interpretation of the student behavior inventory data, the conclusions drawn from the data, and of the prescription of a student intervention plan. Instructional Decision Making Many instructional decisions are inappropriate and not pedagogically sound. Teacher treats class as “one plan fits all” with no modifications. Modifications in instruction lack congruence with learning goals. Some instructional decisions are appropriate, but some decisions are not pedagogically sound. Some modifications of the instructional plan are made to address individual student needs, but these are not based on the analysis of student learning, best practice, or contextual factors. Modifications in instruction are somewhat congruent with learning goals. Analysis of Student Learning Presentation is not clear and accurate; it does not accurately reflect the data. Analysis of student learning is not aligned with learning goals. Interpretation is inaccurate, and conclusions are missing or unsupported by data. Analysis of student learning fails to include evidence of impact on Presentation is somewhat understandable and/or contains several errors. Analysis of student learning is partially aligned with learning goals and/or fails to provide a comprehensive profile of student learning relative to the goals for the whole class, Interpretation of student behavior inventory data is somewhat meaningful, some appropriate conclusions are drawn from the data, and a somewhat accurate and appropriate intervention plan is prescribed for the student that is linked to the student data. Most instructional decisions are pedagogically sound (i.e., they are likely to lead to student learning). Appropriate modifications of the instructional plan are made to address individual student needs. These modifications are informed by the analysis of student learning/performanc e, best practice, or contextual factors. Includes adequate explanation of why the modifications would improve student progress. Modifications in instruction are congruent with learning goals. Presentation is understandable and contains few errors. Analysis of student learning is adequately aligned with learning goals provides an satisfactory profile of student learning relative to the goals for the whole class, subgroups, and two individuals. Interpretation is Interpretation of student behavior inventory data is meaningful, appropriate conclusions are drawn from the data, and an accurate and appropriate intervention plan is prescribed for the student that is explicitly linked to the student data. All instructional decisions are pedagogically sound (i.e., they are likely to lead to student learning). Resourceful and suitable modifications of the instructional plan are made to address individual student needs. These modifications are informed by the analysis of student learning/performance, best practice, and contextual factors. Includes clear explanation of why the modifications would improve student progress. Modifications in instruction are clearly congruent with learning goals. Presentation is easy to understand and contains no errors of representation. Analysis is fully aligned with learning goals and provides a comprehensive profile of student learning for the whole class, subgroups, and two individuals. Interpretation is meaningful, and appropriate conclusions student learning in terms of numbers of students who achieved and made progress toward learning goals. Collaboration Displays little or no understanding of a school and stakeholder partnership plan including activities, timeline, persons involved, and resources needed. Displays little or no understanding of what is to be accomplished through the implementation of the school and stakeholder partnership plan and how the impact on student learning will be measured. subgroups, and two individuals. Interpretation is technically accurate, but conclusions are missing or not fully supported by data. Analysis of student learning includes incomplete evidence of the impact on student learning in terms of numbers of students who achieved and made progress toward learning goals. Displays minimal understanding of a school and stakeholder partnership plan including activities, timeline, persons involved, and resources needed. Displays minimal understanding of what is to be accomplished through the implementation of the school and stakeholder partnership plan and how the impact on student learning will be measured. TOTAL POINTS POSSIBLE = 36 accurate and most conclusions are supported by data. Analysis of student learning includes sufficient evidence of the impact on student learning in terms of numbers of students who achieved and made progress toward learning goals. are drawn from the data. Analysis of student learning includes clear evidence of the impact on student learning in terms of number of students who achieved and made progress toward each learning goal. Displays general understanding of a school and stakeholder partnership plan including activities, timeline, persons involved, and resources needed. Displays general understanding of what is to be accomplished through the implementation of the school and stakeholder partnership plan and how the impact on student learning will be measured. Displays clear and specific understanding of a school and stakeholder partnership plan including activities, timeline, persons involved, and resources needed. Displays clear and specific understanding of what is to be accomplished through the implementation of the school and stakeholder partnership plan and how the impact on student learning will be measured. TOTAL POINTS EARNED: ___________/36 NOTE TO STUDENTS: After you submit this critical performance, the scores on this analytic rubric will be provided to you for constructive feedback. However, only an overall “holistic score” will be entered into the Electronic Portfolio System (EPS) based on the following scale: 1 – Beginning, 2 – Developing, 3 – Proficient, or 4 – Distinguished. This holistic score will be based on the following ranges of possible points on this analytic rubric: Holistic Score of 1 = Analytic Rubric Score Range 9-13 Holistic Score of 2 = Analytic Rubric Score Range 14-22 Holistic Score of 3 = Analytic Rubric Score Range 23-31 Holistic Score of 4 = Analytic Rubric Score Range 32-36 Additionally, you may only receive a holistic score of 4 in the EPS if the critical performance required no revision. This means that, if revisions are required and you make the necessary revisions, even if you score 32 or above on this analytic rubric, the highest score you will receive in the EPS is still “3”.