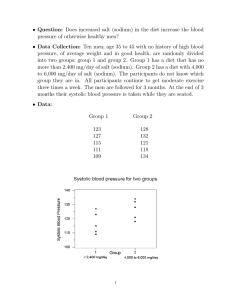
Reducing Salt and Sodium in Your Diet About Us
advertisement

Tips on Lowering Sodium Eat fresh fruits and vegetables (naturally low in sodium) Read nutrition labels Purchase low-sodium products When using canned items, wash the food item with water to remove excess salt About Us The Texas Obesity Research Center (TORC) promotes interdisciplinary research, education and training and fosters local community collaborations to develop state-of-the-art Obesity Prevention and Control methodologies through cross sectional and longitudinal research investigating psychosocial, environmental and biologic determinants of obesity and its consequences Prepare food using little or no salt- Ex: Ramen noodles- try not using the flavor packets Use more herbs and spices instead Limit salty snacks like chips and pretzels Limit the consumption of processed foods Avoid fast food. Most meals contain more than your daily recommended intake of sodium in just one serving. For more information about the Texas Obesity Research Center contact: Texas Obesity Research Center 3855 Holman St., Garrison Gym, Rm. 105H Houston, TX 77204-6015 713.743.1183 torc@uh.edu Visit us at https://www.uh.edu/torc Follow us on Reducing Salt and Sodium in Your Diet Determining Sodium Content What is Sodium? Foods High in Sodium Sodium is an essential nutrient that is required in a small amount. It helps to maintain water balance within the cells, along with the function of nerve impulses and muscle contractions. Processed and prepared foods Tomatoes and tomato products Soups Table salt Cheese Deli meats Canned vegetables How much Sodium? Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend that sodium intake should be limited to 2,300 mg a day. 1/2 teaspoon of salt = 1,200 mg of sodium 1 teaspoon of salt = 2,400 mg of sodium Some products include terms related to sodium. Here are some common terms and their meanings: Sodium-free – fewer than 5 milligrams of sodium per serving Very low-sodium – 35 milligrams or fewer per serving Low-sodium – 140 milligrams or fewer per serving Reduced sodium – usual sodium level is reduced by 25 percent Unsalted, no salt added or without added salt – made without the salt that's normally used, but still contains the sodium that's a natural part of the food itself Disadvantages of Too Much Sodium Consumption Increase in blood pressure Increase risk of heart attack and stroke Increase risk of kidney diseases Increase risk of stomach cancer