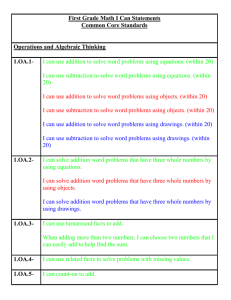
1 Grade Math Common Core Standards
advertisement
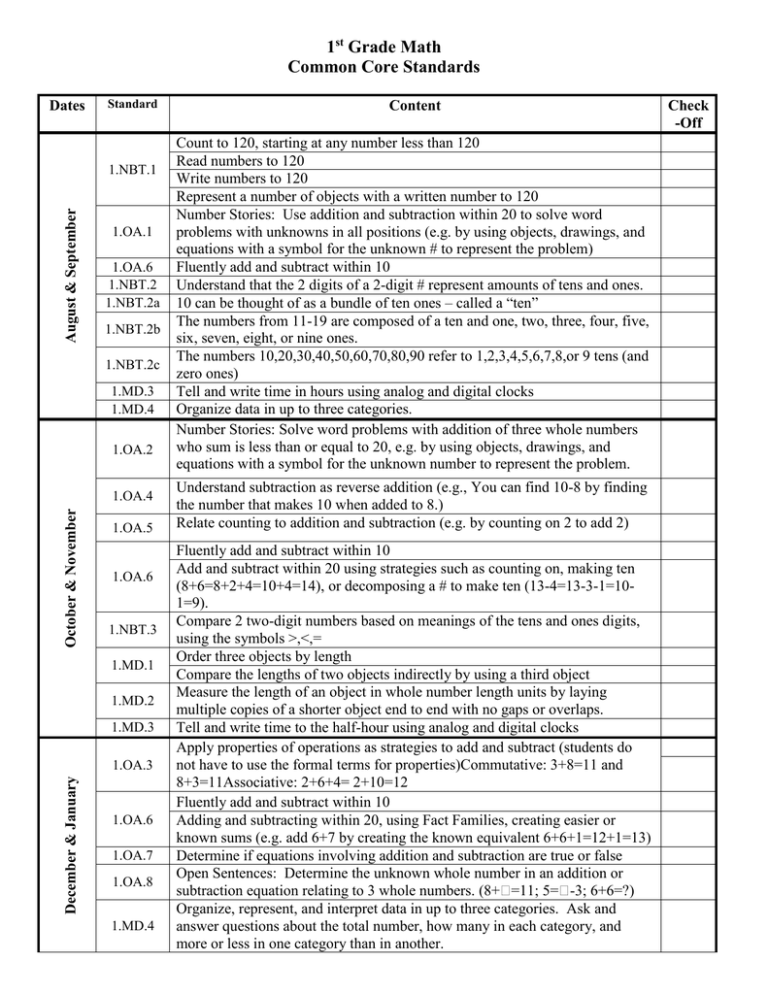
1st Grade Math Common Core Standards Dates Standard August & September 1.NBT.1 1.OA.1 1.OA.6 1.NBT.2 1.NBT.2a 1.NBT.2b 1.NBT.2c 1.MD.3 1.MD.4 1.OA.2 October & November 1.OA.4 1.OA.5 1.OA.6 1.NBT.3 1.MD.1 1.MD.2 1.MD.3 December & January 1.OA.3 1.OA.6 1.OA.7 1.OA.8 1.MD.4 Content Count to 120, starting at any number less than 120 Read numbers to 120 Write numbers to 120 Represent a number of objects with a written number to 120 Number Stories: Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems with unknowns in all positions (e.g. by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown # to represent the problem) Fluently add and subtract within 10 Understand that the 2 digits of a 2-digit # represent amounts of tens and ones. 10 can be thought of as a bundle of ten ones – called a “ten” The numbers from 11-19 are composed of a ten and one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine ones. The numbers 10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90 refer to 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,or 9 tens (and zero ones) Tell and write time in hours using analog and digital clocks Organize data in up to three categories. Number Stories: Solve word problems with addition of three whole numbers who sum is less than or equal to 20, e.g. by using objects, drawings, and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. Understand subtraction as reverse addition (e.g., You can find 10-8 by finding the number that makes 10 when added to 8.) Relate counting to addition and subtraction (e.g. by counting on 2 to add 2) Fluently add and subtract within 10 Add and subtract within 20 using strategies such as counting on, making ten (8+6=8+2+4=10+4=14), or decomposing a # to make ten (13-4=13-3-1=101=9). Compare 2 two-digit numbers based on meanings of the tens and ones digits, using the symbols >,<,= Order three objects by length Compare the lengths of two objects indirectly by using a third object Measure the length of an object in whole number length units by laying multiple copies of a shorter object end to end with no gaps or overlaps. Tell and write time to the half-hour using analog and digital clocks Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract (students do not have to use the formal terms for properties)Commutative: 3+8=11 and 8+3=11Associative: 2+6+4= 2+10=12 Fluently add and subtract within 10 Adding and subtracting within 20, using Fact Families, creating easier or known sums (e.g. add 6+7 by creating the known equivalent 6+6+1=12+1=13) Determine if equations involving addition and subtraction are true or false Open Sentences: Determine the unknown whole number in an addition or subtraction equation relating to 3 whole numbers. (8+=11; 5=-3; 6+6=?) Organize, represent, and interpret data in up to three categories. Ask and answer questions about the total number, how many in each category, and more or less in one category than in another. Check -Off Dates Standard Content 1.OA.6 Fluently add and subtract within 10 Distinguish between defining attributes (e.g. triangles are closed and 3-sided) vs. non-defining attributes (e.g. color, orientation, overall size) Build and draw shapes that show defining attributes Compose two-dimensional shapes (rectangles, squares, trapezoids, triangles, half-circles, and quarter-circles) to create a composite shape and compose new shapes from the composite shape Compose three-dimensional shapes (cubes, right rectangular prisms, right circular cones, right circular cylinders) to create a composite shape and compose new shapes from the composite shape Divide circles and rectangles into two and four equal parts. Describe the parts using the words halves, fourths, and quarter and the phrases half of, fourth of, and quarter of. Describe the whole as two of, or four of the parts Understand that decomposing into more equal parts creates smaller parts. February & March 1.G.1 1.G.2 1.G.3 1.OA.6 April & May 1.NBT.4 1.NBT.5 1.NBT.6 Fluently add and subtract within 10 Add within 100, including adding a 2-digit number and a 1 digit number using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or relationships between add. and sub. Add within 100, including adding a 2-digit number and a multiple of ten using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or relationships between add. and sub. Add within 100, understanding that in adding 2-digit #’s, tens and tens are added, ones and ones are added, and sometimes regrouping is necessary. Relate the strategy used to add or subtract to the written equation, explaining the reasoning used. Given a 2-digit number, mentally find 10 more or 10 less than the number without having to count; Explain the reasoning used Subtract multiples of 10 from other multiples of ten in the range of 10-90 using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or relationships between add. and sub. Relate the strategy used to add or subtract to the written equation, explaining the reasoning used. Check -Off