5.4 Imaginary Numbers Warm Up Solve the following equations :
advertisement

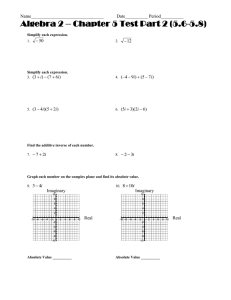
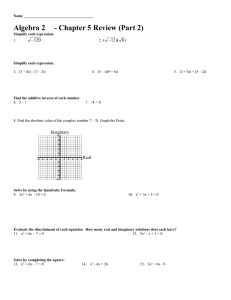
5.4 Imaginary Numbers Warm Up Solve the following equations : 1.) 2( x − 1) 2 = −40 2.) 5 x 2 − 15 = −5 Quadratic Equations with no real solution use an imaginary unit to represent their answers. Imaginary unit __________ =____________ 1.) i = 2.) i 2 = 3.) i 3 = 4.) i 4 = 5.) i 5 = Using the information you learned above decide whether the power of i is equal to 1, − 1, i, or − i. 1.) i 9 = 3.) i 22 = 2.) i 40 = 4.) i 100 = 5.4 Imaginary Numbers For the below equations solve the equation, simplify the radical, and write the answer in terms of i if necessary. 1.) x 2 + 64 = 0 2.) x 2 + 1 = 0 Check: Check: 3.) 3 x 2 + 10 x = −26 4.) 2 x 2 + 26 = −10 1 5.) − ( x + 1) 2 = 5 2 6.) − 6( x + 5) 2 = 120 5.4 Imaginary Numbers GRAPHING Standard form of an imaginary number is: ______________________ Graph: 1.) -2+3i 2.) 4i 3.) 1-5i imaginary real Absolute Value and Complex Numbers: The absolute value of a complex number denotes how far away the complex number is from the origin. If z = a + bi , the absolute value of z is defined as: ___________________ Plot the following numbers in a complex plane. Then find the absolute value of each complex number to determine which number is the furthest from the origin. 1.) 3 + 4i 2.) -2i 3.) -1+5i real imaginary Homework: Pg. 277-279 #17-36, 65-71 odd 5.4 Imaginary Numbers