1. Chapter 10 Deafness and Hard of Hearing

1. Chapter 10 Deafness and Hard of Hearing
2. Deaf Culture
Use of person 1 st language
Galluadet
American Sign Language
3. Definitions
Deafness: A hearing impairment that is so severe that the child is impaired in processing linguistic information through hearing, with or without amplification, that adversely affects a child’s educational performance
Hard of Hearing: perceives some sound and has sufficient hearing to use auditory-based method of communication, sometimes with visual supplements.
Table 10.1 p. 355
4. Definitions
Hard of Hearing
Prelingually deaf
Postlingually deaf
Deafness
25% of deaf and hard of hearing students have additional disabilities
5. Types of Hearing Loss
Conductive: blockage or damage to the outer or middle ear that prevents
sound waves from traveling to the inner ear
Sensorineural: damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve (most common in young children)
6. Identification
Hertz (Hz) unit of measure for sound frequency
Decibel (Db) unit of measure for intensity of sound
7. Debate
Oral vs. Manual method of Instruction and Communication
Deaf pride/Deaf culture
8. Causes
Heredity
Maternal Rubella
Meningitis
Otitis Media
Noise
Other causes
9. Prevention
Medical Terminology
Makers of noisy equipment install noise-limiting devices or graphic warning lights on their products
10. Possible Signs of Needed Intervention
Do not show recognition of being spoken to
Continue playing and do not stop to listen to signs
Do not recognize their mothers’ voices
Have difficulties following oral instructions
Speak too loudly/softly
Watch speakers’ lips carefully
Limited vocabulary
11. Possible Signs of Needed Intervention
Articulate speech sounds poorly
Delayed language development
Inattentive during lecture/discussions
Complain of earaches
Runny discharge from ears
Frequent colds or sinus or ear infections
Radio or television on is very loud
12. Academic Achievement
Substantially lower than those of their peers without disabilities
Two major educational goals
– To reduce the achievement gap between students without disabilities and deaf students
–
–
To develop the speech and language skills to these individuals potential
Reading
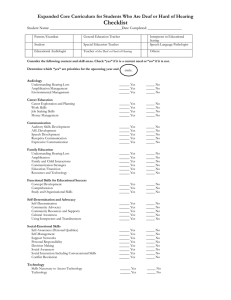
13. Assistive Learning Devices
Hearing aids
Digital hearing aids
Cochlear implants
14. Telecommunication Devices
Captions
Open captions
Closed captions
Rear window captioning
Text telephone
Telecommunications relay service
Voice carry over
Personal data assistants
15. Technology Continued
Speech to text
Alerting Devices
16. Early Identification
Universal newborn hearing screening
Pre-referral
Formal-Assessment by the SP/L or audiologist
17. LRE and Placement Considerations
Severity of Loss
Potential for using residual hearing
Academic achievement
Communication needs
Preferred mode of communication
Placement preference
18. Validated Practices
Oral-only approach
Total communication approach
Cued speech
Bilingual-bicultural approach
19. Accommodations-general
Placement of the child
Equipment checks
Reduce background noise
Articulate clearly, speak slowly, repeat
Do not chew gum or cover mouth when speaking
Face the receiver
Overhead Projector
Watch movement
CONSULTATION p. 378, 385 effective teaching
20. Issues
Methodology
Transition
LRE
Language Development
Families
Technology
Cochlear Implants
Collaboration and Role of Interpreter