Counting Atoms
advertisement

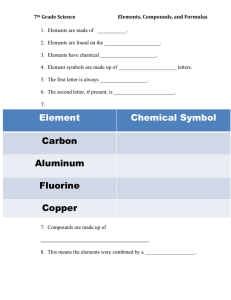
Counting Atoms DO NOW MONDAY • Begin your Pre-Test over Chemistry Unit Part 2. • When you finish, turn it in to the side cart and pick up a sheet of notebook paper. • Number the notebook paper 1-36. TODAYS PLAN • To demonstrate Mastery of Chemistry Part 1 Learning Targets on a written Exam. TODAYS DO • We will do retake and/or enrichment over Chemistry Part 1 Learning Targets. – Made 80% or Greater, you will get a ChromeBook, go to my Seventh Grade Science page, click on Periodic Table Enrichment, and play the games on the websites located there. – Made less than 80%, you will be using your notes and asking the teacher questions to redo the questions you missed on the Chemistry Part 1 Test. DO NOW TUESDAY • Tell what you think is the difference between an element and a compound. TODAYS PLAN • Distinguish between symbol and formula. • Conclude the number of atoms of each element that exists in a molecule/compound. • Distinguish between elements and compounds according to their properties (original vs. after a chemical change) • Differentiate between the model of a compound versus a model of an element. TODAYS DO • We will do guided notes about elements, compounds, and compound formulas. • We will practice counting the atoms in compound formulas and drawing models of compounds Elements • Are made of atoms • Are found on the periodic table • Have chemical SYMBOLS Element Chemical Symbol • • • • Symbol for the element on the Periodic Table Made up of ONE OR TWO letters First letter is always capitalized Second letter, if present, is lowercase Element Chemical Symbol Carbon C Aluminum Al Fluorine F Copper Cu Compounds • Made up of two or more elements chemically combined • This means the elements were combined by a chemical change. • The atoms of the atoms are held together by chemical bonds-a “stickiness” between the atoms that holds them together. • The compound is a NEW substance and has different properties than any of the elements that are in the compound. • Compounds have chemical FORMULAS. Examples of Compounds Element + Element = Compound Sodium (Na) + Chlorine (Cl) = Sodium Chloride (NaCl) + = Explosive metal + green poison gas = table salt (edible) Examples of Compounds Element + Element = Compound Hydrogen (H) + Oxygen (O) = (H2O) + = Colorless flammable gas + colorless flammable gas Water = colorless liquid (edible) (nonflammable) COMPOUND CHEMICAL FORMULAS • All compounds have Chemical FORMULAS. • These formulas tell us WHAT ELEMENTS are in the compound AND • HOW MANY atoms of each element are in the compound COMPOUND CHEMICAL FORMULAS Tell us: 1. What ELEMENTS AND 2. HOW MANY ATOMS Practice • Tell whether each of the following is an element or a compound: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Element I Br Element KCl Compound NaOH Compound K2CO3 Compound 6. 7. 8. 9. N Element Ba Element CaO Compound Mn Element 10. N2O3 Compound Counting Atoms • The symbol of an element represents ONE atom of that element 2 atoms total CO = 1 C and 1 O • A subscript in a chemical formula is a number written at the lower right corner after the symbol for the element. It represents the number of atoms of an element in a compound (when there is more than one atom of that element. 6 atoms total Na2CO3 = 2 Na 1 C and 3 O Counting Atoms: Practice • Tell which elements are in the compound AND how many atoms of each element there are: 1. NaHCO3 2. N4H3 Counting Atoms • When there is a subscript written outside parentheses in a chemical formula, the subscript MULTIPLIES by all of the elements inside of the parentheses. (SO4)3 = 1 x 3 S = 3 S 4 x 3 O = 12 O 15 atoms total Counting Atoms • A coefficient is a number written in front of a chemical symbol. • The coefficient also MULTIPLIES by the element and/or subscript. Example 1: 4 H2O = 4 x 2 H = 8 H 12 atoms total =4x1O=4 O Example 2: 2 (NH4)3PO4 = 2x 1 N = 2 N = 2 x 4 x 3 H = 24 H =2x1P=2P 36 atoms total =2x4O=8O Reading Models of Formulas Na Cl NaCl H2O Reading Models of Formulas O C O O Ca CaCO3 Drawing Models of Formulas Na2Cl2 2H2O Cl Cl Na Na