Document 14300584
advertisement

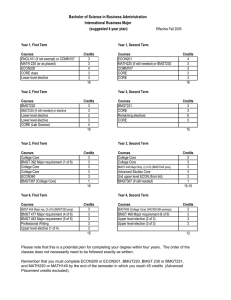
UNIVERSITY OF 11 19 M.un Adrn~n~stmtlon Dullding Collrgr Park, Maryland 207-12-503 1 301.405.5252 T E L 301.105.8195 FAX NTAPAND 7 OFFICE O F T H E S E N I O R VICE PRESIDENT F O R ACADEMIC AFFAIRS A N D PROVOST May 23,2006 MEMORANDUM TO: Howard Frank Dean, Robert H. Smith School of Business FROM: Phyllis Peres Associate Provost for Academic Planning and Programs SUBJECT: Proposal to Modify the Curriculum of the Information Systems major (PCC Log No. 05037) At its meeting on April 21, the Senate Committee on Programs, Curricula, and Courses approved your proposal to modify the curriculum of the Information Systems major. A copy of the approved proposal is enclosed. Please accept my apologies for the delay in formal notification. The changes are effective in Fall 2006. The College should ensure that the new requirements are fully described in the Undergraduate Catalog and in all relevant descriptive materials, and that all advisors are informed. Enclosure cc: James Baeder, Chair, Senate PCC Sarah Bauder, Office of Student Financial Aid Mary Giles, University Senate Barbara Hope, Data Administration Kathy McAdams, Undergraduate Studies Anne Turkos, Archives Linda Yokoi, Office of the Registrar Brian Horick, Robert H. Smith School of Business Gnanalingam Anandalingam, Robert H. Smith School of Business THE UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND, COLLEGE PARK PROGRAMICURRICULUM PROPOSAL action. Keep this form to one-page in length. Forms and appropriate attachments should be submitted to the Office of Academic Affairs, who will assign a Log Number to each proposal. Also submit an electronic version of as much of the proposal as is possible. PCC LOG NO. DATE SUBMITTED November 30,2005 105037 COLLEGEISCHOOL Robert H. Smith School of Business DEPARTMENTIPROGRAM Decision & Information Technologies/UnderrrraduateMaior: Informations Systems-Business PROPOSED ACTION (A separateform for each) ADD DELETE CHANGE X DESCRIPTION (Provide a succinct account of theproposed action. Details should be provided in an attachment. Provide old and new sample programs for curriculum changes.) The Decision & Information Technologies Department would like to update the curriculum of its Information Systems-Businessmajor. See attached for more details. JUSTIFICATION/REASONS/RESOURCES(Briefly explain the reasonfor theproposed action. Identlfi the source of new resources that may be required. Details should be provided in an attachment.) No new resources required. See attached for additional information. ~ p p ~ ~ p p p p p - ~- p p p p p p p p p p p p p - APPROVAL SIGNATURES DATE 2. Department Chair 3. College/School PCC Cha 5. Dean of the Graduate School (if required) 6. Chair, Senate PCC 7. Chair of Senate 8. Vice Resident fa Academic Affairs 8r Pmvost A (?llrr,(l~ [& %b VPAAP Rev. 3/1/04 REASONS FOR PROPOSED ACTION After benchmarking other IS programs across the nation and examining the course requirements for other majors, the Decision & Information Technologies (D&IT) department is proposing changes to the Information Systems-Business (IS) Major. These changes will provide the IS majors with a solid foundation in information systems and also give them the flexibility to align their skills with the changing market requirements. The proposed changes are based on: a benchmarking study of top undergraduate IS programs nationwide, a focus group of undergraduate IS majors in Fall 2005 (including input from Business & Information Technology Society – the IS undergraduate students’ association), study of the career paths of IS undergraduates, discussions with employers, faculty input from within and outside the IS group, and discussions with the Associate Dean, and the Associate Director of undergraduate studies at RHS. Below is the benchmarking data. Benchmarking of Undergraduate Majors in Information Systems (December 2005) Rank* Electives Total for Major 1 MIT-Sloan School 2 CMU-Tepper** 3 UT-Austin-McComb 4 Arizona-Eller 5 Minnesota-Carlson 2 1 or 2 2 1 1 1 2 or 1 0 1 1 2 4 6 6 4 (4 cr each) 2 4? 1 1 4 (2 cr each) 4 8? 7 7 8 6 Maryland-Smith 1 1 1+4*** 2 7 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 4 1 1 4 + 2 Proj 2 3 4 1 6 4 5 7 7 8 9 10 University* Michigan-Ross Penn-Wharton NYU-Stern Georgia State Calculus Required STAT Required Required Core * The order of the universities reflect the rank order in US News and World Report , 2006 ** The CMU Curriculum is quite complicated. For the Math core, the students are allowed to take either 2 calculus and 1 stat, or 1 calculus and 2 stats. The four required electives courses should be from a concentration area; but many ** The Smith School at Maryland requires ALL undergraduates to take a required course called "Introduction to Information Systems" The existing requirement in the IS-Business Major is too rigid as students are required to complete 24 credits (~ 6 courses) to obtain the Major. Most of the top-10 peer schools require 12 to 21 credits with the exception of Minnesota. Our new curriculum requires 21 credits including a core-IS courses required of all Smith School of Business undergraduates. Previously, the core requirement in the IS-Business major had 18 credits, leaving little room to pursue elective courses in their individual areas of interest. Benchmarking with other schools suggested that peer programs offer a much larger number of electives, and generally require anywhere from 3 to 18 credits. We are now requiring 15 credits (including the School core) and this will allow the students to take more electives. In addition, most of our peer institutions require just 1 calculus and 1 statistics courses at the Sophomore level. We used to require 2 calculus classes. We have brought the Freshmen/Sophomore requirements in line with the peer institutions and also the other majors in the Smith School of Business. In addition, we strongly require IS-Business majors to take additional mathematics based courses as Sophomore/Freshmen electives. Note that the undergraduate IS program was ranked #6 by U.S.News & World Report, 2005. The proposed changes are intended to further strengthen this highly ranked IS program. DESCRIPTION OF CURRICULUM CHANGE There are approximately 100 Information Systems-Business (IS) majors at the Smith School of Business, and this major is only offered at the College Park campus. Typically, students who select IS as a major pursue careers in management or IT consulting. We propose to drop BMGT 305 from the IS core because this course’s content is now being addressed by BMGT 301 which is a new college core requirement. Further, we propose to drop BMGT 485 from the IS core. BMGT 407 and BMGT 403 will be redesigned to cover the fundamentals of BMGT 485. In addition, BMGT 407 provides a hands-on exposure to project management. BMGT408 Special Topics in Decision and Information Technologies is being added as an option for the major so that emerging IS topics can be included in the curriculum. The freshman/sophomore college requirements for IS majors require that students take both MATH 140 and 141. Based on our benchmarking with peer institutions as well as other majors within the business school, we propose that the second calculus course be dropped as requirement and made a recommended elective. The current college requirements for IS majors require BMGT 231 (Statistical Models for Business). Consistent with the above, we propose that IS majors have the option of choosing between BMGT 230 or BMGT 231 for their statistics requirements. In addition to the required core courses, IS majors will be required to select two courses (six credits) from a streamlined set of electives. The overall 18 credits for major requirements are consistent with the other majors in the business school. These changes will help students tailor their portfolio of skills to a dynamic job market. Old Requirements Major Requirements BMGT 302 Bus. Computer Application Programming BMGT 305 Survey of Business Info. Systems and Tech. BMGT 402 Database Systems BMGT 403 Systems Analysis and Design BMGT 407 Information Systems Projects BMGT 485 Project Management 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr One of the following: BMGT 430 Linear Statistical Models in Business BMGT 434 Introduction to Optimization BMGT 486 Total Quality Management 3 cr One of the following: BMGT 405 Business Telecommunications BMGT 406 Electronic Commerce Application Development 3 cr Total Credits Required: 24 cr Continued on next page. Upper Level Economics Requirements One of the following courses: ECON 305 Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory & Policy ECON 306 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory ECON 330 Money and Banking ECON 340 International Economics Total Economics Requirement 3 cr 3 cr Freshmen/Sophomore Smith School Requirements MATH 140 and 141* - Calculus I & II BMGT 220 & 221 - Principles of Accounting I & II BMGT 231 - Business Statistics ECON 200 & 201 - Principles of Micro & Macro Economics COMM 100, 107 or 200 - Foundations of Speech Communications, Speech Communication, or Critical Thinking and Speaking 8 cr 6 cr 3 cr 8 cr 3 cr Total 28 cr New Requirements Major Requirements BMGT 302 Bus. Computer Application Programming BMGT 402 Database Systems BMGT 403 Systems Analysis and Design BMGT 407 Information Systems Projects 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr Two courses from List A or 1 course from List A and 1 course from List B: 6 cr List A: BMGT 405 Business Telecommunications BMGT 406 Electronic Commerce Application Development BMGT 408 Special Topics in Decision & Information Technologies (repeatable if content differs) BMGT 326 Accounting Systems BMGT 476 Applied Computer Models in Supply Chain Management BMGT 484 Electronic Marketing List B: BMGT 332 Operations Research For Management Decisions BMGT 385 Operations Management BMGT 430 Linear Statistical Models in Business BMGT 434 Introduction to Optimization BMGT 485 Project Management BMGT 486 Total Quality Management Total Credits Required: Continued on next page. 18 cr Upper Level Economics Requirements One of the following courses: ECON 305 Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory & Policy ECON 306 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory ECON 330 Money and Banking ECON 340 International Economics Total Economics Requirement 3 cr (no change) 6 cr Freshmen/Sophomore Smith School Requirements (match requirements of all other BMGT majors) MATH 220 or 140 - Elem.Calculus I or Calculus I BMGT 220 & 221 - Principles of Accounting I & II BMGT 230 or 231 - Business Statistics ECON 200 & 201 - Principles of Micro & Macro Economics COMM 100, 107 or 200 - Foundations of Speech Communications, Speech Communication, or Critical Thinking and Speaking 3-4 cr 6 cr 3 cr 8 cr 3 cr Total 23-24 cr Note: It is recommended that IS Majors take additional mathematics based courses as electives. Additional Degree Requirements of the Information Systems Major At the Smith School of Business, a minimum of 120 credit hours is required to complete a Bachelor of Science degree. Besides the major requirements, economics requirements and freshmen/sophomore requirements listed above and junior/senior level Smith School of Business core requirements listed below, a student must complete the University's CORE General Education Requirements and sufficient lower and upper level elective credit to accumulate a total of 120 credit hours. A minimum of 58 credit hours of the required 120 hours must be in 300-400 (upper) level courses. A detailed explanation including additional Smith School of Business degree requirements are listed on the next page. Freshmen/Sophomore Smith School Requirements MATH 220 or 140 - Elem.Calculus I or Calculus I 3-4 cr BMGT 220 & 221 - Principles of Accounting I & II 6 cr BMGT 230 or 231 - Business Statistics 3 cr ECON 200 & 201 - Principles of Micro & Macro Economics 8 cr COMM 100, 107 or 200 - Foundations of Speech Communications, 3 cr Speech Communication, or Critical Thinking and Speaking Total 23-24 cr Note: It is recommended that IS Majors take additional mathematics based courses as electives. Junior/Senior Smith School Requirements BMGT 301 - Introduction to Information Systems BMGT 340 - Business Finance BMGT 350 - Marketing Principles BMGT 364 - Management and Organization BMGT 367 - Career Search Strategies and Business BMGT 380 - Business Law BMGT 495 - Business Policies Total 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr 3 cr 1 cr 3 cr 3 cr 19 cr General Business Major Requirements (details listed previously) 18 cr Upper Level Economics Requirements (details listed previously) 3 cr University CORE General Education Requirements not fulfilled by Smith School requirements listed above. - Total Credits Lower Level Electives 28 cr 16-17 cr Upper Level Electives 12 cr Grand Total Required 120 cr Current Catalog Description The Business Area of Concentration in the Information Systems (IS) program prepares students to be effective users and managers of information technologies and systems in the current environment of the technology-enabled business firm. The IS major focuses on the data processing skills, the analytical skills and the managerial plus organizational knowledge required to design and manage information systems and applications based on business and customer requirements. The major’s core emphasizes the concepts of system analysis and design and database management systems. In addition to a broad grounding in key functional areas of marketing, operations, accounting, and finance, this major develops in-depth knowledge of information processing technology, information systems implementation, project management, and management science and statistics. Updated Catalog Description The Business Area of Concentration in the Information Systems (IS) program prepares students to be effective planners, users and managers of information technologies and systems in the current environment of the technologyenabled business firm. The IS major focuses on the systems design and implementation skills including database and web design, analytical skills for both strategic planning of IT and performance evaluation, and the managerial plus organizational knowledge required to manage information systems and applications based on business and customer requirements. The major’s core emphasizes the concepts of system analysis and design, and the strategic use of information systems. In addition to a broad grounding in key functional areas of marketing, operations, accounting, and finance, this major develops in-depth knowledge of information systems design and implementation, evaluation and planning of information technology investments, and managing dynamic technology projects. Typical 4 Year Plan Year 1, First Term Courses ENGL101 (if not exempt) or elective MATH 220 (or as placed) ECON200 CORE class Lower level elective Year 1, Second Term Credits 3 3 4 3 3 16 Year 2, First Term Courses BMGT220 BMGT230 (if still needed) or elective Lower level elective Lower level elective CORE (Lab Science) Courses ECON201 MATH220 (if still needed) or BMGT230 COMM107 or 200 CORE CORE Credits 4 3 3 3 3 16 Year 2, Second Term Credits 3 3 2 3 4 15 Courses BMGT221 CORE Remaining electives CORE Credits 3 3 6 3 15 Year 3, First Term Courses Major requirement (BMGT 302) College Core – BMGT 340 College Core – BMGT 350 College Core – BMGT 301 Upper level ECON (from list) College Core – BMGT 367 Year 3, Second Term Credits 3 3 3 3 3 1 16 Year 4, First Term Courses Major requirement (BMGT 403) Major requirement (from options) Upper level elective (2 of 4) Professional Writing Upper level elective (3 of 4) Courses College Core – BMGT 364 Major requirement (BMGT 402) College Core – BMGT 380 Advanced Studies CORE Upper level elective (1 of 4) College Core - BMGT367 (if still needed) Credits 3 3 3 3 3 1 15-16 Year 4, Second Term Credits 3 3 3 3 3 15 Courses College Core - BMGT495 Major requirement (BMGT 407) Major requirement (from options) Upper level elective (4 of 4) Credits 3 3 3 3 12 Major/Economic Requirements: Prerequisite/Course Sequencing Structure Junior/Senior Year - The IS major course requirements do not have any long prerequisite sequences so students will not find it difficult to complete the major over the junior/senior years (also consult 4yr plan above). BMGT 301 (prerequisite: proficiency with Excel) BMGT 302 (prereq: Proficiency in Microsoft Office or BMGT 201 or CMSC 102 or CMSC 103) BMGT 402 (prereq: BMGT 301, recommended: 302) BMGT 403 (prereq: BMGT 301, recommended: 302) BMGT 405 (prereq: BMGT301) BMGT 406 (prereq: BMGT 302 and BMGT 402) BMGT 407 (prereq: BMGT 402 and BMGT 403) BMGT 408 (prereq: will typically be BMGT301 and/or 302) BMGT 326 (prereq: BMGT201 and BMGT221) BMGT 476 (prereq: BMGT370 and BMGT372) BMGT 484 (prereq: BMGT350) BMGT 332 (prereq: BMGT230 or 231) BMGT 385 (none) BMGT 430 (prereq: BMGT230 or 231) BMGT 434 (prereq: MATH220 or MATH140, recommended MATH221 or MATH141) BMGT 485 (prereq: BMGT230 or 231) BMGT 486 (prereq: BMG230) Upper Level ECONs (prereq: ECON200 & 201, some options also require MATH 220/140) Course Descriptions BMGT 301 Introduction to Information Systems (3) Prerequisite: Knowledge of Excel or similar spreadsheet tool. Comprehensive overview of information systems (IS), which explores the strategic and tactical nature of IS. The basic concepts in analyzing and designing information systems for business applications will be presented. Aspects of data management such as databases, data warehousing, data analysis, and data mining will be analyzed, and the basics of web page and web site design will be outlined. Students will also be introduced to modern information systems infrastructure such as telecommunications, networks, and information systems security. The course will include a significant laboratory component that will enable the students to use concepts learned in class in a practical setting. BMGT 302 Business Computer Application Programming (3) Prerequisite: Proficiency in Microsoft Office or BMGT 201 or CMSC 102 or CMSC 103 or permission of the department. Considers characteristics of business data programming and common software development processes and practices. Covers the designing, writing, documenting, and testing of an efficient, structured program in Visual Basic. BMGT 305 Survey of Business Information Systems and Technology (3) Introductory course for the decision and information science major. Covers the components of modern business information systems as well as the consequences of information technology on society and the environment. BMGT326 Accounting Systems (3) Prerequisites: BMGT201 and BMGT221. A study of accounting systems and computer and communications technology. BMGT 332 Operations Research For Management Decisions (3) Prerequisite: BMGT 230. Surveys the philosophy, techniques and applications of operations research to managerial decision-making. Techniques covered include: linear programming, transportation and assignment models, Markov processes and inventory and queuing models. Emphasis is placed on formulating and solving decision problems in the functional areas of management. BMGT 385 Operations Management (3) Studies the design, management and improvement of a firm's processes and systems for creation and delivery of products and services. Includes strategic and operational views of supply chain, product development, and capacity analysis, highlighting the competitive advantages that operations management can provide the firm. BMGT 402 Database Systems (3) Prerequisites: BMGT 301 or equivalent. Recommended: BMGT 302. Introduction to basic concepts of database management systems. Relational databases, query languages and design will be covered. File-processing techniques are examined. BMGT 403 Systems Analysis and Design (3) Prerequisites: BMGT 301 or equivalent. Recommended: BMGT 302. Techniques and tools applicable to the analysis and design of computer-based information systems. System life cycle, requirements analysis, logical design of data-bases, performance evaluation. Emphasis on case studies. Project required that involves the design, analysis and implementation of an information system. BMGT 405 Business Telecommunications (3) Prerequisites: BMGT 301 or equivalent. Concepts of business data communications and data processing. Application of these ideas in computer networks, including basic principles of telecommunications technology, computer network technology, data management in distributed database systems and management of the technical and functional components of telecommunications technology. BMGT 406 Electronic Commerce Application Development (3) Prerequisites: BMGT 302 and BMGT 402. Develops understanding of the fundamental principles of usability as they apply to electronic commerce applications. Aspects of web site evaluation are examined. Course will also cover the design of usable business web sites using current tools and techniques. BMGT 408 Special Topics in Decision and Information Technologies (3) Prerequisite: permission of department. Repeatable to 09 credits if content differs. Selected advanced topics in the various fields of study in decision and information technologies. BMGT 430 Linear Statistical Models in Business (3) Prerequisite: BMGT 230 or BMGT 231 or permission of department. Model building involving an intensive study of the general linear stochastic model and the applications of this model to business problems. The model is derived in matrix form and this form is used to analyze both the regression and ANOVA formulations of the general linear model. BMGT 434 Introduction to Optimization (3) Prerequisite: MATH 220 or MATH 140; or permission of department. Introduces concepts and techniques of operations research to model and solve business decision problems, focusing on optimization and commercially available software tools. Models include linear programming, integer programming, the transportation and assignment problems, network flow models, and nonlinear programming. Emphasis is placed on analyzing business scenarios and formulating associated decision models. (revised title, description and prerequisites) BMGT476 Applied Computer Models in Supply Chain Management (3) Prerequisites: BMGT370 and BMGT372. Introduction to the expanding base of computer software in the field of supply chain management. Applications include: demand planning and forecasting, transportation planning, warehouse management systems and other relevant modules. BMGT484 Electronic Marketing (3) Prerequisite: BMGT350. For BMGT majors only. Examines the process of developing, implementing and analyzing strategies for successfully marketing a variety of existing and potential products and services on the Internet. Special attention devoted to the tools and techniques unique to the electronic media. BMGT 485 Project Management (3) Prerequisite: BMGT 230 or 231 or equivalent. This course covers modern project management techniques that are used by modern practicing professionals. Particular attention is given to the management of technology based systems and projects in a business enterprise. The topics covered include: defining project scope, alignment of projects with enterprise strategy, managing project cost, time and risks using tools such as CPM/PERT, and measuring project performance. (revised title, description and prerequisites) BMGT 486 Total Quality Management (3) Prerequisite: BMGT 230 or equivalent. Total Quality Management and the synergy required between functions to obtain the customer's quality demands. Statistical tools which are mandatory in any successful quality effort. ECON 305 Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory and Policy (3) Prerequisites: ECON 200; and ECON 201; and MATH 220. Analysis of the determination of national income, employment, and price levels. Discussion of consumption, investment, inflation, and government fiscal and monetary policy. ECON 306 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory (3) Prerequisites: ECON 200; and ECON 201; and MATH 220. Analysis of the theories of consumer behavior and of th firm, market systems, distribution theory and the rol of externalities. ECON330 Money and Banking (3) Prerequisite: ECON200 and ECON201. Credit will be granted for only one of the following: ECON330 or ECON430. Formerly ECON 430. The structure of financial institutions and their role in the provision of money and near money. Analysis of the Federal Reserve System, the techniques of central banks, and the control of supply of financial assets in stabilization policy. Relationship of money and credit to economic activity and the price level. ECON 340 International Economics (3) Prerequisite: ECON 200 and ECON 201. Credit will be granted for only one of the following: ECON 340 or ECON 440. Formerly ECON 440. A description of international trade and the analysis of international transactions, exchange rates, and balance of payments. Analysis of policies of protection, devaluation, and exchange rate stabilization and their consequences. Learning Outcomes/Assessment Plan Information Systems (IS) (PROGRAM OF STUDY / MAJOR / DEGREE LEVEL, ETC.) Program Contact: Kazim Ruhi Date submitted to Academic Unit Head: Phone: 55203 E-mail: kruhi@rhsmith.umd.edu September 1, 2005 Program Goals: Provide students with the required business management skills, the general business knowledge, and the specific knowledge of the fields of Information Systems, to be future leaders in the knowledge-based “digital” economy. Relevance of goals to the mission statements and/or strategic plans of the University, College, or Program as applicable: Important business management skills required to succeed in the knowledge-based economy include critical reasoning, and oral and written communication. These are skills outlined in the University’s learning goals and objectives. The R.H. Smith School’s Vision Statement stresses the importance of training students to be future leaders in the knowledge and information-based, “digital” economy. Student Learning Outcomes Assessment Measures and Criteria Assessment Schedule (list the three-to-five most important) (describe one or more measures for each outcome and criteria for success) (initial year, and subsequent cycle) 1. Students will be able to demonstrate a clear understanding of important concepts in the core business disciplines and in the specific fields of Information Systems. All Information Systems (IS) students registered in BMGT 495, Business Policies (the capstone course for business students) during the semester in which assessments occur, are required to take a two-part test. Part 1 tests their knowledge of core business disciplines while Part 2 tests their knowledge of Information Systems. Spring semester of 2006 and every third spring semester subsequently. Seventy percent of students should answer, correctly, 80 percent of the questions in Part1 of the exam, and 70% of the students should answer, correctly, 80% of the (Note, approximately 40 percent of majors enroll in BMGT 495 in the spring semester.) MBA and Ph.D. students will be assessed in the two questions in Part 2 of the exam. other years of the three year cycle. 2. Students will demonstrate critical reasoning and written communication skills through the individual analysis and write-up of a business case. All IS students are required to analyze a business case for BMGT 495 and prepare a written analysis of the case. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations (25 out of 35 available points) in an assessment of their critical reasoning and written communication skills. See attached Critical Reasoning and Written Communication grading rubric. Spring semester of 2006 and every third spring semester subsequently. 3. Students will demonstrate their oral communication skills by presenting an analysis of a business case to their class. All IS students are required to make a presentation in BMGT 495 on a business case. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations in an assessment of their oral presentation skills (18 out of 24 available points). See attached Oral Communications grading rubric. Spring semester of 2006 and every third spring semester subsequently. 4. Students will demonstrate their leadership skills by leading a class discussion on a business case. After first making a class presentation on a business case, all IS students are required to lead a class discussion based on the case and the presentation. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations (12 of 18 available points) in an assessment of their skills in leading the class discussion. See attached Leadership grading rubric. Spring semester of 2006 and every third spring semester subsequently. 5. Students will demonstrate their abilities to work effectively with other members of a team in the preparation of a group project. All IS majors are required to participate in a the completion of a group project as part of the requirements for BMGT 495 The group generally consists of 4 6 Spring semester of 2006 and every third spring semester subsequently for BMGT 495. The group generally consists of 4-6 students. The group is required to analyze a business case, a major industry or a market segment. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations (10 of 15 points) in an assessment of their teamwork skills. The assessment will be made by the instructor but will, in part, be based on student evaluation of other team members. See attached Teamwork grading rubric. subsequently. Assessment Results Information Systems (IS) (PROGRAM OF STUDY / MAJOR / DEGREE LEVEL, ETC.) For Time Period: 3 Year Cycle Beginning Spring 2006 Program Contact: Kazim Ruhi Date submitted to Academic Unit Head: Phone: ext. 55203 E-mail: kruhi@rhsmith.umd.edu September 1, 2005 Student Learning Outcomes Assessment Criteria and Results Impact of Results Criteria: All Information Systems (IS) students registered in BMGT 495, Business Policies (the capstone course for business students) during the semester in which assessments occur, are required to take a two-part test. Part 1 tests their knowledge of core business disciplines while Part 2 tests their knowledge of Information Systems). Seventy percent of students should answer, correctly, 80 percent of the questions in Part1 of the exam, and 70% of the students should answer, correctly, 80% of the questions in Part 2 of the exam. Expected Impact: Re-evaluation of the core business courses and the required courses for IS majors to determine how to strengthen the teaching of the course content. Feedback will be passed to course coordinators and follow-up meetings arranged to assess the implementation of teaching changes. (list only those assessed during this time period) 1. Students will be able to demonstrate a clear understanding of important concepts in the core business disciplines and in the specific fields of Information Systems. Results: TBA 2. Students will demonstrate critical reasoning and written communication skills through the individual analysis and write-up of a business case. Criteria: All IS students are required to analyze a business case for BMGT 495 and prepare a written analysis of the case. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations (25 out of 35 available points) in an assessment of their critical reasoning Expected Impact: Critical reasoning and written communication skills are developed through the evaluation and write-up of business cases. In order to improve performance, increase case and written communication skills. See attached Critical Reasoning and Written Communication grading rubric. content in the IS curriculum and work with professors on evaluating critical reasoning and written communication skills and providing feedback to students. Results: TBA 3. Students will demonstrate their oral communication skills by presenting an analysis of a business case to their class. 4. Students will demonstrate their leadership skills by leading a class discussion on a business case. Criteria: All IS students are required to make a presentation in BMGT 495 on a business case. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations in an assessment of their oral presentation skills (18 out of 24 available points). See attached Oral Communications grading rubric. Results: TBA Expected Impact: Students improve their oral communication skills by making presentations and obtaining feedback on their presentations. In order to improve performance, increase the number of required presentations in the IS curriculum and work with professors on evaluating oral communication skills and providing feedback to the students. Criteria: After first making a class presentation on a business case, all IS students are required to lead a class discussion based on the case and the presentation. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations (12 of 18 available points) in an assessment of their skills in leading the class discussion. See attached Leadership grading rubric. Expected Impact: Students improve their leadership skills by practicing leadership roles. In order to improve performance, work with professors on developing opportunities for students to assume leadership roles, evaluating leadership skills, and providing feedback to the students. Results: TBA 5. Students will demonstrate their abilities to work effectively with other members of a team in the preparation of a group project. All IS majors are required to participate in a the completion of a group project as part of the requirements for BMGT 495. The group generally consists of 4-6 students. The group is required to analyze a business case, a major industry or a market segment. Eighty percent of students should meet expectations (10 of 15 points) in an assessment of their teamwork skills. The Expected Impact: Students improve their teamwork skills by participating in group projects. In order to improve performance, work with professors on developing opportunities for students to participate in group projects, evaluating teamwork skills, and providing feedback to the students. assessment will be made by the instructor but will, in part, be based on student evaluation of other team members. See attached Teamwork grading rubric. Results: TBA feedback to the students.