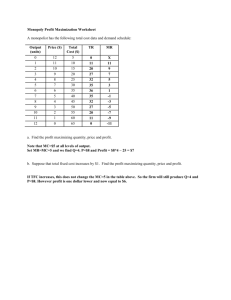
Mr. Maurer Name: __________________________ AP Economics
advertisement

Mr. Maurer AP Economics Name: __________________________ Chapter 12 – Monopoly Quiz Review 1. What is a natural monopoly? What happens to average total cost over the entire range of market demand under the conditions of a natural monopoly? (“Economies of Scale” p. 256-7) 2. How are the demand and marginal revenue curves different for a monopolist and for a perfectly competitive firm? (“Monopoly Demand” 257-9) 3. If a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolist both wanted to increase the quantity they sold, how would their decisions about price be different? (“Monopoly Demand” 257-9) 4. On the diagram on page 260, at which quantity and price is total revenue (not profit) maximized? Explain. (See graphs on 260) 5. If a monopolist is producing at a quantity where marginal revenue is negative, how should it adjust its output? Why? (“The Monopolist Sets Prices In the Elastic Region of Demand” 259-60) 6. What is the relationship between price and marginal revenue for the monopolist? Explain why. (“Marginal Revenue is Less Than Price” 258-9) 7. If marginal revenue for a monopolist is negative, what does that tell you about the elasticity of demand for its product at that level of output? (See graphs on p. 260). 8. Under what conditions will a monopolist choose to shut down production in the short-run? In the longrun? (“Possibilities of Losses by a Monopolist” 263) 9. Looking at figure 24.5 in your text, will the monopolist depicted choose to produce or shut down in the short-run? Explain. Will the firm continue operating in the long-run? Explain (263) 10. What production and pricing decisions tend to make monopolies inefficient? (Lecture notes and “Price, Output, and Efficiency” 263-264) 11. What three conditions are necessary for a firm to practice price discrimination? (“Price Discrimination – Conditions” 268.) 12. When a firm practices perfect price discrimination, what factors does it use to determine the price it charges? What role does the firm’s cost play in determining price? (“Price Discrimination” 268-9) 13. Assume that a monopolist is charging a single price (not practicing price discrimination). If the firm is able to switch to practicing perfect price discrimination, what will happen to: (p 268-9.) a. quantity produced b. consumer surplus c. total revenue d. total cost e. profit 14. In the graph below, what would consumer surplus be at the monopolist’s profit-maximizing output? What would it be at the allocatively efficient level of output? 15.If government wants to regulate a monopoly so it makes only a normal profit, it will set price equal to ____________________________________. (“Regulated Monopoly” 270-2.) 16. Assume that a monopolist is producing in the inelastic portion of its demand curve. What will happen to each of these if it lowers its price? Explain. (Use a graph of a monopolist to figure it out.) a. quantity produced b. marginal revenue c. total revenue d. total cost e. profits