Honors Chemistry Name______________________________ Matter and Energy
advertisement

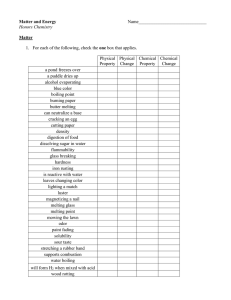
Honors Chemistry Matter and Energy Name______________________________ Matter 1. For each of the following, check the one box that applies. Physical Physical Chemical Chemical Property Change Property Change a pond freezes over a puddle dries up alcohol evaporating blue color boiling point burning paper butter melting can neutralize a base cracking an egg cutting paper density digestion of food dissolving sugar in water flammability glass breaking hardness iron rusting is reactive with water leaves changing color lighting a match luster magnetizing a nail melting glass melting point mowing the lawn odor paint fading solubility sour taste stretching a rubber band supports combustion water boiling will form H2 when mixed with acid wood rotting 2 Classification 2. Match each of the following statements with one or more of the following forms of matter. A. Solution B. Mixture (heterogeneous) C. Element D. Compound _____ soil _____ nitrogen gas _____ CH3OCH3 _____ air _____ perfume _____ jello _____ tin _____ carbon dioxide _____ pizza _____ helium _____ hot chocolate _____ hot chocolate + marshmallows _____ salt _____ tap water _____ baking soda (NaHCO3) _____ mercury _____ distilled water _____ gold ring _____ diamond _____ sand (SiO2) _____ liquid dish detergent _____ calcium _____ steam _____ Italian salad dressing _____ oxygen _____ smog Elements 3. Write the correct chemical symbol for each of the following elements. hydrogen tungsten mercury oxygen helium manganese boron sulfur lithium iron aluminum fluorine sodium nickel carbon chlorine potassium palladium silicon bromine beryllium platinum tin iodine magnesium copper lead neon calcium silver nitrogen argon strontium gold phosphorus krypton barium zinc arsenic xenon chromium cadmium antimony radon 3 Compounds 4. Complete the following table FORMULA a) 2NaHCO3 b) 3H3PO4 c) (NH4)3PO4 d) 4CaCO3 e) 2Al2O3 f) 3Ba(OH)2 g) CH3CH2OH h) 4Ca(ClO3)2 i) Al2(SO4)3 j) 3(NH4)2SO4 # FUNDAMENTAL PARTICLES 2 # INDIVIDUAL ATOMS Na: 2 H: 2 C: 2 O: 6 # TOTAL ATOMS 12 4 Mixture Separation 5. Complete the following sentences using the correct separation technique term. filtration crystallization (evaporation) chromatography distillation a. Heterogeneous mixtures are often separated by __________________________. b. Separating sand from water can be done by ___________________________. c. The sugar in sugar water can be removed by ___________________________. d. The technique that takes advantage of different boiling points is __________________. e. Removing chlorophyll pigment from leaves might be done by ______________________. f. Crude oil is broken down by heat, vaporized, and allowed to condense into various liquids such as gasoline. This process is called __________________________. 6. How could you separate a mixture of iron filings and aluminum filings? What property of these metals would allow such a separation? 7. How could you separate a mixture of alcohol, water, oil, and sand? 8. Explain what it means to say that a mixture of substances can be separated by physical means. Give an example. 9. Explain what it means to say that a substance can be separated by chemical means. Give an example. 5 10. A liquid sample of unknown composition arrives in your laboratory. Although the sample appears uniform throughout, you have been told that it is a mixture of at least two different liquids. You set up the distillation apparatus pictured below to separate the sample. a. You notice that your sample begins to boil at 96.2°C and liquid begins to drip into the collection flask. What is happening? b. Why is it a good idea to remove the collection flask and replace it with another as soon as the temperature of the solution begins to rise again? c. The temperature rises steadily and the solution begins to boil again at 102.3°C. What is happening now? d. The temperature again rises until it reaches 108°C and the rest of the solution boils. How many different liquids were contained in your sample? Explain. e. As you complete the distillation, you notice a white, crystalline film lining the inside of the flask that contained the original sample. What could this substance be? Why didn’t you notice it in the original solution? 6 Percent Concentration of Solutions 11. A 197.5 g sample of a solution is found to contain 61.5 g of sodium nitrate. Calculate the percent concentration of this solution. 12. Determine the percent concentration of a solution containing 25.0 g of table salt dissolved in 137 g of water. 13. How many grams of water must be added to 65.5 g of glucose to make a 14.5 % solution? 14. What is the mass of water in a 23.5 % solution containing 15.9 g of potassium chlorate? 15. A student attempts to experimentally determine the percent concentration of an aqueous solution by boiling off the water of a sample of the solution in an evaporating dish. Given the data below, calculate the concentration of the solution. Mass of empty evaporating dish Mass of evaporating dish and solution Mass of evaporating dish and dry residue 42.983 g 58.841 g 62.139 g 7 Energy Concepts 16. _________________ is the capacity to do work or cause change0 17. Sunlight is an example of _________________ energy. 18. The gasoline in your car is an example of chemical ___________________ energy. 19. The SI unit for energy is the _____________. 20. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that in any process, energy is neither ________________ nor ___________________. 21. ____________________energy is the energy of motion. 22. Match the energy-requiring process with the correct energy transformation it involves. ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ burning gas to drive a car friction photosynthesis electric mixer steam turbine making electricity flashlight a. electrical to mechanical b. light to chemical c. mechanical to heat d. chemical to electrical to light e. thermal to mechanical to electrical f. chemical to thermal to mechanical 23. If a process is endothermic, then: a. Energy is ___________________________________. b. The system has __________________ energy at the end of the process. c. The temperature of the surroundings will ___________________________. 24. If a process is exothermic, then: a. Energy is ___________________________________. b. The system has __________________ energy at the end of the process. c. The temperature of the surroundings will ___________________________. . 8 Phase Changes E VAPOR D CONDENSATION C BOILING B FREEZING A LIQUID MELTING SOLID 25. Answer the following questions using the heating curve above. a. Does the temperature increase during melting? __________________________ b. Is energy required for both melting and boiling? __________________________ c. What state(s) of matter is(are) present at region A? __________________________ d. What state(s) of matter is(are) present at region D? __________________________ e. Is condensation endothermic or exothermic? __________________________ f. Is melting endothermic or exothermic? __________________________ g. How would you describe the change in arrangement of particles as heat energy and temperature increase region A to region E. h. What is the name given to the temperature at region D? __________________________ i. What happens to the density of water as it moves from point A to point C? _____________ j. What happens to the density of water as it moves from point C to point E? _____________ k. Describe the change in the motion of particles from regions A to E. 26. Explain the roles of intermolecular forces and kinetic energy in the states of matter and in phase changes. 9 27. How much heat is required to melt a 10.0g ice cube at: a. 0°C? b. −15°C? 28. How many calories of heat are required to melt 157 g of gold at its melting point? 29. Aluminum has a melting point of 660.4˚C. How much heat is required to melt a 10.0 kg block of aluminum at 77.0˚C? 30. Benzene, C6H6, boils at 80.1˚C and has a density of 0.877 g/cm3. Determine the quantity of heat, in kilocalories, that are required to boil a 64.3 mL sample of benzene at 25.0˚C. 31. Determine the amount of heat required to convert 50.5 g of ice at 0°C to steam at 100°C. 10 32. How many grams of ice at 0°C can be melted by the condensation of 12.39 g of steam at 100°C, assuming a complete transfer of thermal energy? 33. How much heat is required to convert 31.5 g of H2O from 45°C to 145°C? 34. How many grams of iron at its melting point can be melted by the addition of 39.5 kJ of heat? 35. A jet of steam at 100°C is applied to a 2.00 kg block of titanium at its melting point. How many grams of steam would be required to completely melt the titanium assuming a complete transfer of thermal energy? Gas Laws 36. What happens to the volume of a gas if: a. the pressure is doubled? _____________________________ b. the pressure is quartered? _____________________________ 37. What happens to the pressure exerted on a gas if: a. the volume is halved? _____________________________ b. _____________________________ the volume is tripled? 11 38. What happens to the volume of a gas if: a. the temperature is doubled? _____________________________ b. the temperature is quartered? _____________________________ 39. What happens to the temperature of a gas if: a. the volume is halved? _____________________________ b. the volume is tripled? _____________________________ 40. What happens to the pressure of a gas if the temperature: a. is quadrupled? ______________________ b. is halved? ______________________ 41. What happens to the volume of a gas if: a. the pressure is halved and the temperature is doubled? ______________________ b. the temperature is halved and the pressure is doubled? ______________________ c. both the temperature and pressure are tripled? ______________________ 42. The volume of a helium balloon is 2.9 L at 91.2 kPa. Determine the volume at standard pressure. P1 = P2 = V1 = V2 = 43. A gas occupies of volume of 29.5 mL at 25°C. If the pressure remains constant, determine the volume of the gas if the temperature is increased to 57°C. V1 = V2 = T1 = T2 = 12 44. A sample of carbon dioxide has a volume of 2.88 L at 73°C and 655 torr. Determine the volume of this gas at STP. P1 = P2 = V1 = V2 = T1 = T2 = 45. A gas with a pressure of 1560 torr at 198°C is cooled to −16.3°C. Calculate the new pressure. 46. What is the pressure on a sulfur dioxide sample with a volume of 346 mL if it occupies a volume of 0.790 L at 125 kPa? 47. A gas has a volume of 41.3 mL at 19°C. What temperature would this gas have at 0.121 L? 48. What is the volume of a gas at STP if it occupies of volume of 14.9 L at –16.8°C and 136 kPa? 13 49. The pressure of a gas at 55°C is increased from 169.2 kPa to 3.65 atm. What will its Celsius temperature become? 50. What is the Celsius temperature of 68.2 mL of methane, if it occupies a volume of 0.022 L at 50.0°C? 51. A sample of ammonia gas has a volume of 592 mL at 119°C and 3.71 atm. What is the Celsius temperature if the pressure of the gas is changed to 232 kPa and its volume becomes 1.10 L? 52. A rigid container has 25.0 g of steam at 100°C that is exerting a pressure of 93.5 kPa on the walls of the container. If 857 J of heat are added to the container, what pressure will the steam exert? 53. A piston contains 37.9 g of steam. The piston is able to expand and contract to maintain a constant pressure. If the steam occupies a volume of 455 mL at 100°C, what will the volume be after the addition of 549 cal of thermal energy? 14 Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures 54. The total pressure of a mixture of helium, neon, and hydrogen is 498 mm Hg. If the partial pressures of helium and neon are 168 mm Hg and 192 mm Hg respectively, what is the partial pressure of hydrogen? 55. A gas is collected over water at 20.0°C in a eudiometer tube until the pressure is equilibrated with the atmospheric pressure. What is the pressure of the dry gas if the barometric pressure is 771 torr? 56. A gas is collected over water in a eudiometer tube until the pressure is equilibrated with the atmospheric pressure. The volume of gas in the eudiometer is 32.9 mL. The temperature of the water is 40.0°C and the barometric pressure is 754 mm Hg. What is the volume of this gas at STP? 57. A gas is collected over water in a eudiometer tube until the pressure is equilibrated with the atmospheric pressure. The volume of gas in the eudiometer is 25.3 mL. The temperature of the water is 50.0°C and the barometric pressure is 760 mm Hg. If the pressure remains constant, what will the volume of the gas be at 75.0 °C? 15 58. Refer to the diagram below. If the valves were both opened and all three gases were allowed to diffuse and mix equally, what would the total pressure be? Review 59. List five properties that would be considered physical properties. 60. List three properties that would be considered chemical properties. 61. Indicate if the following changes are chemical or physical in nature. a. Knocking down bowling pins b. Chopping a log c. Burning a log d. Frying an egg e. Water boiling f. Dissolving sugar into water g. Combining vinegar and baking soda h. A precipitate is formed i. A liquid freezes j. A gas is produced in a reaction 16 62. Complete the following chart Homogeneous or Heterogeneous Element, Compound, Mixture, Solution salt water iron salt magnesium bromide chocolate chip cookie ocean water carbon dioxide manganese paint snickers bar 63. Explain the difference between separating the components of a mixture and separating the components of a compound. Give one concrete example of each. 64. What is the primary difference between a mixture and a solution? What do they have in common? 65. What is the primary difference between an element and a compound? What do they have in common? 17 66. Given: 4 (NH4)3PO4 a. How many formula units are present? __________ b. How many nitrogen atoms? __________ c. How many hydrogen atoms? __________ d. How many phosphorus atoms? __________ e. How many oxygen atoms? __________ f. How many total atoms? __________ 67. Use the given heating curve to answer the questions below Heating Curve for Iron 4000 3500 Temperature (oC) 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 2 6 4 8 10 12 Time (minutes) a. What is the melting point for iron? ______________ b. What is the freezing point for iron? ______________ c. What is the boiling point for iron? ______________ d. What is the condensation point for iron? ______________ e. What phase is iron at room temperature? ______________ f. What phase is iron at 1000°C? ______________ g. What phase is iron at 2000°C? ______________ h. What phase is iron at 3000°C? ______________ i. What happens to the temperature of iron during melting? ___________________________ 18 68. List the names of the 6 phase changes and indicate if they are endothermic or exothermic. 69. How many calories of heat are required to change 35.0 g H2O at −7.0°C to 90.0°C? 70. Determine the volume of a gas at 25.0 atm if it has a volume of 2.30 L at 1025 mmHg. 71. The volume of a gas is 12.54 mL at 455 torr. What pressure is required to change the volume to 0.750 L? 72. A mixture carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide has a total pressure of 0.659 atm. If the carbon dioxide has a partial pressure that is twice that of carbon monoxide, determine the partial pressure of each gas in torr. 19 73. A gas is collected by water displacement at 23°C and the pressure is equilibrated with the air. The eudiometer reads 45.0 mL and the barometer reads 72.3 cmHg. Convert to STP. 74. A balloon is filled to a volume of 758 mL with 169 grams of steam at 125°C. After a brief period of cooling, the balloon’s volume is measured to be 745 mL. How much heat energy did the steam lose? Cumulative Questions 75. The density of copper was experimentally determined to be 8.52 g/mL. The accepted density of copper is 8.92 g/mL. What is the percent error? 76. What is the density of a 55.5 g object, in g/L, if the dimensions of the object are as follows: 5.4 cm x 1.2 cm x 3.8 cm? 77. Convert the following measurements to the specified unit: a. 2.55 nL = ____________________________ daL b. 340 cg = ____________________________ μg 20 78. Convert 35.98 kilograms into pounds and express the answer in scientific notation. 79. A block occupies 0.2587 ft3. What is its volume in mm3? 80. If a car is traveling at 55 mph, what is its speed in nm per second? 81. A 28.9 grams sample of silicon dioxide was heated from 22.4°C to 65.0°C. How much heat energy was absorbed by the silicon dioxide in this process?