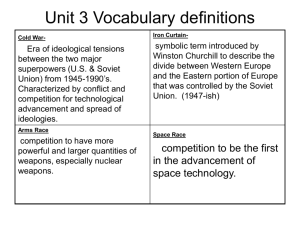
THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE Europe
advertisement

THE EASTERN HEMISPHERE Europe Europe Europe can be divided into four major landforms. The Northwest Highlands-Ireland, England, Scotland, most of the Iberian Peninsula, Norway, and Sweden. The Northern European Plains-extends from France into Russia, bordering the sea. The Central Uplands-includes the plateaus of Germany and the Czech Republic. The Alps-western and central Europe’s highest mountain range, extending from the Mediterranean coast of France through Switzerland, Austria, and northern Italy to the Balkan Peninsula. (Mont Blanc is the highest peak in the Alps.) Climate Most of Europe has mild climate conditions throughout the year. Natural Resources The Mediterranean Sea is the largest sea bordering Europe. Other major seas include the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. Europe’s coastline is about 37,877 miles long. The Rhine and Danube rivers are Europe’s most developed rivers. Most of Europe’s original forests were cut for timber or cleared for farming centuries ago. Only Finland and Sweden have large areas of timberproducing forest. Europe relies heavily on imports to meet its current industrial and energy needs. There are some deposits of iron and coal. France has been successful in producing ocean tidal power and in using solar energy. Historical Geography Europe has seen many wars and changes in leadership that have changed the political map frequently. France was Europe’s strongest power until the British defeated Napoleon’s army at Waterloo in 1815, after which Britain was Europe’s leading political and economic power. Britain’s colonial empire became the largest in the world, including ¼ of the world’s population and 1/5 of the world’s land area. Human Geography Rapid population growth occurred between 1000 and 1300. Major declines occurred due to diseases, famines, and wars between 1300 and 1450. As the Industrial Revolution took hold during the 1800s, Europe’s population grew dramatically. Millions of Europeans immigrated to the United States, Canada, Australia, and South America seeking new opportunities, or escaping religious persecutions, wars, famine, and poverty. The English language is the most widely spoken language in Europe, although there are many other languages. 90% of all Europeans between the ages of 15 and 24 speak a second language fluently. Roman Catholicism dominates Southern Europe. Northern and Central Europe is mainly Protestant. Small numbers of Jews live in many parts of Western Europe, while significant numbers of Muslims live in southeastern Europe. World War II put severe stress on Europe’s economy. To strengthen their economies, the nations of Western Europe formed economic associations. – European Union (EU) was formed in 1957 and today is comprised of 15 nations: Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, France, West Germany, and Italy; the United Kingdom, Ireland, Denmark, Greece, Spain, Portugal, Austria, Finland, and Sweden. In 1998, 11 EU nations adopted the euro, a common currency which will rival the U.S. dollar and may help unify the continent. – The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is made up of Switzerland, Norway, Liechtenstein, and Iceland. Society Europe is a society of consumers. Advanced transportation and communication networks crisscross much of Europe. Social programs often provide for the health care, education, and welfare of citizens throughout their lives. These programs are supported by high taxes. Unemployment, crime, traffic congestion, limited energy resources, and environmental pollution are all growing concerns in Europe. The nations of Europe The United Kingdom Composed of England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. The people are often referred to as British because most of them live on the island of Great Britain. London is the United Kingdom’s capital and largest urban area. The United Kingdom The Republic of Ireland In 1921, Ireland became a British dominion, called the Irish Free State. In the 1930s, the Irish government cut most of its ties with Britain, and in 1949, a completely independent republic of Ireland was recognized by Britain. Today, the Irish Republic covers about 80% of the island. Dublin is the capital. The Republic of Ireland The Nordic Countries Norway (Oslo)-Europe’s leading fishing nation. Sweden (Stockholm-a major commercial center). Denmark (Copenhagen)-very densely populated. Greenland (Nuuk)-85% of the island is covered by thousands of feet of ice cap. Iceland (Reykjavik)-a land of lava rocks, volcanoes, and glaciers. Finland (Helsinki)-has 50,000 lakes. Lapland-a land of reindeer herders. France (Paris) A nation fiercely protective of their rich culture. Germany (Berlin) Reunified in the late 1980s. The Benelux Countries Belgium (Brussels)-known for quality carpets, cut diamonds, and fine chocolate; headquarters for the EU and NATO. The Netherlands (Amsterdam)sometimes referred to as Holland; the people are known as Dutch. Luxembourg-a world banking center. The Alpine Countries Switzerland (Bern)-a confederation of 26 cantons, or states. Zurich is a leading world-banking center; Geneva is home to many international organizations. Austria (Vienna)-on the banks of the Danube River supports tourism. Spain (Madrid) Has one of the world’s largest tourist industries Portugal (Lisbon) A powerful nation between the 15th & 17th centuries. Italy (Rome) Unified in the late 19th century; a nation rich in cultural heritage. Greece (Athens) One of the poorest nations in the EU. The Golden Age of Greece took place between 477 B.C. and 431 B.C. Eastern Europe After World War II, the Soviet Union came to dominate Eastern Europe, forming a boundary with the west known as the Iron Curtain. Beginning in 1989, the countries of Eastern Europe were successful in establishing independent governments, however many ethnic conflicts have resurfaced. The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, or COMECON, oversaw economic ties between the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe. With the breakup of the Soviet Union, economic reorganization among these countries has varied. The nations of Eastern Europe Poland (Warsaw) In 1980, Solidarity formed in Poland becoming a popular focus for Polish nationalism and anti-Soviet activities. The Czech Republic (Prague) and Slovakia (Bratislava) Formerly Czechoslovakia, peacefully dividing in 1993. Hungary (Budapest) A major agriculture producer. Romania (Bucharest) A developing country. Bulgaria (Sofia) A developing country. Albania (Tirane) Eastern Europe’s least developed and poorest country. A region in conflict: Yugoslavia was created after World War I by Allied policy makers. The main Slavic groups in former Yugoslavia were the Serbs, Croats, Bosnians, Slovenians, and Macedonians. Serbs and Croats think of themselves as separate peoples. Most Croats and Slovenians are Roman Catholic. Serbs and Macedonians are Eastern Orthodox Christians. Many people in Bosnia are Muslims. Yugoslavia began to unravel violently in 1980. Serbia and Montenegro have claimed the name Yugoslavia. Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Slovenia, and Macedonia have all declared their independence. Due to the ethnic and religious differences, civil war broke out in Bosnia between Serbs, Croats, and Bosnians. The once-beautiful city of Sarajevo was destroyed by civil war. The history of the Balkan region is being rewritten every day. Russia and Northern Eurasia-Muscovy rule was prevalent from 1547 to 1917 when the Bolshevik party overthrew the government in the Communist Revolution. Thus was formed the Soviet Union. After World War II, the Soviet Union and the United States were bitter rivals in a competition known as the Cold War. In 1985, Mikhail Gorbachev became what turned out to be the last leader of the Soviet Union. He introduced glasnost (a policy of openly discussing the country’s problems) and perestroika (major economic reforms). On August 20, 1991, conservative Communist party leaders staged a coup against Gorbachev. Gorbachev and his family were imprisoned in their vacation home. The coup was unsuccessful, thanks in part to the efforts of Boris Yeltsin. Gorbachev later resigned as the Communist party leader. The Soviet Union was replaced with the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Physical Geography of Russia and Northern Eurasia The Ural Mountains divide Asia from Europe. Russia has many rivers forming a network of waterways that provide transportation and produce hydro-electric power. Economy The economy is struggling. Moscow, Russia’s capital, has a population of 9 million people, and is the heart of the country’s industrial region. Large areas of Siberia are nearly uninhabited. Ukraine Economic progress has been slow. Belarus People are often referred to as white Russians. Byelo means “white” in Russia. The Caucasus A broad isthmus of mountains that separate the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. Quarreling occurs between Islamic groups and traditionally Orthodox Christians. – Georgia – Armenia – Azerbaijan Central Asia Islam is the dominant religion. This area is the least-developed region of the former Soviet Union. Since the 1980s, regional and political turmoil has contributed to violence and instability in this region. Central Asia Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Uzbekistan Turkmenistan Tajikistan Eastern Hemisphere Southwest Asia & Africa Physical Geography A desert climate covers most of Southwest Asia. Agriculture is a major occupation. Resources and industry Oil is the region’s richest mineral resource. The main deposits lie along the shores of the Persian Gulf and in Iraq. Much of the oil is available for export. Other than oil, the countries here have few resources important for developing industry. Israel is the only country in the region that is considered developed. The world’s first civilizations developed in the Fertile Crescent (Mesopotamia: between the rivers of the Tigris and Euphrates). Three major world religions originated in this area: Judaism-the first major religion to center around the belief of one God. Christianity-the dominant religion of the Western Hemisphere. Islam-followers are called Muslims. Nations of Southwest Asia: Israel (Jerusalem) The Jews established their first kingdom more than 3,000 years ago. Over time, the Jews were forced to leave and the region became populated by Arabs. The Zionist Movement grew in the 19th century, with many believing that a Jewish state should be established in Palestine. After millions of Jews were killed during the Holocaust, The Jewish state of Israel formed in 1948, in the midst of the Arab countries. The United Nations suggested that lands west of the Jordan River be divided between Jews and Arabs. Arab lands west of the river, called the West Bank, were joined to Jordan. The Arab-Israeli conflict has led to several wars (1948, 1956, 1967, & 1973) and, although both sides seek peace, dominates political issues in Southwest Asia. The Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO) is the leader of the Palestinian cause, attacking Israeli citizens, airplanes, and property, but has pursued peace agreements. Turkey (Istanbul) Industrial development, education, and improved standards of health and housing are helping Turkey to become a modern nation. Syria (Damascus) After the Cold War, Syria has proposed peace negotiations with Israel. About 20,000 Syrian troops took part in the 1991 Persian Gulf War as part of the alliance of nations opposing Iraq. Lebanon (Beirut) More than 1/3 are Christians. Periodic civil wars have been fought between Christians and Muslims. Jordan (Amman) Jordanian and Israeli leaders signed a peace treaty in 1994. Iraq (Baghdad) Iraq has some of the world’s largest oil deposits. Iraq has been an aggressive state in recent years, invading Iran in 1980 and Kuwait in 1990. Iran (Tehran) Stormy politics have long characterized Iran. In the decades after World War II, the Shah, Iran’s ruler, used the country’s oil income to launch a program of modernization and industrialization. In 1979, the Shah fled after increasing unrest and violence. A fundamentalist Islamic government, led by the Ayatollah Khomeini, came to power. The government is struggling to redirect the country’s future. Afghanistan (Kabul) A dry, mountainous country landlocked between Iran, Pakistan, and the Central Asian republics. Afghanistan is one of the world’s least developed countries. Farming and grazing livestock are the main occupations. Civil war raged during the 1980s and into the 1990s. This included intervention by the Soviet Union. Almost all Afghans are Muslims, and in recent years, a fundamentalist group, the Taliban, has led the government, supporting terrorist Osama bin Laden, using this nation as a hideout, prompting attacks from the United States and its allies for sponsoring terrorism. Saudi Arabia (Riyadh) Mecca and Medina are important holy cities. People live where there is either oil or water. Saudi Arabia gives aid to the poorer states of the region and is working for a peaceful settlement of the Arab-Israeli issue. Kuwait An oil-rich slice of land; has one of the highest per capita incomes in the world, as well as an extensive social welfare program. Gulf States (all oil rich) The United Arab Emirates Qatar Bahrain The United Arab Emirates Qatar Bahrain Oman Oil rich. Yemen The country has one of the world’s lowest per capita incomes. Africa Physical Geography: The land is comprised of mostly high plateaus and wide plains. The Nile River (the world’s longest at 4,187 miles) is the most famous in Africa. The world’s greatest desert, the Sahara, is found here. Diseases are a constant threat in Africa. Contact with Europe: Most Europeans first dealt with Africans from trading posts along the African coast. After Europeans started to settle the Americas, African slaves became a major source of labor. The Europeans divided Africa at a conference in Berlin in 1884-1885, adding boundaries to the map of Africa. By 1900, all of Africa, except for Liberia and Ethiopia was under the rule of one European country or another. Pressure for independence grew after World War II. Today, African nations are trying to achieve the progress of developed countries, but economic progress is slow. Nations of North Africa: Egypt (Cairo) Nearly 97% of Egypt’s cultivated land is irrigated by the Nile, producing rich farmland. Cotton is the largest cash crop. Oil is Egypt’s main export. Some call Egypt the “Hollywood” of the Arab world because of its large film industry. Libya (Tripoli) Became the first African nation to gain independence in 1951; led by Muammar al-Qaddafi. Tunisia A former French colony; center in Mediterranean culture for years. Algeria Oil and natural gas provides most of its income. Morocco More than 3 million people live in Casablanca, the country’s largest city. Nations of West Africa Droughts of the 1970s and 1980s have devastated the region. The Live Aid concert in July, 1985 raised an estimated $70 million for the drought-stricken areas of Africa. The Sahel Mauritania Mali Niger Burkina Faso Chad Senegal Gambia Guinea Guinea-Bissau Cape Verde Liberia Sierra Leone – (Both Liberia and Sierra Leone were founded as settlements for freed slaves.) Nigeria Ghana Cote d’Ivoire Togo Benin Nations of East Africa Kenya Its population growth rate is one of the world’s highest, with half of its population under the age of 15. 95% of the young people are enrolled in school, learning in both English and Swahili, the country’s two official languages. Tanzania Greatest landform is Mt. Kilimanjaro. Rwanda Ethnic conflict between the Hutu and Tutsi has caused hundreds of thousands of deaths. Burundi Uganda This country has been hit particularly hard by AIDS. Sudan One of Africa’s least developed countries. Ethiopia Periods of drought have hit hard during the past 30 years. Eritria Somalia Early in the 1990’s, the country was devastated by a civil war. Violence came during a period of severe drought. Nearly a whole generation of children died. The United Nations sent troops to Somalia to provide humanitarian aid. Djibouti Nations of Central Africa Democratic republic of the Congo/Zaire Central African Republic Republic of the Congo Cameroon Sao Tome and Principe-Island countries Equatorial Guinea Gabon Angola Zambia Malawi Nations of South Africa Republic of South Africa After 1848 elections, the white-run government formally established the policy of apartheid: a series of laws that separated the races, where they lived, worked, and went to school. In the 1950’s, the African National Congress openly protested apartheid by disobeying apartheid laws. Leaders included Nelson Mandela, who received life prison sentences for treason. Apartheid began to disappear in 1989. In 1990, Mandela was released from prison and was elected president in allrace elections in 1994. Nambia Botswana Zimbabwe Mozambique Madagascar – Largest of the island countries. East and Southeast Asia McFarland Physical Geography Rugged mountains, plateaus, and hills dominate the region. The Himalayas form a boundary between East Asia and South Asia. As a protection against foreign invaders, the Chinese built the Great Wall of China. Climate Extremes of rainfall characterize much of the region. Winter months are dry, while summer months are humid and rainy. The island nations receive rain even during the winter. Economic Geography Most of the people of the region are involved in either agriculture or fishing. Japan and China are the region’s major economic powers, heavily involved in industrialization. Human Geography Roughly 1/3 of the world’s people live in East and Southeast Asia. Population growth in much of the region continues at a rapid rate, although some nations now have programs to control their population growth (China instituted a one-child-perfamily rule). A tremendous variety of cultures exists among the region’s peoples. Human Geography Hundreds of different languages are spoken throughout the region. While some countries have adopted one official language to unify the people, English has become the business language of many nations throughout the region. Human Geography In the 18th and 19th centuries, many parts of East and Southeast Asia came under the control of foreign countries. Great Britain-Myanmar, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, and Hong Kong Netherlands-Indonesia France-Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam Portugal-small possessions on island of Timor, and Macao The United States-Philippines Europeans also dominated the coastal ports of China. Japan invaded China in the 1930s and 1940s. Republic of China After World War II, the countries in the region sought independence. Maps of the region were redrawn. The People’s Republic of China was established in 1949. Korea In the early 1950s, the Korean War pitted South Korean, U.S., and the United Nations forces against North Korea and China. Vietnam In the late 1960s and early 1970s, the Vietnam War ended in the unification of North and South Vietnam under a Communist government. Political systems vary widely throughout the region. Today, tensions continue. The Nations of East and Southeast Asia: China & Taiwan China & Taiwan-In 1912, Sun Yat-sen overthrew the Chinese dynasty and formed the Republic of China. Chiang Kai-shek took over after Sun’s death in 1925. China & Taiwan To establish a strong central government Chiang wanted to defeat the warlords and the Chinese Communist party. China & Taiwan After World War II, a civil war broke out. In 1949, the Communists, under Mao Zedong, defeated the Nationalists and set up the People’s Republic of China. China & Taiwan The Nationalists retreated to the island of Taiwan and set up the Republic of China. Both claim to be the true government of China. China & Taiwan The government of China has been resistant to political reform, as evidenced by the 1989 mass pro-democracy demonstrations by students and workers in Beijing. Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked nation surrounded by China and Russia. Japan Japan is made up of four large islands and more than 3,000 smaller ones. More than 70 percent of Japan is mountainous. Japan Throughout its history, thousands of people have been killed by harbor waves called tsunami (rising up to 100 feet). Japan After World War II, Japan established itself as a democratic government. Japan Japan has the largest fishing industry in the world, and began a period of great economic growth in the 1950s Tokyo Bay The Tokyo Bay area is the world’s largest urban agglomeration, being the center of communications, government, banking, education, and trade. Japan’s urban areas face three problems: – Unaffordable housing – Air pollution – Traffic congestion Tokyo Bay Area North Korea & South Korea North Korea & South Korea-Korea is a 600-mile-long peninsula. After World War II, Korea was divided at the 38th parallel. The Soviet Union occupied the north. The United States occupied the South. North Korea & South Korea Occupation forces withdrew in 1949, and in 1950, the Korean War started when North Korea invaded South Korea. The Korean War ended in 1953 with a truce line established near the original 38th parallel. Vietnam Vietnam-occupies the eastern portion of the Indochina Peninsula. In 1954, Vietnam was divided along the 17th parallel. North Vietnam established a Communist regime; while South Vietnam established a government friendly to the U.S. In 1963, North Vietnamese troops invaded South Vietnam. The U.S. military supported South Vietnam. In 1975, North Vietnamese forces occupied Saigon, and the country was officially united in 1976. The war devastated Vietnam’s economy. Laos Laos-one of the poorest countries in the world. Cambodia Cambodia-faces challenges after years of war. Thailand Thailand-the only Southeast Asian country that was not a European colony, and is a constitutional monarchy, with Bangkok as its capital. Myanmar Myanmar-still recognized as Burma by the U.S. Malaysia Malaysia-attracts high-tech industries and has expanded its tourism industry. The world’s tallest buildings are in Kuala Lumpur, with only 88 stories, but measuring at 1,483 feet. Singapore and Brunei Singapore and Brunei-two of the smallest and wealthiest nations in the region. Living in Singapore means accepting considerable government regulation of personal choices. Chewing gum, for example, is banned by a government obsessed with eliminating potential littering problems. Failing to flush a toilet can win you a government fine. Yet, these dictates have made Singapore one of the world’s cleanest and most prosperous countries. Singapore Indonesia Indonesia-the largest nation in Southeast Asia, comprised of 13,660 islands that stretch for some 3,000 miles between the Indian and Pacific oceans. Indonesia remains a poor, agricultural country. In Indonesia there is an average of one television set for every 16 people, one radio for every 6.8 people, and one telephone for every 59 persons. Indonesia By contrast, in the United States, there is one television set for every 1.2 people, 1 radio for every .5 person, and 1 telephone for every 1.6 people. The Philippines The Philippines-comprised of 2 large islands and 7,000 smaller ones; Spain controlled the Philippine islands for 300 years. After the Spanish-American War in 1898, the U.S. took over the islands. The Philippines In 1946, the islands became independent with a history of troubles, including government corruption and violent Muslim rebel movements. Philippines Spratly Islands The Spratly Islands-a collection of 100 islands and reefs in the South China Sea claimed by the Philippines, China, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Taiwan. South Asia Physical Geography The region is home to the Himalayan Mountain rim, the world’s highest mountains. Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak, is part of the Himalayas. Climate The climate is characterized by monsoons, seasonal winds that blow from the oceans in the summer and from the interior of the Asian continent in the winter, bringing thunderstorms and heavy rains. Flooding is a constant threat to many villages. Human Geography Colonialism had a major impact on this area with Europeans arriving in India during the 16th century. A series of conflicts began in the 1740s, and in 1858, almost all of the Indian subcontinent officially became part of the British empire. Poverty characterizes the region. There is a high rate of unemployment and crime. The Nations of South Aisa: India India-The Indian independence movement was led by Mohandas Gandhi, who believed in “non-violent non-cooperation.” His methods included boycotts, marches, and fasts. Britain granted independence to India in 1947. Taj Mahal Pakistan Pakistan-More than 95 percent of the people are Muslim. The country’s major cities include Islamabad, the capital; Karachi, the largest city and major seaport; and Lahore, the cultural center and second largest city. Pakistan Kashmir Kashmir-In 1949, the UN gave Pakistan control of the northern portion of Kashmir, and India control over the southern part. Pakistan and India have fought over Kashmir for over 50 years. Nepal Nepal-Mount Everest rises above Nepal’s border with China. Bhutan Bhutan-remains somewhat cut off from the rest of the world. Bangladesh Bangladesh-surrounded by India on the north, west, and east; the major challenge facing Bangladesh is how to feed, educate, and employ its more than 125 million people. Sri Lanka Sri Lanka-just off the southern tip of India, the world’s largest exporter of tea, which is the country’s leading source of income. The Maldaves The Maldaves-a group of tropical islands in the Indian Ocean. Australia Australia Australia-the world’s smallest continent. Because of its island location, many of Australia’s animals and plants are found nowhere else in the world. Australia is known for its marsupials, such as the kangaroo and the koala. Managing unique wildlife is a source of concern. Australia The Great Barrier Reef is located in the Coral Sea off the northeastern coast of Queensland, the home to the world’s greatest variety of ocean life. The Great Barrier Reef Australia Australia produces about 1/3 of the world’s wool supply, and is the world’s leading beef exporter. The Outback is a storehouse of mineral wealth (iron ore, bauxite, coal, diamonds, opals, uranium, and oil). About 85% of all Australians live in urban areas. The country’s three largest cities include Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane. Canberra is the capital of Australia. Canberra Islands of the Pacific Islands of the Pacific-formed by volcanoes rising from the deep sea Melanesia Melanesia-includes a number of independent nations including Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands, and the Fiji Islands. New Guinea is the world’s second largest island and the most populated island in the Pacific (The western half is part of Indonesia; the eastern half is Papua New Guinea). Melanesia Micronesia and Polynesia Micronesia and Polynesia-includes more than 2,000 islands and stretches across the North Pacific Ocean. New Zealand New Zealand-an island nation that lies 1,000 miles southeast of Australia; a major exporter of lamb, wool, beef, butter, and cheese. In 1893, New Zealand became the first nation in the world to give women the right to vote. New Zealand Antarctica Antarctica-the frozen continent.