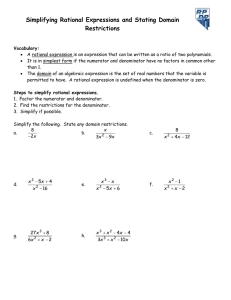
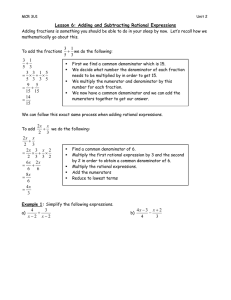
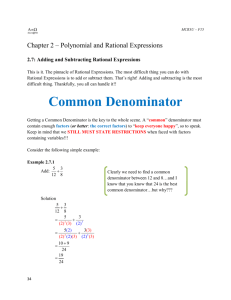
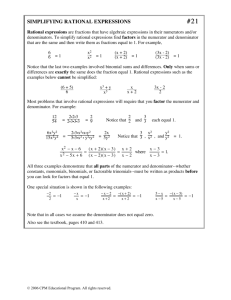
3 2 + 7
advertisement
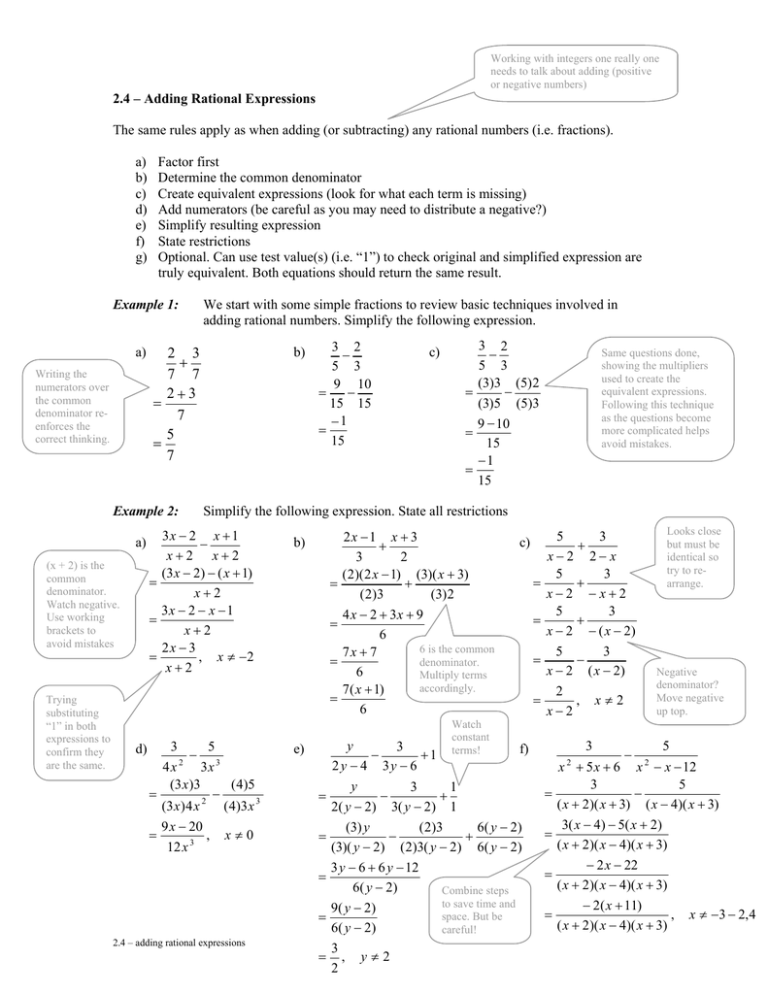
Working with integers one really one needs to talk about adding (positive or negative numbers) 2.4 – Adding Rational Expressions The same rules apply as when adding (or subtracting) any rational numbers (i.e. fractions). a) b) c) d) e) f) g) Factor first Determine the common denominator Create equivalent expressions (look for what each term is missing) Add numerators (be careful as you may need to distribute a negative?) Simplify resulting expression State restrictions Optional. Can use test value(s) (i.e. “1”) to check original and simplified expression are truly equivalent. Both equations should return the same result. Example 1: a) Writing the numerators over the common denominator reenforces the correct thinking. We start with some simple fractions to review basic techniques involved in adding rational numbers. Simplify the following expression. Example 2: a) (x + 2) is the common denominator. Watch negative. Use working brackets to avoid mistakes Trying substituting “1” in both expressions to confirm they are the same. b) 2 3 + 7 7 2+3 = 7 5 = 7 3 2 − 5 3 9 10 = − 15 15 −1 = 15 3 2 − 5 3 (3)3 (5) 2 = − (3)5 (5)3 9 − 10 = 15 −1 = 15 Same questions done, showing the multipliers used to create the equivalent expressions. Following this technique as the questions become more complicated helps avoid mistakes. Simplify the following expression. State all restrictions 3x − 2 x + 1 − x+2 x+2 (3 x − 2) − ( x + 1) = x+2 3x − 2 − x − 1 = x+2 2x − 3 , x ≠ −2 = x+2 b) = = = = d) c) 3 2 − 5 e) = = = = 2.4 – adding rational expressions c) = = = = = y 3 f) − +1 2 y − 4 3y − 6 y 3 1 − + 2( y − 2) 3( y − 2) 1 (3) y ( 2 )3 6 ( y − 2) − + (3)( y − 2) ( 2)3( y − 2) 6( y − 2) 3 y − 6 + 6 y − 12 6( y − 2 ) Combine steps to save time and 9 ( y − 2) space. But be 6( y − 2 ) careful! 3 , y≠2 2 Looks close but must be identical so try to rearrange. 3 5 + x−2 2− x 5 3 + x−2 −x+2 5 3 + x − 2 − ( x − 2) 5 3 − x − 2 ( x − 2) 2 , x≠2 x−2 Watch constant terms! 3 4x 3x (3 x )3 ( 4 )5 = − 2 (3 x ) 4 x ( 4)3 x 3 9 x − 20 = , x≠0 12 x 3 2x −1 x + 3 + 3 2 ( 2)( 2 x − 1) (3)( x + 3) + ( 2)3 (3) 2 4 x − 2 + 3x + 9 6 6 is the common 7x + 7 denominator. 6 Multiply terms accordingly. 7( x + 1) 6 3 = = = 5 x + 5 x + 6 x − x − 12 3 5 − ( x + 2)( x + 3) ( x − 4)( x + 3) 3( x − 4) − 5( x + 2) ( x + 2)( x − 4)( x + 3) − 2 x − 22 ( x + 2)( x − 4)( x + 3) − 2( x + 11) , x ≠ −3 − 2,4 ( x + 2)( x − 4)( x + 3) 2 = − Negative denominator? Move negative up top. 2 2.4 – Adding Rational Expressions Practice Questions 1. Simplify the following expressions and state any restrictions. a) 2 5 − x +1 x +1 b) 2 +4 x2 c) 3x 5 x x − + 8 6 3 d) 2x + 3y 4x − y − 5 2 e) 2 3 + x−2 2− x f) 2 3 + x +1 x + 2 g) 3 1 − 3 x + 15 6 x + 24 h) 2x 3 + x − 4x − 5 x − 5 i) 6x 3 − 2 6 x − 6 3x − 4 x + 1 j) 4y 2y + 2 y − 9 y + 18 y − 11y + 30 2 2. Simplify; 2 k) 2x −1 2x + 1 + 2 2 x + 3x + 1 3x + 4 x + 1 2 2 x + 5 x − 5 3x × + x − 5 x +1 x +1 3. Two triangles have the same base length of x. One has a height of x -1 while the other has a height of x + 3. Write a simplified expression for the total area of both triangles. −16 x + 11 y −3 −1 x 2 + 4x 2 , x ≠ −1 b) d) e) ,x ≠ 2 , x ≠ 0 c) − 8 10 x +1 x−2 x2 5x + 7 5 x + 19 5x + 3 , x ≠ −1,−2 g) , x ≠ −4,−5 h) , x ≠ −1,5 f) 6( x + 5)( x + 4) ( x − 5)( x + 1) ( x + 1)( x + 2) Answers 1. a) i) 2 y (3 y − 13) 3x 2 − x + 3 1 , y ≠ 3,5,6 , x ≠ ,1 j) ( y − 3)( y − 6)( y − 5) ( x − 1)(3 x − 1) 3 k) 10 x 2 + 3 x 1 1 , x ≠ −1,− ,− ( 2 x + 1)( x + 1)(3 x + 1) 2 3 2.4 – adding rational expressions 2. a) 5, x≠-1,5 3. At=x(x+1)