Document 14261754
advertisement

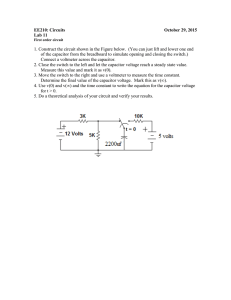
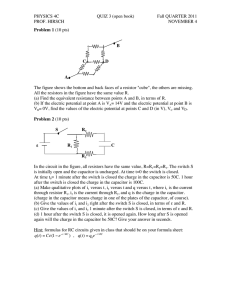
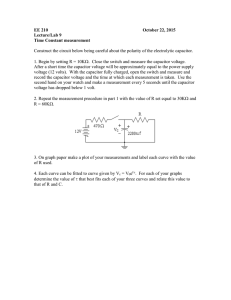
Here are some test type questions for Ch 16­20. The real test might have 15 such questions, with roughly a third requiring essentially no math other than perhaps simple ratios. All questions will actually be multiple choice for this first hour exam. 1) Sphere A carries a net positive charge, and sphere B is neutral. They are placed near each other on an insulated table. Sphere B is briefly touched with a wire that is grounded. Which statement is correct? Explain. A) Sphere B remains neutral. B) Sphere B is now positively charged. C) Sphere B is now negatively charged, D) The sign of the charge on sphere B cannot be determined without additional information. 2) A point charge of +Q is placed at the center of a square. When a second point charge of ­Q is placed at one of the square's corners, an electrostatic force of 2.0 N acts on the positive charge at the center. Now, identical charges of ­Q are placed at the other three corners of the square. What is the magnitude of the net electrostatic force acting on the positive charge at the center of the square? Explain 3) List three properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium. 4) State the basic definition of Electric Field either as an equation or in words. 5) If the electric field has a magnitude of 60 N/C a certain distance from a point charge, what is the magnitude of the electric field twice as far away but on the opposite side of the source charge? Explain. 6) Two identical aluminum objects are insulated from their surroundings. Object A has a net charge of excess electrons. Object B is grounded. Which object is at a higher electrical potential? Explain 7) A negative charge is moved from point A to point B along an equipotential surface. Explain answer. A) The negative charge performs work in moving from point A to point B. B) Work is required to move the negative charge from point A to point B. C) Work is both required and performed in moving the negative charge from point A to point B. D) No work is required to move the negative charge from point A to point B. 8) The absolute potential at the center of a square is 3.0 V when a charge of +Q is located at one of the square's corners. What is the absolute potential at the square's center when a second charge of +2Q is placed at one of the remaining corners? Explain. 9) If the electric field between the plates of a given capacitor is weakened, the capacitance (Explain reasoning) A) increases. C) does not change B) decreases. D) cannot be determined from the information given 10) A parallel­plate capacitor is connected to a battery and becomes fully charged. The capacitor is then disconnected, and the separation between the plates is increased in such a way that no charge leaks off. The energy stored in this capacitor has (Explain reasoning) A) increased. C) not changed. B) decreased. D) become zero. 11) A uniform electric field, with a magnitude of 500 V/m, is directed parallel to the +x axis. If the potential at x = 5.0 m is 2500 V, what is the potential at x = 2.0 m? Explain. 12) What charge appears on the plates of a 2.0­μF capacitor when it is charged to 100 V? 13) If a 10­μF capacitor is charged so that it stores 2.0 × 10­3 J of energy, what is the voltage across it? 15) The resistance of a wire is defined as A) (current)*(voltage). B) (current)/(voltage). C) (voltage)/(current). D) none of the given answers 16) If the current flowing through a circuit of constant resistance is doubled, the power dissipated by that circuit will A) quadruple. B) double. C) decrease to one half. D) decrease to one fourth. 16) What length of copper wire (resistivity 1.68 × 10­8 Ω∙m) of diameter 0.15 mm is needed for a total resistance of 15 Ω? [note that answers vary by factor of 10 so you only need to think approximate numbers –check factors of 10] A) 16 mm C) 1.6 m B) 16 cm D) 16 m 17) A 1500­W heater is connected to a 120­V line for 2.0 hours. How much heat energy is produced? Explain. 18) When resistors are connected in parallel, we can be certain that A) the same current flows in each one. B) the potential difference across each is the same. C) the power dissipated in each is the same. D) their equivalent resistance is greater than the resistance of any one of the individual resistances. 19) What is the total resistance for the circuit at the right ? 20) A 2.0­μF capacitor is charged to 8.0 V and then discharged through a 4.0 × 106 Ω resistor. How long will it take for the voltage across the capacitor to drop to 3.0 V? Explain 21) A 1.0­μF and a 2.0­μF capacitor are connected in series across a 3.0­V battery. What is the voltage across the 2.0­μF capacitor? Explain. 22) 5.00 μF, 10.0 μF, and 50.0 μF capacitors are connected in parallel across a 12.0­V battery. How much charge is stored in the 5.00­μF capacitor? Explain 23. If identical point charges of Q = − 4nC are placed at the four corners of a square that is 12 cm on a side. What is the force acting on the charge at each corner ? 24 What maximum force could act on a 10 cm long wire with a current of 1.2 A if placed in a magnetic field of 0.5 T ? How must the wire carrying this current be oriented in order for this maximum force to be realized ? 25 Set up the equations needed to determine the three currents for the circuit shown. . 26. When a 200 µF capacitor is fully charged using a 15 volt power supply and then discharged through a resistor, the decay time constant is measured to be 60 ms. a) How much charge is on the capacitor when fully charged ? b) How large is the current at the instant the capacitor starts to discharge ? c) What is the resistance through which the capacitor is discharged ? d) How much energy is turned to heat by the time the capacitor is fully discharged ? 27. List two different types of sources for a magnetic field. 28. A solenoid has 500 turns and is 10 cm long. How much current will produce a magnetic field of 27 mT at its center ? 29. What is the strength of a magnetic field 5.0 cm from a long straight wire carrying 4.0 A of current? A) 3.8 × 10­6 T C) 1.6 × 10­5 T B) 4.9 × 10­6 T D) 4.7 × 10­5 T 30. A uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T is directed into the page. If a proton is moving to the right with a velocity of 104 m/s, what is the force acting on it ? What path will it take ? 31. Two long parallel wires carry equal currents. The magnitude of the force between the wires is F. The current in each wire is now doubled. What is the magnitude of the new force between the two wires? A) 4F C) F/4 B) 2F D) F/2 32. A stationary proton is in a uniform magnetic field of 0.20 T. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on the proton? A) zero C) 3.2 × 10­20 N B) 1.6 × 10­20 N D) 1.6 × 10­21 N 33. An electron moves with a speed of 8.0 × 106 m/s along the +x axis. It enters a region where there is a magnetic field of 2.5 T, directed at an angle of 60° to the +x axis and lying in the xy plane. Calculate the magnetic force of the electron. A) 2.8 × 10­10 N B) 3.2 × 10­10 N C) 2.8 × 10­12 N D) 3.2 × 10­12 N