The atmosphere of Earth is what allows life to be... Without the atmosphere, temperatures would be extreme. The days...
advertisement
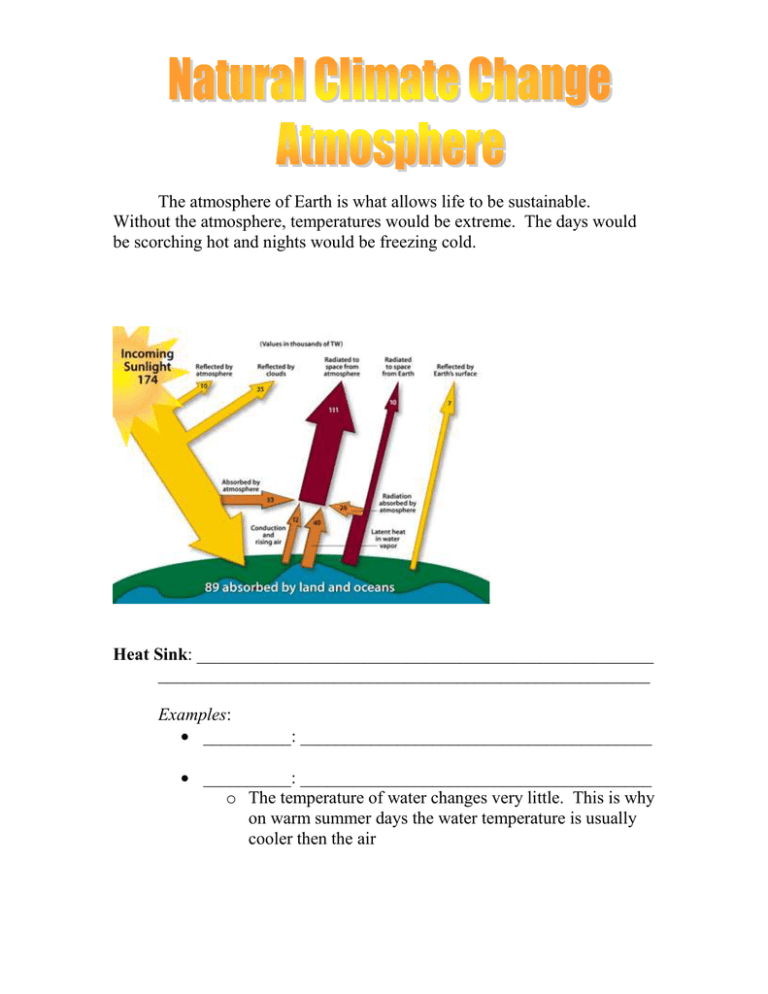
The atmosphere of Earth is what allows life to be sustainable. Without the atmosphere, temperatures would be extreme. The days would be scorching hot and nights would be freezing cold. Heat Sink: ____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ Examples: __________: ________________________________________ __________: ________________________________________ o The temperature of water changes very little. This is why on warm summer days the water temperature is usually cooler then the air ___________________________________________________ Albedo: ______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Changes in Albedo Warming Effect o Melting ______________________. o Less _________________________ o More ________________________ o Temperature __________________ o More _____________________ … Cooling o Volcanic Eruptions spew ___________ o More ___________________________ o Less ____________________________ o Temperature _____________________ o Snow ___________________________ o Albedo __________________________ Some of the energy from the Sun that is absorbed is ______________. This is why the planet is not in a constant state of _____________ even though it is always ______________________________________________ Greenhouse Effect: ___________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ This is a natural part of Earth’s climate system. It helps keep Earth’s temperature suitable for life. The gases that absorb heat form Sun and Earth’s surface are called _______________. The gases then radiate the heat back to Earth to help warm the planet. Type of Greenhouse Gas Common Sources Evaporation of _________ Given off by ________, ___________________ ___________________ Other Details Most abundant greenhouse gas Scientists believe it accounts for about 70% of the greenhouse effect Amount in the atmosphere varies with temperature (higher temperature results in more water vapour) Produced during cellular respiration and certain plan processes ___________________ ___________________ ____________________ ____________________ Second most abundant greenhouse gas Produced in and by the cells of most living organisms through cellular respiration Certain species of ____________ and other microorganisms that live in and around bogs, wet lands, melting permafrost Certain species of bacteria that live in the gut of some animals such as _________________ Cents and other openings in _________________ ____________________ Bacteria that live in ____________________ _____________________ _____________________ A byproduct of certain types of cellular processes that enable some species of microorganisms to extract energy from food in the absence of oxygen Produced when certain species of bacteria break down nitrogen-rich compounds for food . Heat Distribution Homework: 1. Describe what happens to solar energy once it reaches Earth. 2. In terms of energy, why does Earth’s temperature remain fairly constant? 3. In terms of absorbed and reflected energy what would have to happen for Earth to have cooler temperatures? 4. Fresh snow has an albedo of about 85% and old snow has an albedo of about 50%. Which will reflect more of the Sun’s radiation? Why? 5. Scientists think that a giant meteorite crashed into Earth millions of years ago, resulting in the extinction of dinosaurs. The meteorite impact produced a thick cloud of particles that prevented some sunlight from reaching Earth, Why do you think this might have lead to the extinction of dinosaurs? 6. The ice caps at Earth’s poles are becoming smaller as the ice melts. Explain how the melting of the polar ice caps might change Earth’s temperature. 7. Predict what would happen if the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increased? 8. Why might scientists believe that water vapour accounts for so much of the greenhouse effect?







