19 Century Russia th Revolution to Reform to Revolution
advertisement

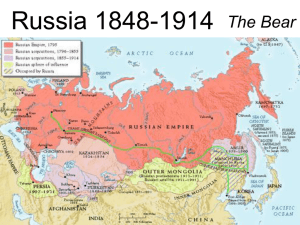
th 19 Century Russia Revolution to Reform to Revolution (again) 19th Century Czar overview The last of the Romanov Dynasty-Alexander I 1801-1825 (Decembrists) Nicholas I 1825- 1855 Alexander II 1855- 1881(reformer= kaboom!) Alexander III 1881-1894 Nicholas II – 1894-1917 (last one) Alexander I 1801-1825 Czar defeated Napoleon I Congress of Vienna Holy Alliance Liberal to Conservative agenda Dies suddenly in 1825 Brother Constantine refuses thronehesitation leads to Decembrist- youngest brother Nicholas takes throne Nicholas I 1825-1855 Conservative Secret Police Little reform agrarian economy Territory expansion in Balkan – Black Sea area Begins Crimean War 1854- dies 1855 Consequences of Crimean War New warfare technologies-RR, shell-firing cannon, breech loading rifle, steam powered ships Telegraph effects news coverage of front lines-created negative public opinion ***severed alliance of Austria & Russia ****ended Russia territory gain in Black Sea region Alexander II 1855-1881 “Great Reforms” Defeated in Crimean-forces path of reform Military reform- end serf conscription farm to industry Emancipation of serfs Better farming techniques Reduce power of nobility Emancipation of Serfs 1861-50 million serfs freed Mir- community of former serfs, male leader Allocation of land – not free -paid to government through long term loans Huge debt burden to freed serf Yet freedom means more rights– somewhat!! Local administration Reform Zemstovs--regional councils where aristocrats directed local matters ex. education, public health , welfare Conservative but relaxation of censorship and travel for nobility Exposed to European ideas use new ways to solve problems Military Reform 1874- government ends 25 year conscription- now 6 years Promote education Increased military efficiency Humane treatment of recruits Fitness of Russian soldiers improves— close to level of other European counterparts Judicial Reform All Russians access to modern courts Remove serf from landowner or secret justice Principle of equal justice before the law introduced– but not always followed Reforms bring resistance Nobility sees power diminished Nihilist- youthful nobles reject aristocratic leisure- turn to peasant & worker lifestyle Russification against ethnic groupslanguage education repression to reduce threat of rebellion Throughout Reforms- Czar and inner circle allow few other to share in power Russia + Imperialism East through Asia Siberia- Vladivostok Trans-Siberian Railroad Port Arthur on Pacific-1898 leased from China Turkistan Parts of Afghanistan Unrest in Russia-Secret societies 1871- Reform runs course Youth turn to revolutionary ideas to stimulate additional social and political reform-Secret police increase Populists- incite indebted peasants to revolt Land and Liberty-then People’s Will – assassinate Alexander II in 1881 Alexander IIIConservative- rejects all liberal reform New wave of oppressionOpriniche- secret police unchecked power to spy Intensifed Russification program Oppression of Russian Jews Pogroms- Pale of Settlement- scapegoats Dies in 1894 Nicholas II– last Czar Weak ruler Inherits 18th century country entering the 20th century Still agrarian– little industry Serge Witte- chief minister- increases industrialization pushes for reformpractical man- retires 1908 Peter Stolypin- continues Witte policiesassassinated in 1913 Family Alexandra- wife, German, Victoria’s granddaughter nickname- Sunny Olga Tatiana Marie Anastasia Alexis- hemophilia- Rasputin,( Mad Monk) Political Issues Russo- Japanese War 1904-1905 Humiliating defeat for Russia- but TR got the Nobel Peace Prize for the peace treaty Duma- elected congress- little powerSD’s, Bolsheviks, Mensheviks, Const. D’s Kerensky and Kornilov 1905 Revolution- Bloody Sunday 300 y anniversary- Romanov Rule 1913 Coming of WWI Triple Alliance – FRE/E Assassination of Francis Ferdinand – heir to A-H throne Princip- member of Black Hand, Serbian revolutionary group Leaders of the Bolsheviks Lenin- Land, Bread, Peace Trotsky Bukanin Stalin