Types of Statutory Laws Civil Law Criminal Law
advertisement

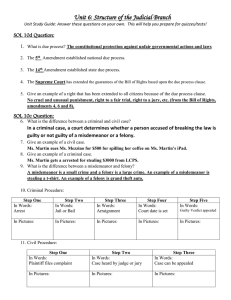
Handout #19 (front) Types of Statutory Laws Civil Law Definition law involving a dispute between two or more private parties (individuals, companies, etc.); disputes may be over damages, property ownership, violation of a contract, etc. Trying to Prove? Liability – responsibility for wrongdoing that usually requires payment/compensation; Could require following an agreement or give authority over someone or property Preponderance of the evidence (meaning who has more persuasive evidence) Defendant vs Plaintiff Usually only requires a majority vote Level of Proof Sides Jury Verdict Jury Size Grand Jury? 12 (mostly) but can be as few as 6 Never Criminal Law law established by your elected lawmakers; in these cases the state brings charges against one of its citizens for violation of the law; your locally elected District Attorney is the prosecution in these cases Guilt – for the sake of handing down a punishment Beyond a reasonable doubt Defendant vs Prosecution (government) Unanimous Usually 12 In some cases. Federal courts use it more. Some states still use it. Types of criminal law: Summary Offense: the most minor types of crimes; punishments range from fines to up to 90 days in jail Misdemeanor: these are moderate crimes; maximum punishments range from 5 years in jail for a 1st degree misdemeanor to as little as 1 year maximum for a 3rd degree misdemeanor Felony: the most serious types of crimes; punishable by death or life in prison for certain crimes; other 1st degree felonies can receive up to 20 years in jail maximum while 3rd degree felonies face up to 7 years maximum Educated Guess Questions: Identify each of the following examples as a matter of civil law, as a felony, misdemeanor, or summary offense. Indicate your choice by writing the word "civil", “summary”, "misdemeanor", or "felony" in the blank. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. A fine for littering. A spouse of has deliberately poisoned his or her partner in an attempt to injure or kill him/her. A suit filed against an automobile manufacturer when the plaintiff's spouse is killed after the vehicle's gas tank explodes in a collision. The plaintiff believes the vehicle suffered from a faulty design. Knowingly selling stolen property. Someone pays $500 to buy a new $5000 TV that they know has been stolen. Someone pays $50 to buy a new $150 pair of sneakers that they know has been stolen. Residents sue a newly operating chemical plant in their community for destroying the resale value of their houses (due to pollution). An escaped criminal burns down a shopping center. A nurse working at a nursing home is charged with negligent homicide when a resident who has not received prescribed medication from the nurse dies. Police charge you with disturbing the peace when you are blasting. . . er, uhm. . . "testing" your new car stereo in the front yard at 2 A.M. A woman causes her ex-fiancée emotional pain and distress after she dumps him and calls off their wedding. He wants her to pay him for the pain and suffering she caused him. Stealing a moped worth $1000. Starting a fistfight with your neighbor. Punching a police officer. A 19 year-old attempts to buy alcohol. A 17 year-old has, for the second time, attempted to use a false ID card.