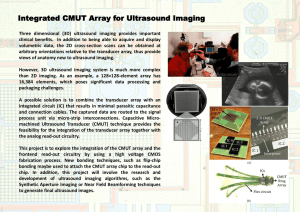
Ultrasound Miniaturization Scott Smith GE Global Research
advertisement

Ultrasound Miniaturization Scott Smith Ultrasound Probes Lab Clinical Systems and Devices GE Global Research 2011 Joint AAPM / COMP Meeting July 31-August 4 Vancouver 1 Acknowledgements Charles Baumgartner Tim Fiorillo Warren Lee Robert Lewandowski David Mills Chet Saj George Sogoian Doug Wildes\ Chris Yetter Carl Chalek Scott Cogan Scott Dianis Congjian Xia Aaron Dentinger Bruno Haider Chris Hazard Ralph Hoctor Srinivasan Jagannathan Jing Jin Larry Mo Suhyun Park Wayne Rigby Kai Thomenius Kieran Wall Kirk Wallace Michelle Bezdecny Tony Brewer Mark Cheverton Robert Pieciuk Prabhjot Singh Venkat Venkataramani Rayette Fisher Robert Wodnicki This project have been supported in part by Award Number 1RC2EB011439 from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), and 1R01CA1152677 from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of NCI, NIBIB or the NIH. Unless otherwise noted, all photography and drawings are the property of General Electric. 2 Ultrasound Systems Broad range of applications and price points 3 System Block Diagram Scan Converter Detector Video Display Transducer Beamformer System Controller User Interface 4 How did the imager get so small? Electronics & ASICs miniaturization CPUs & Software evolution Sensors with embedded beamforming 5 Ultrasound Probes 6 Transducer Array Structure Acoustic Lens Element Isolation Cuts Acoustic Matching Layers Ground Electrode Piezoceramic Signal Electrode Acoustic Absorber Ground Flex Signal Flex 7 How can you make a better image? Goals: Achieve uniform elevation resolution (slice thickness) over an extended range. Preserve lateral & axial image quality Constraints: Limited number of system channels Patient access (probe footprint) 8 Transducer Array Taxonomy Elevation 1D 1.25D 1.5D 1.75D 2D Fixed Discrete Dynamic Dynamic Dynamic Static Static Dynamic, Symmetric Dynamic, No Symmetry Constraint Dynamic, Steerable Aperture Focus 9 Elevation Beamforming 1D array relies on fixed lens for elevation focus. Good resolution at focus; poor in near & far field. Transducer Element Image Slice Thickness Lens Lens Focus Depth of Field Multi-row array with multiple focal zones maintains uniform resolution over much greater range. Depth of Field with Multi-Row Transducer and Multiple Focal Zones 10 Elevation Beam Profiles 1D 1.25D 1.5D 11 Aperture Design: Compromises Performance vs. Probe + System Cost 1D vs. 1.25D vs. 1.5D vs. 1.75D vs. 2D Application => Footprint, Frame rate, ... Number & size of rows, elements Beam quality vs. intercostal or endo access Lens (single vs. multi-focus), Apodization Time delays for elevation beamforming 12 Single- vs. Multi-Row Arrays Single Row MultiRow Phantom with 2 mm Spherical Cysts 13 2D Array Strategies Sparse arrays: use 10% - 25% of elements Active elements in probe = channels in system (256 – 512) + Established probe technology – Poor image quality (grating lobes, weak penetration) Dense arrays: use all elements Active elements in probe (2K – 3K) >> channels in system + Good image quality – Beamforming electronics in probe High voltage Transmit vs. low voltage Receive High density, low power: packaging, interconnect, cooling 14 Sub-Array Beamformer in Probe Power & Control Preamps To System Channel Sum Delays Transmit Digital or Analog? Connects a group of transducer elements to each system channel Low-power analog beamformer: Phase rotation or Delay lines Small delays only: static steering of small sub-aperture Dynamic focusing & full-aperture delays by system beamformer B. Savord & R. Solomon, Philips 2003 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium 15 15 2D Array Strategies II Matrix arrays: Switches connect elements into linear or annular groups Reconfigure switches to change steering direction or change focus (esp. transmit focus) + System sees probe as 1D or annular array – Need many small, high-voltage, low-loss switches tightly integrated with transducer elements To system channel 16 Probe Beamforming Leads to Handheld Systems Modular Beamformer in Probe Handle 2D Transducer Array (vs. human hair) 17 The Other Miniaturizaton: Intracardiac Arrays Lee et.al. IEEE Trans. UFFC 58, 1478, (2011) 18 DMP: Materials & Structures High aspect ratio structures, shapes on demand Materials demonstrated: Alumina, Polymers, PZT, Platinum, Phosphors Pt PZT 50 mm layers, 500 mm tall – Polymer (Photocurable Acrylate) 50 mm layers, sintered, Alumina Pt-PZT co-deposited & co-sintered Mag Z 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Freq (MHz) 15 micron posts, polymer (Photocurable Acrylate) Periodic piezoceramic columnar array ~80 micron columns DMP Piezo Blank keff 0.53 19 Handheld Devices – More Users, Smarter Products • Intuitive: minimal training for new users • Quick exams: < 3 minutes • Limited user interface: 2-3 buttons • Standardized: operator/patient-independent Automation opportunities: Start Imaging Management Document Automatic image optimization Automatic application recognition Imaging guidance Automatic measurements Intuitive indicators Automatic annotation Report generation End Automated Gain Adjustment now in Products 20 Rural Healthcare: Obstetrical Measurements Gestational age from 2D data sets Motivators: Pregnancy dating Placenta previa Multiple gestations, breech Performance Currently automated algorithm within +/- 5 days of manual estimates. BPD = 59.1 mm GA = 23 wk 21 Automated Fetal Measurements: Working with 3D data sets Auto facial Recognition Coming over several years. 22 Automatic Blood Vessel Measurements Edge Tracking Vessel Detection B-Mode Image Ultrasound Waveforms Area Artery Blood Flow Power HR Demodulated Flow Vein 23 Ultrasound R&D Diagnosis/Therapy Beyond Diagnosis •U/S-guided HIFU •U/S-activated drug delivery New capabilities Applications Technology •Redefine clinical workflow Sustaining Innovations for Established Market Segments •Novel •Demonstrable •Clinically relevant Ubiquitous Sensing •Home healthcare •Telemedicine Integrated Systems Image Fusion Primary care Rural healthcare Emerging Applications Miniaturization •Reduce cost & size •Improve quality/price •Increase access New Users 24 25