Plate Tectonic Boundaries
advertisement

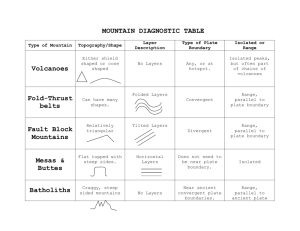
Plate Tectonic Boundaries Earth Science Geology 007 Types of plate boundaries transform divergent convergent Divergent Plate Boundaries continental rift incipient ocean basin mid-ocean ridge Divergent Plate Boundary Central rift valley Shallow earthquakes Volcanoes African continental rift and incipient ocean basins African Volcanoes Kilimanjaro African rift valley - Lake Turkana Global system of mid-ocean ridge divergent plate boundaries Seafloor Age - Mid-Atlantic Ridge Mid-ocean ridge is visible where it crosses Iceland Rifting and volcanism in Iceland Central Rift Valley - Iceland 13 Convergent Plate Boundaries Wadati-Benioff Zone - region of earthquake activity at a subduction zone shallow intermediate deep subduction What is the orientation Seismicity - South America of subduction? uctio subd n Cocas sub duc tio n Caribbean Nazca on ucti subd sub n Caribbean uctio subd duc tio n What is the orientation of subduction? Cocas Nazca on ucti subd Convergent Boundary: Ocean - Continent Convergent Plate Boundary Ocean - Continent Shallow - intermediate - deep earthquakes Wet mantle volcanism - stratovolcanoes Continental compression - high mountain range with volcanoes Seismicity - South America Volcán Tungurahua, Ecuador Cascades Volcanic Range Mt. Rainier Mt. St. Helens Mt. Hood Mt. Adams Mt. Rainier, Seattle, Washington Convergent Boundary: Ocean - Ocean Convergent Plate Boundary Ocean - Ocean Shallow - intermediate - deep earthquakes Wet mantle volcanism - stratovolcanoes Volcanic island arc Mt. Redoubt - Aleutian Islands, Alaska Volcanic Island Arcs - East Seismicity - Southern AsiaAsia and Indonesia cti on bd u su subd su bd u cti on n uctio Volcanism - Central America / Caribbean Seismicity Volcanoes of the Lesser Antilles Soufriere Hills, Montserrat 34 Seismicity - Southern Asia Convergent Boundary: Continent - Continent Convergent Plate Boundary Continent - Continent Shallow earthquakes No volcanism High mountain range and plateau due to crustal thickening Alps Zagros Mtns. Western Himalaya Seismicity - Europe Tibetan Plateau Himalayan Mtns. Mt. Everest Seismicity - Southern Asia Himalaya Mountains Makalu Mt. Everest Everest Transform Plate Boundary Tectonic plates sideswipe each other Shallow earthquakes horizontal displacement of the crust over great distances Transform boundary displaced stream San Andreas Fault Transform boundary Hot Spots • Localized regions of high heat flow in the mantle. • Generates melting in the overlying crust. • Remain fixed for between 20 million and 100 million years while plate rides over. • Many aseismic ridges produced by hot spots. Hot Spots Hawai’ian Ridge and Emperor Seamount hotspot trail Emperor Seamounts Plate motion Hawai’ian Ridge Hawai’ian Islands Hot Spot Causes of Plate Movement • Ridge Push – plates are moving down slope due to gravity, from high elevation at ridges to low elevation in trenches. • Slab Pull – Subducting slab sinking into mantle pulls the rest of the plate behind it. • Both!