Elements and their Origins What is the Earth made out of
advertisement

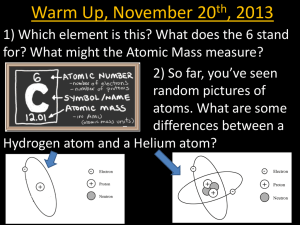
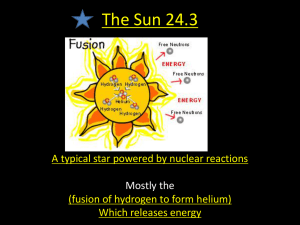
Elements and their Origins What is the Earth made out of and where did it all come from? Elements What are these? What is this? Stars are formed out of hydrogen gas. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. When the universe formed, almost all matter was hydrogen, with some helium. The Big Bang Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Both hydrogen and helium form as protons and neutrons assemble from quarks and then begin to collide together in the first 100 seconds the universe existed. No elements heavier than helium form. So where did the rest of the elements come from? Elements from Helium to Carbon are formed by stellar nuceleosynthesis (nuclear fusion) in all stars. Our sun is currently fusing Hydrogen atoms into Helium atoms, releasing heat as mass is converted to energy. When the Sun runs out of Hydrogen, it will begin to fuse Helium into Carbon. Our sun is too small to burn Carbon, so when it runs out of Helium fusion will stop. fusing hydrogen to helium fusing slowly helium to cooling carbon Elements from Nitrogen to Iron are formed by stellar nucleosynthesis (atomic fusion) in high mass stars. 4 12 16 24 28 32 56 Iron cannot fuse in stars - it is the end of the fusion process. Elements heavier than iron are produced when massive stars go supernova. Massive stars explode when they run out of nuclear fuel and their iron cores collapse catastrophically and rebound - a Supernova! During a supernova atomic nuclei in the exploding star are bombarded by neutrons, growing in mass to form heavy elements. Actual supernova in a distant galaxy Supernovae blast heavy elements into interstellar space. New stars and solar systems like our own form from the elemental debris of older dying stars. Eagle Nebula “We are all made of star stuff.” - Carl Sagan Our solar system began as a nebula - a cloud of interstellar dust and gas, predominantly hydrogen and helium, but also containing heavier elements from nearby supernovae. Condensing proto-Sun and solar nebula Elements present in the solar nebula combined to form molecules. Molecules of solid matter began to clump into larger and larger pieces, eventually forming the planets. The Great Nebula in Orion Metals and Silicates Hotter Hydrogen, Helium, Ices Cooler Refractory molecules condense Snow Line Volatile molecules condense The inner planets formed predominantly from the most abundant refractory elements: Iron Silicon Magnesium Sulfur and their oxides. Early on, the Earth melted, causing most of the iron to sink to form a metallic core. The lighter oxides separated to form a rocky mantle and crust. We are not certain how the Earth acquired its abundance of volatile compounds such as N2, CO2 and H2O. One possibility is that volatiles were delivered to the Earth from the outer solar system by comets and icy asteroids. Abundance of Elements in Earth’s Crust