Chapter 4 ECE 3800 John Stahl Western Michigan University
advertisement

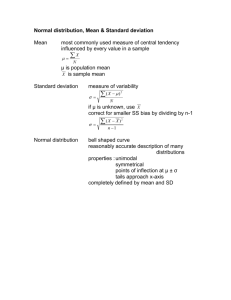
Chapter 4 ECE 3800 John Stahl Western Michigan University Vocab Population (N): a set of data being studied. Population mean(𝐗): the average within the population. Sample (n): a subset of data taken from the population. Sample Mean(𝐗): the average within the sample True Mean(m or 𝑿): Population mean. Unbiased Estimator: when the sample mean is equal to the true mean. Vocab True Variance: The actual variance of the population. Sample Variance (S2): The variance of the sample population. Sampling with Replacement: When samples taken from the population after measurements are returned to the population. Sampling without Replacement: The samples taken from the population are not returned after measurement. Example 4-2.1 An endless production line is turning out solidstate diodes and every 100th diode is tested for its reverse current (IR) and its forward current (IF) by applying ±1v. a. IR has a true mean of 10-6 and a variance of 10-12. How many diodes must be tested to obtain a sample mean (𝐗) whose standard deviation is 5% of the true mean? Part 4-2.1.a Standard Deviation (± 𝜎 2 ) will relate to the % difference around the mean. Since we want 5% around the true mean, than SD = 5% ⋅ 𝑋. 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 0.05 ⋅ 𝑋 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 0.05 ⋅ 10−6 2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 0.25 × 10−12 𝜎2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 𝑛 0.25 × The sample variance can be related to the true variance. 2 10−12 10−12 = 𝑛 10−12 𝑛= = 40 0.25 × 10−12 𝑛 =40 Part 4-2.1.b IF has a true mean (𝑿) of 0.1 and a variance of 0.0025. How many diodes must be tested to obtain a sample mean (𝐗) whose standard deviation is 2% of the true mean. 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 0.02 ⋅ 𝑋 2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 0.02 ⋅ 0.1 2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 4 × 10−6 𝜎2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 𝑛 4 × 10−6 2.5 × 10−3 = 𝑛 2.5 × 10−3 𝑛= = 625 4 × 10−6 Part 4-2.1.c Using the large sample size what is the standard deviations of the sample mean for each test? We use 625 samples since we need to capture the 2% SD for test performed in part b). Part a. Part b. 𝜎2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 𝑛 𝜎2 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 𝑛 10−12 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 625 𝑆𝐷 = 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 𝑆𝐷 = 4 × 10−8 1.6 × 10−15 0.0025 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 625 𝑆𝐷 = 𝑣𝑎𝑟 𝑋 = 𝑆𝐷 = 2 × 10−3 4 × 10−6