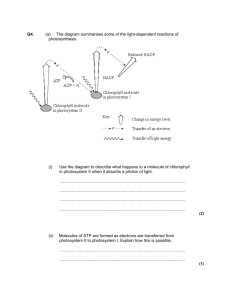
Photosynthesis ____________________in this way: _________________________ Converts ___________energy into the chemical energy of a
advertisement

• • • • Photosynthesis Converts ___________energy into the chemical energy of a ____________________in this way: Solar energy + carbon dioxide + water → _________________________ Photosynthetic organisms include plants, algae, and certain bacteria. These organisms are called ___________________; they synthesize organic molecules from raw materials. Photosynthetic Organisms Nearly all life is dependent on solar energy because: 1) Photosynthetic organisms use _______________to produce organic nutrients. 2) Almost all organisms depend either directly or indirectly on these organic nutrients to sustain themselves. 3) Photosynthetic organisms provide food for other organisms, known as _________________. 4) The _____________________became the coal or other fossil fuels used today. • • • • Structure and Function of Chloroplasts ____________________are the organelles that carry on photosynthesis. ___________________in the middle of a leaf house chloroplasts Mesophyll cells are protected from drying out by a __________________________. Pores called _____________ allow CO2 and O2 to enter the leaf. Visible Light • Radiant energy from the sun (solar energy) can be described in terms of its ____________________________________. • The colors in visible light range from _________ (the shortest wavelength and highest energy) to blue, green, yellow, orange, and __________ (the longest wavelength and lowest energy). Visible Light & Plants • _______________ (chlorophylls and carotenoids) found within photosynthesizing cells, are capable of _______________various portions of visible light. • Both ____________________________absorb violet, blue, and red light best. • Leaves appear green because _________________________and only minimally absorbed. Photosynthetic Reactions •It is an oxidation-reduction reaction, or redox reaction for short. •Oxidation is the loss of electrons; hydrogen atoms are removed from glucose. •Reduction is the gain of electrons; oxygen atoms gain electrons. •Remember OIL RIG (oxidation is loss, reduction is gain) Overview of Photosynthesis • A simplified overall equation for photosynthesis is: • __________________________________________________ • During photosynthesis, water molecules are __________________; they lose electrons (e-) along with hydrogen ions (H+). • Also, ______________and gains electrons given up by H2O. • Electrons from H2O are energized _________________. Two Sets of Reactions • Photosynthesis is divided into two sets of reactions, as implied by the term “photosynthesis”: • ___________refers to the light-dependent (needs light) reactions that capture energy from the sun • ___________________ • ___________________ • “Synthesis” refers to the ____________________ (does not need light) reactions that produce carbohydrate. • ___________________ Light-Dependent Reactions • During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules. _______________________is produced. • Inside the chloroplast, water is split to produce _________________ _________________________, the starting ingredients for photosynthesis Photosystem II • The electrons are excited by ___________________(from the sun). These excited electrons are passed through a series of electron carriers. Energy from these excited electrons is used to ____________________________through the chloroplast • An enzyme (___________________) uses the energy from these moving ions to generate ATP. Light-Dependent Reactions Photosystem I • Electrons are excited by incoming light energy (from the sun). These excited electrons are passed through a series of different electron carriers (_____________________________). • As electrons pass down this chain, they combine with the molecule _____________________________ Electron Transport System Light-Independent Reactions • The light-independent reactions do not need light and consist of the _____________________. • During the Calvin Cycle, ____________________is taken up by the plant (from the atmosphere) • During the Calvin cycle, ____________________(made from the light dependant reactions) add phosphates and electrons to CO2, and convert it to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate, or G3P • G3P is a type of sugar which a plant can easily convert to ________________. This glucose can then be used as a source of stored energy for the plant The Calvin Cycle Overview of Photosynthesis