Law and Society CJUS/POLS 102 Chapter 2: History and the Law
advertisement

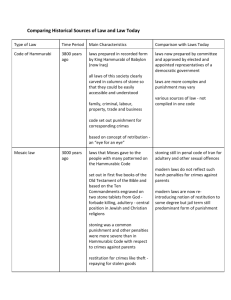
Law and Society CJUS/POLS 102 Chapter 2: History and the Law Early History of Law 1. Developed over thousands of years - first known written law - Code of Hammurabi - King of Babylon, 2000 BC a. Advanced society - unique laws to control / guide - derived from the Gods - directing Hammurabi (1) Dealt with: Early History - administrative / domestic / criminal issues - laws directed towards children (2) Egyptian law - highly developed society also (a) Pharaoh descendent of gods - word was law (b) Egypt: first court system - overseers: aristocracy / priests Early History (3) Ancient laws - came from gods - power bestowed on ruler (a) Religious influence today? (b) Church vs. state b. Influence: centuries of different beliefs (1) Hebrew law Early History - god is source of all law (a) Old Testament: - ‘eye for an eye’ (b) New Testament: - ‘turn the other cheek’ (2) Greek law (4th / 5th centuries) - highly sophisticated - Plato / Aristotle / Sophocles History (a) Criminal acts: crimes against society (b) Serious crime: crime against the state (c) King relied on gods c. Roman law - dominant force - “natural law” (1) Transformed into “civil law” / “canon law” History (a) Civil law - state law - government takes action (b) Canon law - church law - catholic church takes action in domestic matters (2) Defined 3 elements of law: - legislative / administrative / judicial History (a) Developed into English justice system - Rome established legal system - developed into US system (b) Laws passed by Roman senate (c) Enforced by the Emperor (d) Ruled on by Roman courts - judges or priests History (3) Justinian Code - Roman Emperor Justinian (528 AD) - collection of all laws (a) Civil laws - enforced by government - soldiers (b) Canon laws - enforced by soldiers - judges were priests History (c) Term “justice” - came from Justinian (4) Code included 4 parts: (a) The Institutes - text for law students / lawyers (b) The Digest - casebook covering trials / decisions History (c) The Codex - statutes / principles (d) The Novels - proposed laws d. Laws influenced European continent - Roman-Germanic law - Napoleonic Code - Laws of Islam (Constantinople) - the four dominant legal systems: History (a) Common law – England (b) Civil law – Romano-Germanic (c) Socialist law – security / economics (d) Religious law – beliefs / conduct 2. Development of common law - Danes conquered Northern France - Normans History a. William the Conqueror (1066) - developed Anglo-Saxon law (1) Reeve of the Shire (12th century) - King’s enforcement officer - police / judge / executioner (2) Developed an accusatory system - 12 freemen appointed - made accusations - became our jury of 12 History b. Roman civil law - integrated with English traditions (1) King’s court - dealt with common law - criminal and civil matters (2) Church courts - dealt with canon law - family and church matters History (3) England: canon law / civil law - developed into ‘common law’ - King Henry VIII (a) Judges replaced sheriff as court official - traveled throughout a Shire (b) Judges made law - decisions became common - followed each other’s rulings - became known as “common law” History c. Landowners / aristocrats - based rules on king’s law - nobility revolted (1) Magna Carta – 1215 - Great Charter (Latin) (2) Established laws of England (3) US Constitution - modeled after Magna Carta History (4) 18th century England - becoming an industrialized society - new business / technology - new laws to manage (a) United States of America - struggling - to form a new government 3. Law in the new America History - common law of England - adapted to Continental United States a. Principles of common law - still in effect - left intact where did not interfere with state / federal law (1990s) (1) Never legislated - accepted practice by the courts - have codified common law History b. Federalism - federalist form of government (1) Union of states - under a federal government (2) Two or more levels (a) Federal - provides certain services - protection / taxes / representation History (b) State - provides certain services - highways / schools / taxes (c) Local - provides certain services - garbage / fire / taxes (3) Based on common law - unwritten law - follow precedent / make up new law History (a) Doctrine of Stare Decisis - “let the decision stand” (b) Unwritten laws that were appealed - became “case law” - which is written law 4. Articles of Confederation - first governing document - combined 13 colonies - into a loose confederation History a. Ratified - March 1, 1781 b. Replaced by the Constitution - June 21, 1788