Nicotine and Tobacco Drugs and Our Society Part 14
advertisement

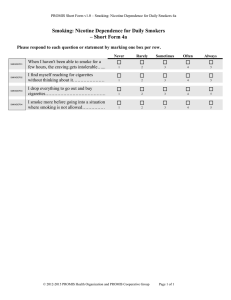
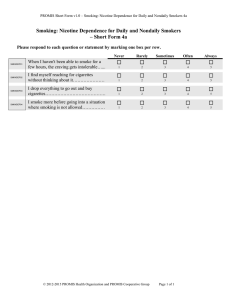
Nicotine and Tobacco Drugs and Our Society Part 14 Nicotine and Tobacco 1. One of the most pervasive / destructive drugs known - entrenched in our culture - integral role in our history - “War of Independence” a. Efforts to regulate - latter part of 1800s b. Anti-tobacco legislation - characterized by two themes Nicotine / Tobacco, cont. - fire hazards - morality of smoking c. Beginning of 1900s - became less important - economic benefits associated - tobacco taxes source of revenue d. Today: $45 billion industry - significant revenue source (state / federal) Nicotine / Tobacco, cont. 2. 1995: FDA proposal to regulate - unsuccessful due to politics a. Current emphasis - control sale to minors - control promotion of cigarettes b. Rate of smoking declined: adult smoker - 50% less from 20 years ago Nicotine / Tobacco, cont. c. Perception of tobacco - increasingly negative - once viewed: “dirty habit” / “dirty practice” - now a “life-threatening addiction” 3. Nicotine: addictive ingredient - C. Everett Koop (former Surgeon General) - first official to warn of dangers - claimed: nicotine dependence powerful as heroin / cocaine dependence Nicotine / Tobacco, cont. a. Tobacco more available - can be considered more addictive b. 90% of all smokers = become addicted - alcohol also available - most drinkers do not become alcoholics 3. American Psychiatric Association - recognized dependency as a disorder - depression common - suicide: 100% higher than non-smokers Nicotine / Tobacco, cont. a. Comes from green tobacco plant - genus: Nicotiana - 60 species - only nicotiana rustica / tabacum smoked b. Tobacco from these plants are used in: - cigars / cigarettes - pipes - snuff - chewing tobacco Nicotine / Tobacco, cont. 1. History of tobacco use - stone carving / Southern Mexico / 600 – 900 AD - smoke blown through pipe a. Columbus travels - dried tobacco leaves as gifts (late 1400s) - returned with tobacco seeds / planted - became popular in Europe b. Believed to be medical treatment History, cont. - skin disease / injuries / internal disorders - cure diseases of eyes / nose / mouth - smoke could breath life into another person c. 1828: nicotine isolated - poisonous / addictive - medical value declined d. Next 30 years: - religious leaders / physicians /educators questioned the medical value History, cont. e. Attacked for causing problems in society - mental illness / delirium tremens / impotence - and sexual perversions f. Despite warnings: - tobacco use for pleasure flourished 2. Jamestown: early settlement in the colonies - early 1600s / brutal winters / food shortages - settlers prepared to abandon History, cont. a. John Rolfe - convinced to plant tobacco - crop flourished / Jamestown prospered b. Tobacco farming spread - established as valuable commodity - used as form of currency c. Financed by French government - funded Revolutionary War History, cont. 3. Late 1800s: cigarettes rolled by hand - 1883: invented rolling machine - started being massed produced a. 1891: Richard Joshua Reynolds (RJR) - saccharine in tobacco - sweeter / longer shelf life b. Also introduced Prince Albert (1907) - sterilized in licorice casing History, cont. - delightful / harmless tobacco d. Introduced other brands: - Camel - Turkish / domestic leaves - less expensive / highly popular e. Competition: - American Tobacco Co / Lucky Strike - Liggett and Meyers / Chesterfield History, cont. 4. Opposition escalated - first critic: Dr. Benjamin Rush (1798) - condemned for adverse health effects a. Women’s Christian Temperance Union - with others - supported controlling use / sale b. Several states banned sale to children - chewing / smoking History, cont. c. Wisconsin / Nebraska - possession illegal - both adults / children 5. Despite efforts: popularity continued - WWI: YMCA / US Army distributed to soldiers - after war: use escalated a. Morality / medical concerns took backseat - public desire first History, cont. - taxes contributed to revenue b. WWII - manufacturer’s donated to soldiers - patriotic gesture 6. Costs of Smoking - one factor to reduce demand - increase cost a. 1992: average tax = .62 cents Costs, cont. - states continue to raise - proceeds to government programs - smoking prevention / treatment / schools - Washington state, 2nd highest ($3.025) b. Lawsuit settlement - billions given to states - programs for anti-tobacco use - health care cost for tobacco related illness - “bartered” away Costs, cont. c. Sold half of award = get money now - offset state budget deficits d. Used in other programs - not going to anti-smoking - nor treatment for illness 7. Extent of tobacco use - 1975 – 2000: 62.5% high school seniors smoked - 11.3% half pack or more daily Extent, cont. a. Office on Smoking / Health - Center for Disease Control / Prevention b. 2003: more than 65% high school seniors - Caucasian = higher than Hispanic - African-Americans least likely c. Peaked in 1964 - Surgeon General’s Report - dangers of smoking Extent, cont. d. 1964 – today: - more than 43 million quit - continues to decline among adults e. Data confusing: - total number of smokers = increased - percentage has decreased - cigarettes smoked per capita: not decreased f. People who smoke tend to smoke heavily Extent, cont. g. Filters more popular than plain tip - 2% in 1952 - 60% in 1963 - 90% today h. Tar / nicotine sharply reduced - cause people to smoke more - seek same amount nicotine - inhale more deeply / hold in lungs longer - just smoke more cigarettes Demographics of Smoking 1. More adult males smoke - females gaining a. Manufacturer’s market to women - link to independence / equality - “Virginia Slims” b. College students - 28% recent increase - all ethnic groups Demographics, cont. - average starting age: 19 - 18%: 5 or more attempts to stop c. Teens: more likely if sibling smokes - high school or less: more likely than college - blue-collar: more likely than white-collar 2. Women / smoking - differences diminishing a. 22% women smoke / 26% men (4%) Demographics, cont. - 1965: 52% men / 34% women (18%) b. Level of education (correlation) - through 11th grade: 3 times more likely - than women with 16 years / more c. Since 1980: over 3 million women died - prematurely from related diseases d. Reduces life by 14 years Demographics, cont. e. 25% of all cancer deaths 3. Tobacco Use by Young People - begin during childhood / adolescence - 89%: initiated by age 19 a. Average 2 / 3 years to become regular smoker - earlier in life - more likely regular smoker b. Study of childhood smokers: Young People, cont. - 4%: 3rd / 4th grade students - 42%: 8th / 9th grade students - most experimental - 8th / 9th grades: 9% current smokers - mean age to start: 12.5 years c. Teenage rates gone up - as advertising expenditures go up - 3 times more responsive than adults d. 89% start as teenagers Young People, cont. e. 14.9% age 12 – 17 current smokers (21/2 mil) - currently smoke: more likely to use drugs Nicotine Tolerance / Dependence 1. Build up tolerance quickly / matter of weeks a. Continue to use: it is addictive - usually associate with narcotics - ignore nicotine addictiveness b. Effects: highly reinforcing Tolerance / Dependence, cont. - reaches brain in seconds c. Not last long in body - to compensate: light up another - characteristic: other forms of addiction d. Develop tolerance - need more nicotine - strong desire: continued use - if not: undergo withdrawals Tolerance / Dependence, cont. 2. Rituals – become ingrained - light up after eating - talking on phone - driving vehicle - after sex a. Symptoms of withdrawal - not fatal - varies - uncomfortable Tolerance / Dependence b. Proportional to intake - more nicotine / greater withdrawal (1) Most acute: 24 to 48 hours after ending - craving: last weeks / months / years (2) Symptoms: - lower heart rate / blood pressure / heart palpitations / difficulty maintaining attention / aggressiveness / insomnia / tremors / hunger / headaches / fatigue Pharmacology 1. Nicotine - 6000 chemical substances in tobacco smoke - insecticide - carcinogenic a. Stimulant - similar to amphetamines / cocaine (1) Injected intravenously - 5 to 10 times more reinforcing than cocaine Pharmacology, cont. (2) Absorbed immediately by lungs - brain: 10 seconds - feel effects every inhale (3) Quickly distributed in body - traverses blood / brain - placenta pregnant women = fetus - breast milk b. Liver metabolizes Pharmacology, cont. - almost all before kidney excretion - stays: 8 to 12 hours 1. Passive smoke - involuntary / environmental / second-hand - detrimental effects: not limited to smokers a. Indoor pollution - home / workplace b. Blamed for 3,800 lung cancer deaths yearly Passive Smoke, cont. - 8,000 to 26,000 asthma cases in children - extent of harm: degree of exposure - emotional discomfort around smokers c. Classified: mainstream / sidestream (1) Mainstream - smoke exhaled - 58% nitrogen/13% carbon dioxide/12 % oxygen/8% particles (nicotine, tar, waxes dyes)/3.5% carbon mono./0.5% hydrogen Passive, cont. (2) Sidestream - comes from burning end of product - not pass through filter - hotter temperature - more nicotine / carbon monoxide c. Laws against smoking in public places - precipitated by effects of sidestream smoke 2.Effects on non-smokers Effects, cont. - besides irritating nose / eyes - passive causes significant health problems a. Linked to: lung / urinary tract problems - also liver / pancreatic cancers - increase in breast cancer b. Lung cancer: higher living with smoker - smoke at work increases risk (bar / restaurant) - 3 times more likely Effects, cont. c. EPA (1993): secondhand smoke a carcinogen - 1998 smoking prohibited California bars/taverns - NYC passed ban on smoking in public places d. Effects on children - more likely: respiratory infections - colds / bronchitis / pneumonia (1) 17% lung cancer deaths - high levels of exposure Effects, cont. (2) Women who smoke during pregnancy - children exhibit impulsiveness / risk-taking / rebelliousness 3. Rights of smokers vs. nonsmokers - difficult to balance a. Anti-smoking legislation - federal (1998): minimum age of 18 to buy - under age 27 must show ID Rights, cont. (1) Occurred because: - local laws passed - 1,000 local ordinances (2) Tobacco petitioned state legislators - 75% support measures to limit - sales / possession (3) Laws vary: - Greensboro, NC = restricted smoking Rights, cont. - San Francisco = no smoking in public / private workplaces - Massachusetts = police / fire fighters - Vermont = raised taxes .26 pack - Washington = .50 cents - Congress = 1 of 4 warnings (rotate) - Depts. Of Labor / Defense = smoking ban (4) Airlines (1990) - no smoking = domestic flights Rights, cont. - flights shorter than 6 hours b. Companies / corporations - passed non-smoking policies c. Local governments - will not hire smokers - upheld d. Tobacco settlement - $206 billion / over 25 year period