NAME ______________________________________ PERIOD # _______ DATE ___________________ A. MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE 1.
advertisement
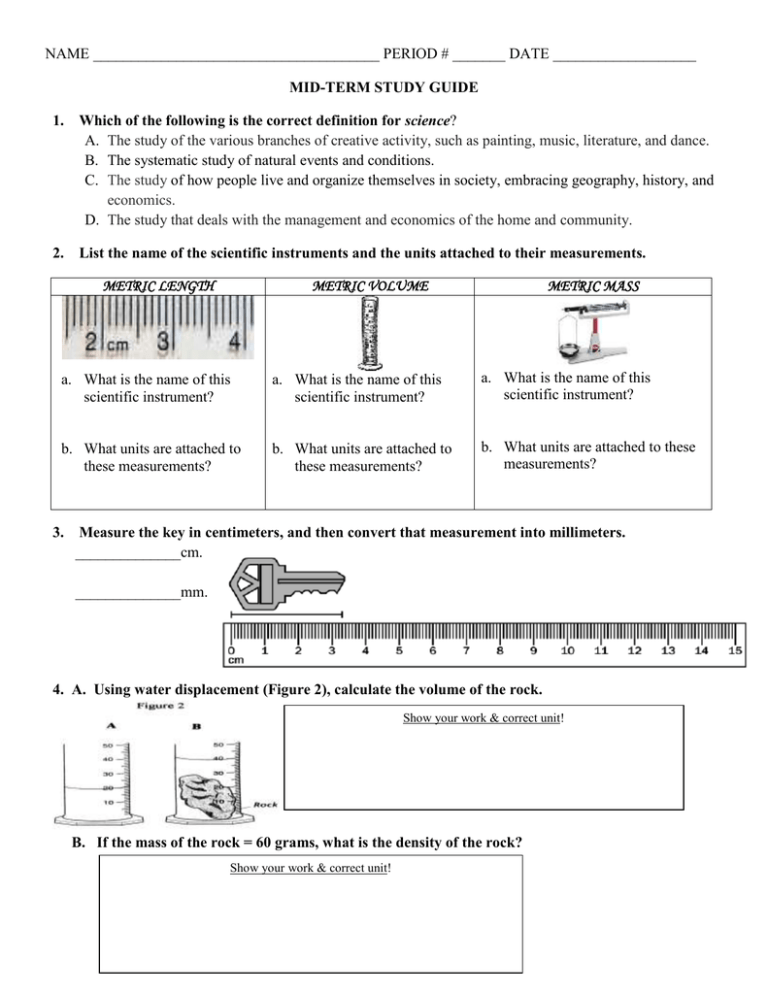
NAME ______________________________________ PERIOD # _______ DATE ___________________
MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE
1.
Which of the following is the correct definition for science?
A. The study of the various branches of creative activity, such as painting, music, literature, and dance.
B. The systematic study of natural events and conditions.
C. The study of how people live and organize themselves in society, embracing geography, history, and
economics.
D. The study that deals with the management and economics of the home and community.
2.
List the name of the scientific instruments and the units attached to their measurements.
METRIC LENGTH
METRIC VOLUME
METRIC MASS
a. What is the name of this
scientific instrument?
a. What is the name of this
scientific instrument?
a. What is the name of this
scientific instrument?
b. What units are attached to
these measurements?
b. What units are attached to
these measurements?
b. What units are attached to these
measurements?
3.
Measure the key in centimeters, and then convert that measurement into millimeters.
______________cm.
______________mm.
4. A. Using water displacement (Figure 2), calculate the volume of the rock.
Show your work & correct unit!
B. If the mass of the rock = 60 grams, what is the density of the rock?
Show your work & correct unit!
5. Compare and contrast the 3 states of matter. Include information about each one’s shape, volume,
and the arrangement and motion of particles. {Phases of Matter Class Notes}
Three Set Venn
Diagram Key
6. Study the atomic structure diagram below. Identify the location and charge (+ or -) of a proton,
neutron, and electron. {Basic Chemistry Handouts}
A proton is:
A neutron is:
An electron is:
7. Use the information provided by the Periodic Table to answer the bulleted questions below.
Nitrogen
7
14.0
The atomic number equals:
The mass number equals:
How do you find the number of neutrons for the element Nitrogen, and all
other elements on the Periodic Table?
8. What is the difference between an element, a compound and a mixture? Give an example of each.
Definitions {Science Fusion Text Page # 142}
Example
Element:
Compound:
Mixture:
9. Use the table below to answer the question that follows.
Substance
Oxygen Gas (O2)
Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4)
Helium (He)
Water (H2O) + Table Salt (NaCl)
Element, Molecule, Compound, or Mixture
Molecule
Compound
Element
Mixture
Which of the following substances is a compound?
A. Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
B. Table Sugar (C12H22O11) + Water (H2O)
C. Nitrogen Gas (N2)
D. Liquid Mercury (Hg)
10. What is the difference between a chemical change and physical change? Give an example of each.
Definition
Example
Chemical Change:
Physical Change:
11. Which combination of substances caused a chemical change that formed a new substance?
Combination
#1
#2
#3
#4
Substance # 1
iron filings
table salt (NaCl)
colorless liquid
white talcum powder
Substance # 2
colorless liquid
tap water
yellow liquid
brown liquid
What Happened When the Substances Were Combined?
The iron filings sank to the bottom of the colorless liquid.
The combination was stirred forming salt water.
The liquids bubbled.
The white talcum powder floated on the surface of the liquid.
A. Combination # 1
B. Combination # 2
C. Combination # 3
D. Combination # 4
12. Fill in the blanks in the table below. {Phases of Matter Class Notes}
Phase Change Name
Nature of Change
Gain or Loss of Heat Energy
___________________________
GAS TO SOLID
HEAT ENERGY IS LOST
MELTING
SOLID TO LIQUID
HEAT ENERGY IS ______________________.
CONDENSATION
_________ TO _________
HEAT ENERGY IS LOST
___________________________
LIQUID TO GAS
HEAT ENERGY IS GAINED
FREEZING
_________ TO _________
HEAT ENERGY IS LOST
SUBLIMATION
SOLID TO GAS
HEAT ENERGY IS ______________________.
13. When the liquids listed below are poured into a beaker, they will
create a layered column as a result of their differing densities. Using
the densities provided, label the beaker by placing the letters of the
different liquids in the boxes on the beaker.
Density of Liquid A = 1.98 g/mL
Density of Liquid B = 0.75 g/mL
Density of Liquid C = 1.14 g/mL
Density of Liquid D = 0.50 g/mL
14. Write the formula to calculate density in the box below.
Density Formula:
Correct Units?
?
Density = --------------- {
?
}
?
Use the density formula to calculate the density of an object if its mass is 250 grams, and its
volume is 500 ml? Show your work.
The density of water is 1 g/cmᵌ. Will the object above sink or float when placed in water? Explain
your answer.
15. Below is a science scenario. Read the scenario carefully, and answer the bulleted questions that follow.
A. Elizabeth wanted to find out if flowers grew faster with sugar in the water.
B. Elizabeth believed the sugar would make the flowers grow faster.
C. Elizabeth filled 4 jars with 200 ml of water. Jar A had 10 ml of sugar added; Jar B had 20 ml of sugar
added, and Jar C had 30 ml of sugar added.
D. Jar D had no sugar in it.
E. The flowers in the sugar water all died. The more sugar in the water, the faster the flowers died.
F. The flower in Jar D (no sugar) lasted for 10 days.
Which letter represents the problem? __________
In which statement does Elizabeth state her hypothesis? __________
What is the control in the experiment? ___________________________________________________
What is the independent variable in this experiment? _______________________________________
What is the dependent variable in this experiment? _________________________________________
Which letter represents a statement of Elizabeth’s conclusion? ______________
Use the chart below to answer questions 16 and 17.
16. Explain how you could distinguish between the minerals magnetite and hematite?
17. Which mineral in the table will scratch every other mineral in the table? ____________________
18. List the hardness of the following items according to the field scale of hardness. {Mineral Lab}
Item
Fingernail
Hardness #
Copper Penny
Glass
19. Which physical property of a mineral is determined by rubbing the mineral on an unglazed porcelain
plate? {Science Fusion Text Page # 148}
_____________________
20. Identify two harmful effects that strip mining has on the environment? {Natural Resources Handout}
21. Bedrock has been exposed at the Earth’s surface. Explain the 4 steps/processes involved in creating a
well-developed soil profile? {Science Fusion Text Pages 58 & 59}
I.
Weathering:
II.
Plant Roots:
III.
Burrowing Animals:
IV.
Microorganisms:
22. Complete the matching table regarding the agents of physical weathering. {Science Fusion Text Pages 20-26}
Description of Conditions That Cause Physical Weathering
Occurs when the outer layers of rock slowly peel away over time
as a result of changes in pressure. An example of this is when
roads are cut through mountains.
The breaking down and wearing away of rocks over time as
a result of the flowing water in streams, strong winds, moving
glaciers, or gravity.
Burrowing animals break apart and mix rocks and soil. Their
actions also improve soil drainage and allow oxygen to get
underground which increases the rate of weathering.
Causes cracks in rocks to expand as liquid water seeps in
during the day when the temperatures are above freezing, and
then the water freezes at night and pushes the rock apart.
Roots start as tiny strands of plant matter that can grow inside of
the small cracks in rocks. As the roots grow bigger, they push the
rocks apart.
Type of Weathering
A. Ice-Wedging
B. Abrasion
C. Plant Growth
D. Exfoliation
E. Animal Actions
23. Compare and contrast rocks and minerals. How are they similar but different? {SF Text Pages 142 & 156}
Minerals
Rocks
24. Explain why fossils are usually found in sedimentary rocks rather than igneous or metamorphic
rocks. {Science Fusion Text Page # 82}
25. Identify the processes within the rock cycle that occur to form each type of rock.
1. ______________________
2. ______________________
3. ______________________
4. ______________________
1. _______________________
&
2. _______________________
5. ______________________
1.
________________________
26. Complete the matching table below. {Rock Labs and Science Fusion Text 172-180}
Rock Classifications and Characteristics
An organic sedimentary rock that forms from the remains of dead
plants and animals.
When Halite “comes out of solution,” this type of chemical
sedimentary rock forms.
When clay grains accumulate, they form this type of clastic
sedimentary rock.
This fine-grained, extrusive igneous rock is dark-colored. It is
composed of iron and magnesium.
When the clastic sedimentary rock called Shale is subjected to
the heat and pressure of metamorphism, this rock forms.
Quartz Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock. When it is
undergoes metamorphism, this rock forms.
This coarse-grained, intrusive igneous rock is light-colored
containing feldspar, quartz. It composes continental crust.
This clastic sedimentary rock is composed of mostly rounded
pebbles along with sediments of many different sizes.
When sediment grains between .06 – 2.0 mm are compacted
and cemented together, this clastic sedimentary rock forms.
This type of metamorphic rock forms when the sedimentary rock
limestone is subjected to extreme heat and pressure.
Rock Type
A. Sandstone
B. Slate
C. Marble
D. Basalt
E. Conglomerate
F. Rock Salt
G. Shale
H. Quartzite
I. Coal
J. Granite


