Sources of Tension in the Middle East
advertisement

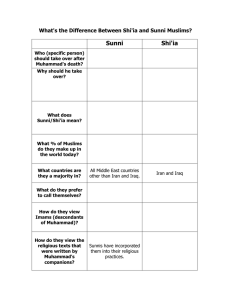
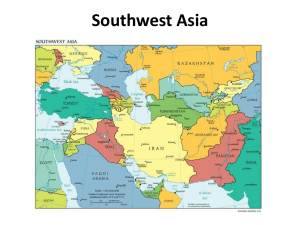
Sources of Tension in the Middle East I. Oil Wealth and the Resource Curse A. The Middle East is home to the world’s largest oil reserves, which have led to: 1. Interventions by foreign powers 2. Internal conflicts over oil wealth 3. Corrupt and dictatorial leaders 4. An overreliance on oil and the lack of development in other parts of the economy II. Foreign Interventions A. Throughout history, many different empires have controlled the Middle East such as the: Babylonians, Persians, Romans, and the Islamic Caliphate. B. Before World War I (1914-1918), the Middle East was controlled by the Ottoman Empire, which was on the losing side with Germany and Austria. C. After the war, the Ottoman Empire was dismantled. With the Sykes-Picot Agreement, the British and French took control and drew new borders in the Middle East. 1. These new borders included many rival groups in the same countries and split the Kurdish area between four nations: Turkey, Iraq, Syria and Iran. 2. Britain and France were weakened by World War II. The United States and the United Nations became more involved in the Middle East. D. During the Cold War, the United States and the Soviet Union were eager to have allies in the Middle East because of its oil reserves, strategic location, and Russia’s need for warm-water ports. As a result, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. supported monarchs and dictators in the region. E. The U.S. has intervened in the Middle East by: 1. Siding with Egypt in the Suez Crisis of 1956 when Britain and France sent troops to seize the Suez Canal. 2. Arming the mujahideen who were fighting the Soviets in Afghanistan from 1979-1989 a. These fighters later became al Qaeda and attacked the U.S. on 9/11/2001 3. Attacking Iraq in the Persian Gulf War of 1990-1991 after Iraq invaded Kuwait 4. Striking against the Taliban in Afghanistan, 2001 to present, for harboring al Qaeda and Osama bin Laden 5. Invading Iraq, 2003-2011, over concerns about Iraq’s possession of weapons of mass destruction 6. Leading international airstrikes against Libya’s Muammar Gaddafi in 2011 that led to his execution and an ongoing civil war. III. Developing Nations A. Middle East nations are young. Most didn’t become independent nations until the end of World War II in 1945. B. They are having growing pains associated with the path to modernization and are experiencing many of the same problems that the West experienced in the past: 1. Revolutions and civil wars 2. Religious and ethnic conflict 3. Conflict between traditional and modern a. Older, religious, rural, traditional people b. Younger, secular, urban, Western-educated modern people C. When they first became independent, Middle East nations put their faith in secular nationalist leaders. 1. Mustafa Kemal Ataturk in Turkey 2. Gamal Abdel Nasser in Egypt 3. Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi in Iran D. Over time, people lost faith in nationalist leaders because they became corrupt and dictatorial. Some turned to religious leaders and movements. 1. Ayatollah Khomeini and the Islamic Revolution of Iran in 1979 2. The Muslim Brotherhood in Egypt and other countries 3. Hamas, a Palestinian militant group 4. Hezbollah, a Lebanese militant group E. Starting in 2010, more modern Arabs started protests and revolts with the Arab Spring. These revolts led to leaders being removed from power in Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, and Yemen. IV. Sunni vs. Shiites A. There has been a conflict between the majority Sunni and minority Shiites for nearly 600 years. B. Iran is overwhelming Shiite and sees itself as the defender of the Shiites. C. Saudi Arabia is the birthplace of Islam and custodian of the two holy cities of Mecca and Medina. It sees itself as the defender of the Sunnis. D. Lebanon is split between Sunnis, Shiites, and Christians. 1. A civil war waged from 1975 to 1990 and included intervention by Israel and Syria. 2. The U.S. sent peacekeepers but later withdrew after U.S. forces came under attack. E. Iraq has a Shiite majority but was ruled by the Sunni minority for much of its history. 1. During the U.S. occupation, power shifted from the Sunnis to the Shiites. 2. Many disenfranchised Sunnis now support the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), which now controls much of Iraq. F. Syria has a Sunni majority but was ruled by Shiites for much of its history. 1. A major civil war grew out of the Arab Spring and has been waging since 2011. 2. ISIS flourished during the civil war and now controls much of Syria. V. Arab-Israeli Conflict A. Israel has been a source of tension since the late 1800s when the Zionist movement and later the Holocaust fueled Jewish migration into what was British controlled Palestine. 1. The British supported a nation for the Jews with the Balfour Declaration of 1917. 2. The United Nations suggested dividing the area into Jewish and Arab nations with the UN Partition Plan of 1947. 3. Israel became independent in 1948, fought four Arab-Israeli Wars, and has controlled the Arab Palestinian areas since 1967. 4. Israel controls the Noble Sanctuary with the al Aqsa Mosque and Dome of the Rock, the third holiest site of Islam. 5. The U.S. is Israel’s strongest ally, which causes tensions with Arab nations. Global Studies Name _________________________________ Sources of Tension in the Middle East I. Oil Wealth and the ____________________________ A. The Middle East is home to the world’s largest _____________________, which have led to: 1. Interventions by ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ over oil wealth 3. _________________ and _________________ leaders 4. An ___________________ on oil and the lack of development in _________________ of the economy II. _______________ Interventions A. Throughout history, many ________________________ have controlled the Middle East such as the: _____________________, Persians, __________________, and the Islamic Caliphate. B. Before ______________________ (1914-1918), the Middle East was controlled by the __________________________, which was on the losing side with Germany and Austria. C. After the war, the Ottoman Empire was dismantled. With the _____________________________________, the __________________ and __________________ took control and drew _______________________ in the Middle East. 1. These new borders included many __________________________ in the same countries and split the _________________ area between four nations: Turkey, Iraq, Syria and Iran. 2. Britain and France were weakened by ___________________. The ___________________ and the ______________________ became more involved in the Middle East. D. During the ___________________, the United States and the Soviet Union were eager to have ____________ in the Middle East because of its ____________________, strategic ________________, and Russia’s need for _______________________. As a result, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. supported ___________________________________ in the region. E. The U.S. has intervened in the Middle East by: 1. Siding with ______________ in the __________________ of 1956 when _______________ and ________________ sent troops to seize the Suez Canal. 2. Arming the _________________ who were fighting the ______________ in ____________________ from 1979-1989 a. These fighters later became ________________ and attacked the U.S. on _______________ 3. Attacking __________ in the _____________________ of 1990-1991 after Iraq invaded ___________ 4. Striking against the _____________ in ___________________, 2001 to present, for harboring ______________ and ________________________ 5. Invading _________, 2003-2011, over concerns about Iraq’s possession of __________________________________________ 6. Leading international _______________ against _________________________________________ in 2011 that led to his ______________________ and an ongoing __________________. III. _________________ Nations A. Middle East nations are ____________. Most didn’t become ___________________ nations until the end of _______________________ in 1945. B. They are having ____________________________ associated with the _______________________________ and are experiencing many of the same problems that the ________ experienced in the past: 1. ____________________ and ____________________ 2. ________________ and _______________ conflict 3. Conflict between ______________ and _________________ a. _______________, religious, ______________, traditional people b. Younger, ________________, urban, ___________________________ modern people C. When they first became independent, Middle East nations put their faith in ____________________________. 1. Mustafa Kemal ______________ in _______________ 2. Gamal Abdel _____________ in ________________ 3. __________ Mohammad Reza Pahlavi in ___________ D. Over time, people ____________________ in nationalist leaders because they became ______________ and _________________. Some turned to _________________ leaders and movements. 1. Ayatollah ____________________ and the Islamic Revolution of _________ in 1979 2. The ______________________________ in ___________ and other countries 3. ____________, a _______________________militant group 4. _________________, a ________________________ militant group E. Starting in 2010, more ________________ Arabs started protests and revolts with the ___________________. These revolts led to leaders being _________________ from power in ______________, _________________, ________________, and _________________. IV. _______________ vs. ________________ A. There has been a ___________ between the majority Sunni and minority Shiites for nearly _______________. B. __________ is overwhelming _____________ and sees itself as the defender of the Shiites. C. _____________________ is the ___________________________ and custodian of the two holy cities of _________________________. It sees itself as the defender of the Sunnis. D. __________________ is split between Sunnis, Shiites, and Christians. 1. A ____________________ waged from 1975 to 1990 and included intervention by ______________ and _____________________. 2. The _________. sent _____________________ but later withdrew after U.S. forces _________________________________. E. ___________ has a ___________ majority but was ruled by the __________ minority for much of its history. 1. During the U.S. occupation, __________________________ from the Sunnis to the Shiites. 2. Many disenfranchised Sunnis now support the ____________________________________________ which now _____________________________________. F. ___________ has a ____________ majority but was ruled by ____________ for much of its history. 1. A major _______________ grew out of the Arab Spring and has been waging since 2011. 2. _________ flourished during the civil war and now ________________________________________. V. _________________________ Conflict A. Israel has been a source of tension since the late 1800s when the _________________ movement and later the ___________________ fueled ________________ migration into what was __________________controlled ______________________. 1. The British supported a nation for the Jews with the ______________________________ of 1917. 2. The ________________________ suggested dividing the area into ________________ and __________________ nations with the _____________________________ of 1947. 3. Israel became independent in 1947, fought four _____________________________, and has controlled the ____________________________________ since 1967. 4. Israel controls the _____________________________ with the al Aqsa Mosque and Dome of the Rock, the ________________________ of Islam. 5. The ________ is Israel’s strongest ally, which causes ________________ with Arab nations.