Bellringer 2.) 1.) 3.)
advertisement
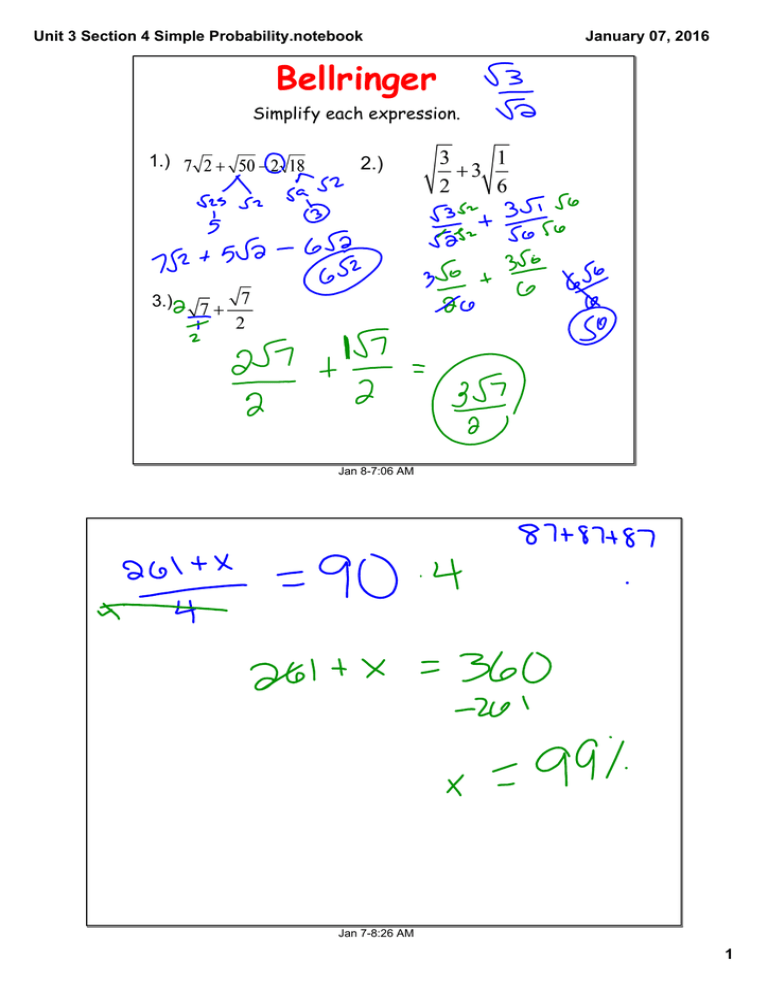
Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Bellringer Simplify each expression. 1.) 2.) 3.) Jan 8­7:06 AM Jan 7­8:26 AM 1 Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Jan 8­7:06 AM Jan 8­7:06 AM 2 Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Simple Probability Unit 3 Dec 13­12:24 PM Vocabulary Probability: the chance that a given event will occur. Some areas where probability is used are sports, weather, politics, and agriculture. Also when you guess answers on a test or play games involving di or enter a sweepstakes. Dec 13­12:25 PM 3 Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Event: Outcome or combination of outcomes Outcomes: Possible results. Outcomes on a di are (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) Probability Formula: Favorable Outcomes: the outcome that you are calculating the likelihood of its occurrence. Dec 13­12:27 PM Example 1: Find each probability. Use the spinner. a) P(2) b) P(blue) 6 1 c) P(10) 2 5 d) P(blue,red, green) 4 3 Dec 13­12:30 PM 4 Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Theoretical Probability: the calculation using the probability formula that a favorable outcome will occur. All Probability Ranges between 0 to 1. The probability of an impossible event is always 0 and the probability of a certain even is always 1. Experimental Probability: what actually does happen in an experiment. Dec 13­12:33 PM Example 2: The hair color of students in class are as follows : 8 brown, 10 black, 2 red, and 3 blonde. If the teacher calls on one student at random, what is the probability of calling on a student with brown hair? What is the probability that the teacher does not choose a student with black hair? Example 3: In a batch of 350 calculators, 7 were found to be defective. What is the probability that a calculator chosen at random will be defective? What the probability as a fraction and a percent. Round the nearest tenth of a percent if necessary. Dec 13­12:35 PM 5 Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Example 4: Suppose two 1-6 number cubes are rolled. Find the probability of each outcome. (Hint: Use the table below as your sample space.) (1, 1) (2, 1) (3, 1) (4, 1) (5, 1) (6, 1) (1, 2) (2, 2) (3, 2) (4, 2) (5, 2) (6, 2) (1, 3) (2, 3) (3, 3) (4, 3) (5, 3) (6, 3) (1, 4) (2, 4) (3, 4) (4, 4) (5, 4) (6, 4) (1, 5) (2, 5) (3, 5) (4, 5) (5, 5) (6, 5) (1, 6) (2, 6) (3, 6) (4, 6) (5, 6) (6, 6) a) P(2 or 6) b) P(both even) c) P(sum less than 7) d) P(odd product) Dec 27­9:14 PM Odds Odds in favor of event E = number of favorable outcomes number of unfavorable outcomes 6 5 7 8 4 3 1 2 Use the spinner above. Find the odds in favor of each event. Number > 3 Blue number Red or Blue number Even number Jan 8­10:49 AM 6 Unit 3 Section 4 Simple Probability.notebook January 07, 2016 Homework Packet pages 8 and 9 Jan 6­8:48 AM 7