Practice Questions Name:________________________ Cell Reproduction
advertisement

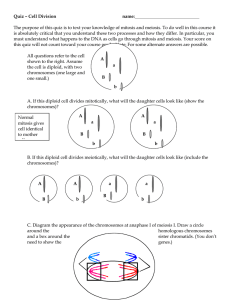
Practice Questions Cell Reproduction Name:________________________ Part I. Meiosis vs. Mitosis. For each statement below, identify whether it refers to mitosis or meiosis. 1. Occurs in body cells, such as skin or bones. 2. Occurs in sex cells. 3. Makes eggs or sperm. 4. Makes haploid cells. 5. Makes diploid cells. 6. Produces cells that are genetically identical to the parent. 7. Produces cells that are genetically different from the parent. 8. Produces 2 cells. 9. Produces up to 4 cells. Part II. Asexual vs. sexual reproduction. Identify whether each statement below refers to sexual or asexual reproduction. 10. Involves 2 parents. 11. Produces offspring that are identical to the parent. 12. Produces offspring that are different from the parent. 13. Examples include processes such as binary fission in bacteria, or budding in yeast or hydra. 14. Involves the union of sex cells – eggs and sperm. 15. Involves only 1 parent. Part III. Meiosis questions. 16. What type of chromosomes are lined up on the equator of the cell during metaphase of meiosis I? 17. What is the total number of chromosomes in each of the two resulting cells from Meiosis I if the parent cell has 12 to start? 18. What is crossing over? 19. How does crossing over contribute to genetic variability? 20. What is being pulled apart in anaphase of meiosis II? 21. How many cells result from meiosis II? Part III. Meiosis questions. Use this diagram to answer Questions 22–24. 22. What does the diagram show? 23. During what phase of meiosis does this process occur? 24. What is the result of this process? Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis 25. Complete the table to compare meiosis and mitosis. Mitosis Form of reproduction Number of daughter cells Change in chromosome number Number of cell divisions Difference in alleles between parent cell and daughter cells Meiosis For Questions 26–31, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words. 26. A diploid cell that enters mitosis with 16 chromosomes will divide to produce daughter cells. Each of these daughter cells will have chromosomes. 27. If the diploid number of chromosomes for an organism is 16, each daughter cell after mitosis will contain chromosomes. 28. A diploid cell that enters meiosis with 16 chromosomes will pass through divisions, producing daughter cells, each with chromosomes. 29. Gametes have a cell number of chromosomes. 30. If an organism’s haploid number is 5, its diploid number is . 31. While a haploid number of chromosomes may be even or odd, a diploid number is always .