Inequalities Common Mistakes
advertisement

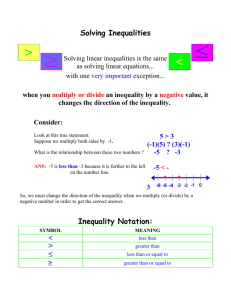
Inequalities Common Mistakes Inequalities – Definition, Types 2x + 3 ≤ 4 Inequality represents a region. It is represented by: Less than <, ≤ >, ≥ Greater than There are multiple ways to write the solutions to inequalities. Ex. x ≥ −3 Graph on a Number line: Ex. -3 It is a closed circle when it is greater than or equal to and less than or equal to. It is an open circle when it is great than or less than Interval Notation : Ex. x ≥ −3 Use Parenthesis when its infinity or an open circle Use Brackets when it is a closed circle Set Builder Notation: Basic Inequality – Ex. [− 3, ∞ ) Ex. x x ≥ −3 −x+4≥8 −x≥4 x ≤ −4 Solve this by treating it like an equation and then graphing on a number line. When you divide by a negative number, flip the inequality sign. Compound Inequality – Ex. − 6 ≤ x + 3 ≤ 4 Solve this type of inequality by separating it into two problems and solving each part; −6 ≤ x+3 −9 ≤ x and x+3≤ 4 x ≥1 Therefore: − 9 ≤ x ≤ 1 Complete Manual: Linear and Absolute Value Inequality Review.docx To view right click to open the hyperlink Inequalities – Definition, Types Absolute Value Inequality – There are 4 types of Absolute Value Inequality, each requires a different way to solve. Problem looks like: |x| = a Ex. |x|=4 Solve by: x = a and x = -a Problem looks like: |x| < a Ex. |x|<4 Solve by: -a < x < a Problem looks like: |x| > a Ex. |r| >8 Solve by: x < -a and x > a Problem looks like: |x| = |y| Ex. |s|=|5| Solve by: x = y and x = -y Quadratic Inequality – These contain either an Ex. x2 or an x in the denominator. , x2 + 4x + 3 ≤ 0 , ( x + 2)( x − 1) ≤0 ( x + 3) (x + 1)(x − 4) ≤ 0 To solve follow these steps. 1. Determine what makes the denominator become zero (this becomes an open circle on your number line) 2. Change the inequality to an equal sign and solve the equation (these become closed circles on your number line) 3. Plot the points 4. Determine where to shade / graph on the number line by testing in-between each point and at the ends by substituting in a number in that range. If the number works, shade the region, if it does not work, don’t shade. Complete Manual: Linear and Absolute Value Inequality Review.docx To view right click to open the hyperlink. Inequalities Common Mistakes A common mistake in working with inequalities is not being able to identify what type of inequality it is so that it is solved correctly. Another mistake students make when working with inequalities is forgetting to flip the inequality when dividing by a negative number. Complete Manual: Linear and Absolute Value Inequality Review.docx To view right click to open the hyperlink