CS475 – Networks Assignments Lecture 19 Chapter 5: End-to-End Protocols
advertisement
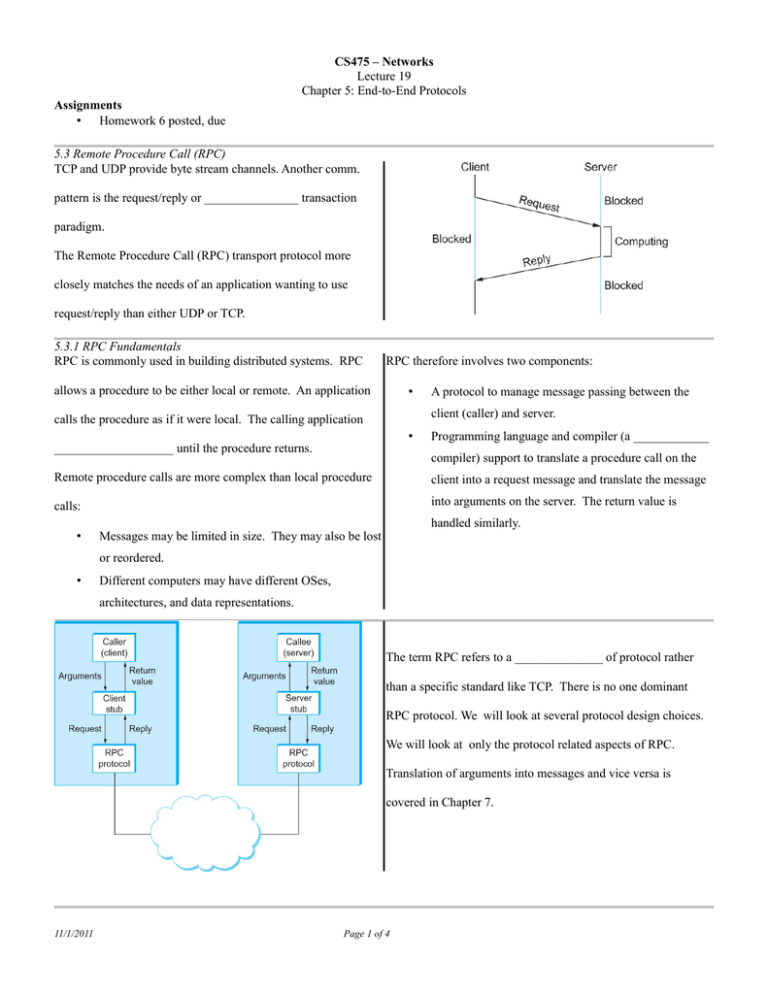
CS475 – Networks Lecture 19 Chapter 5: End-to-End Protocols Assignments • Homework 6 posted, due 5.3 Remote Procedure Call (RPC) TCP and UDP provide byte stream channels. Another comm. pattern is the request/reply or _______________ transaction paradigm. The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) transport protocol more closely matches the needs of an application wanting to use request/reply than either UDP or TCP. 5.3.1 RPC Fundamentals RPC is commonly used in building distributed systems. RPC RPC therefore involves two components: allows a procedure to be either local or remote. An application • A protocol to manage message passing between the client (caller) and server. calls the procedure as if it were local. The calling application • ___________________ until the procedure returns. Programming language and compiler (a ____________ compiler) support to translate a procedure call on the Remote procedure calls are more complex than local procedure client into a request message and translate the message calls: into arguments on the server. The return value is • handled similarly. Messages may be limited in size. They may also be lost or reordered. • Different computers may have different OSes, architectures, and data representations. The term RPC refers to a ______________ of protocol rather than a specific standard like TCP. There is no one dominant RPC protocol. We will look at several protocol design choices. We will look at only the protocol related aspects of RPC. Translation of arguments into messages and vice versa is covered in Chapter 7. 11/1/2011 Page 1 of 4 5.3.1 RPC Fundamentals - Identifiers in RPC RPC must provide a name space for identifying the procedure to An RPC protocol must also match a reply message to the be called. corresponding request. This is done by including a message ID The name space can be either flat or ______________________. in both the request and reply. A flat name space requires central coordination to prevent A client ____________________ may be used as part of the assigning the same ID to different procedures. The ID can be message ID in order to ensure that the correct match in the event carried in a single field in an RPC request. that the client reboots with an outstanding request. 5.3.1 RPC Fundamentals - Overcoming Network Limitations RPC can implement reliability using RPC reliability may implement at-most-once semantics in which ACKs. Each side has a retransmit there is a guarantee that no more than one request is delivered to timer that causes the message to be the server. resent in the event of a time out. A Implementation of zero-or-more or __________________ reply can be used as an implicit ACK. semantics is simpler and sufficient for applications in which _________________ requests can be multiple requests have the same effect as one request. implemented using logical channels. 5.3.2 RPC Implementations - SunRPC SunRPC (aka ONC RPC) was developed by Sun as part of their 8). Network File System (____________). SunRPC can be Different RPC servers are dynamically assigned TCP/UDP port implemented over several different transport protocols (SunRPC numbers. The port mapper RPC server listens on well-known is also considered a transport protocol). port 111. RPC clients can query the _____________________ SunRPC uses a 32-bit program number and a 32-bit procedure to determine the port number assigned to a program. number to identify a procedure (the NFS server has program ID SunRPC does not implement its own reliability or fragmentation 0x100003, the NFS read procedure has ID 6 while write has ID methods. It relies on the underlying protocol. The XID field is a transaction ID that is unique to a request/reply pair. The Program and Procedure contain the corresponding 32-bit IDs. The Version field specifies a version of a program. Multiple versions of a program may be running on the server. The variable length Credentials and Verifier fields are used by the client to _____________________ itself to the server. SunRPC request and reply headers 11/1/2011 Page 2 of 4 5.3.2 RPC Implementations - DCE-RPC DCE-RPC is used in Microsoft's DCE-RPC supports very large messages and implements its own DCOM and ActiveX technologies. It fragmentation scheme. Selective acknowledgment is used is also used in ________________, a allowing only missing fragments to be retransmitted instead of standard for distributed object- the entire message. oriented systems. A typical DCE-RPC exchange is shown at right. If the server responds quickly enough, no Pings are sent. DCE-RPC supports multiple logical channels known as _______________________ and there is an ActivityID field in the header. A SequenceNum field distinguishes between calls in an activity. The sequence number is remembered at the server to Selective acknowledgment is shown above. ensure at-most-once semantics. A WindowSize is used for flow-control. 5.4 Transport for Real Time Apps (RTP) Multimedia applications can be categorized as either streaming RTP can run over many lower level protocols, (audio, video streams) or interactive (VoIP, teleconferencing). but is typically run on top of UDP. RTP is still Interactive applications have the strictest real-time requirements. considered a _______________ protocol. 5.4.1 Requirements A multimedia protocol must allow applications to interoperate. UDP does not provide congestion control and this is desirable in One approach is to specify a particular audio and video coding many real-time apps. The receiver must notify the sender that scheme. RTP allows the sender to indicate which coding method losses are occurring. it wants to use. A real-time protocol should provide some indication of Our protocol must support playback synchronization to prevent _______________ boundaries. ______________ and provide means for audio and video We should be able to associate a particular user (rather than just synchronization. a host) with a stream. The protocol must provide some means to indicate that a packet Finally our protocol should use BW efficiently. is lost, so that the receiver can take appropriate action. 11/1/2011 Page 3 of 4 5.4.2 RTP Design RTP supports a variety of applications. For each class (audio) it The extension (X) bit indicates the presence of an extended defines a ________________ and one or more formats. header following the main header (rarely used). A profile defines the fields in the RTP header. A format defines The 4-bit CC field indicates the number of contributing sources. how the data after the header is to be interpreted (simple audio The mark (M) bit denotes the start of a ____________. The 7-bit samples or an MPEG video stream). payload type (PT) field indicates the type of payload data. The M and PT fields are precisely defined by the application profile. The Sequence number is used at the receiver to detect ______________ or out-of-order packets. The application decides what to do in the case of a missing packet, not RTP. The Timestamp allows samples to be played back at the appropriate interval and allows for synchronization between Header Format different streams. It is the number of ticks from the first sample. The first two bits specify the RTP ________________. The P The synch. source (SSRC) identifies a stream ______________. bit indicates if padding is used. The last byte of padding A node with multiple cameras would have a different ID for each contains the pad count. camera. The contributing source (CSRC) is used when several streams pass through a mixer (combining multiple audio streams). The SSRC is then the ID of the mixer. 5.4.3 Control Protocol A control stream (RTCP) is associated with a data stream (RTP). RTCP defines several different packet types: RTCP (1) provides feedback on performance, (2) correlates and • synchronizes different streams from a sender, (3) conveys info on the identity of the sender. sender reports contain transmission and reception statistics • Multiple streams from a sender are associated with a receiver reports (from non-senders) contain reception statistics. _____________________ name (CNAME) that is assigned to the sender. Association with a CNAME allows different sources • source descriptions carry __________________. • application specific packet • Refer to the rpc and xdr man pages for more information. Start homework. to be synchronized. In Class Exercises • Run the command “rpcinfo -p” on Linux. • Check the portmap and rpcinfo man pages. 11/1/2011 • Page 4 of 4




