Telecommunications
advertisement

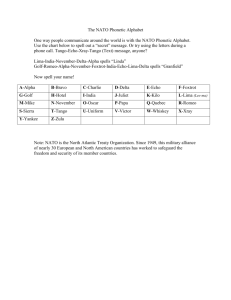
Telecommunications Course Law Enforcement II Unit II Telecommunications Rationale Law enforcement officers are required to communicate. Most agencies use radios and mobile data terminals to communicate with officers in the field. It is important for students to learn these required forms of communication. TEKS §130.294(c) (2)(A)(B)(C)(D) Objectives The student will be able to: 1. Identify the five components of the communication cycle. 2. Define diction, enunciation, and pronunciation. 3. Conduct telecommunications using mobile and hand-held radio systems. 4. Conduct simulated radio communications. 5. Identify policies and procedures for proper mobile data terminal usage. 6. Transmit and retrieve information over the mobile data terminal. 7. Disseminate data to multiple mobilized units using the mobile data terminal. Prior Student Learning Phonetic Alphabet Engage Discuss the following quote and the importance of radio communication to law enforcement officers. Use the Discussion Rubric for assessment. Estimated Time 2 hours “Communication is everything for a police officer. His gun may be his most powerful weapon, but his radio is his best friend. It’s his lifeline to dispatchers.” – King 5 News, Pearson, WA Essential Question What methods of communication do officers have available to them and how are they used? Key Points I. Communication Cycle A. Message – the text or information of the communication; can be verbal or nonverbal, even in a non-visual environment B. Sender – transmits a message by selecting the words or actions to convey meaning to the receiver, and solicits feedback from the receiver to make sure the message was understood correctly C. Medium – how the message is conveyed; represents the actions or text (words, written or spoken) of the message. Noise, figurative or literal, can sometimes hinder the message from being transferred in a medium D. Receiver – translates the sender’s message by giving meaning to its actions or text; should provide feedback to the sender by stating his or her understanding of the message or asking a clarifying question E. Feedback – the receiver’s understanding of the message or lack of understanding is transmitted back to the sender; the most important part of the communication cycle because it performs the 1 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. verification function II. Mobile and Handheld Radio Communications A. Effective Radio Communications 1. Diction – an individual speaker’s accent, inflection, intonation, and speech sound quality, which is usually judged in terms of prevailing standards of acceptability a) Enunciation – forming clear and distinct sounds into words b) Pronunciation – properly saying the sounds of a word while stressing the correct syllable(s) 2. Appropriate rate of speech a) Most people speak at a rate of over 100 words per minute b) Most people write at rate of only 20–30 words per minute 3. Appropriate message length a) Messages should usually take no more than 30 seconds of air time b) Divide longer messages into segments with a 5–10 second break in between segments to allow another user to speak for emergency traffic if necessary c) Strive to provide the greatest amount of information in the shortest period of time 4. Professional – avoid inappropriate language 5. Timely – immediately upon need 6. Easily understood by both the communication center and the field units 7. Use the Phonetic Alphabet to clearly broadcast names, vehicles, identification numbers, and addresses a) Adam b) Boy c) Charles d) David e) Edward f) Frank g) George h) Henry i) Ida j) John k) King l) Lincoln m) Mary n) Nora o) Ocean p) Paul q) Queen 2 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. r) Robert s) Sam t) Tom u) Union v) Victor w) William x) X-Ray y) Young z) Zebra 8. Concise a) Clear speech policy – requires standardized words or phrases with specific meanings; speak in plain language B. Communication Challenges 1. Weather – conditions such as heavy clouds, and ice and snow buildup on antennas can interfere with radio transmissions and reception 2. Terrain – mountains, large bodies of salt water, and mineral deposits can affect radio signal propagation 3. Buildings – those constructed out of metal and concrete attenuate radio signals, particularly when using portable radios inside such structures; apartment complexes also pose transmission problems 4. Low batteries – reduce the level of radio signal output when transmitting C. Radio procedures 1. Know what you want to say before you key the microphone on the radio 2. Press the key-up button located on the side of the radio or on the handset. Hold it down for 5–10 seconds before beginning to speak. 3. Hold the handset or radio 2–3 inches from your mouth so that the transmission is not garbled 4. If the transmission is lengthy, break in the middle to let any emergency radio traffic proceed; transmissions should not be longer than 30 seconds at a time 5. Wait 5 seconds after ending the transmission before letting go of the key button to ensure that the whole message transmits III. Mobile Data Terminal (MDT) Policies and Procedures A. Access 1. No officer may access the Texas Law Enforcement Telecommunications System (TLETS) or the National Law Enforcement Telecommunications System (NLETS) without having a current Texas Department of Public Safety “less than full access” or equivalent certification 2. No officer shall allow another person who does not have the 3 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. less than full access certification to access TLETS or NLETS 3. As soon as the desired TLETS/NLETS information has been obtained from the MDT screen, the MDT screen shall be cleared of the information 4. The MDT screen shall be positioned in a manner to prevent unauthorized access to the information screen B. Operations 1. Officers shall exercise care and caution when utilizing the MDT while operating the vehicle to insure driver and public safety and shall not take unnecessary or unreasonable risks to operate the MDT 2. The MDT shall be adjusted to a position that makes the screen easily readable and the keyboard easily accessible 3. Officers shall log-off from the MDT a) When away from the vehicle for prolonged periods for non-police activity (i.e., meal breaks) b) When transferring the MDT to another user c) At the end of the shift C. Confirmation of all query hits D. Recorded Data 1. All data transmitted over the MDT system is recorded in a storage disk in the MDT server 2. The contents of the storage disk are reviewed periodically for quality control purposes and/or to insure compliance with directives IV. MDT Usage A. Codes for use and operation of MDTs vary by manufacturer. Get assistance from your school resources officer or local law enforcement agencies for demonstrations. Unless your school has purchased radios/dispatch equipment or a MDT, you will need outside assistance B. MDTs allow officers to receive call information, communicate with one another, and run queries on vehicles, persons, and places Activities 1. Phonetic Alphabet Quiz. Give each student a copy of the Phonetic Alphabet Handout during the class session prior to this one. Have the students study the alphabet. Quiz the students during this class session by having them list the phonetic alphabet on a blank piece of paper. Give a quiz the next class. Use the Phonetic Alphabet handout to grade quizzes. 2. Phonetic Alphabet Activity. Give each student a copy of the Phonetic Alphabet Activity and the Phonetic Alphabet handouts. Have the students broadcast (over a radio if available) the names and license 4 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. plates on the Phonetic Alphabet Activity Handout. They may reference the Phonetic Alphabet handout as needed (Note: you may add other license plates and names to the list, including using a student roster from your class). Use the Phonetic Alphabet Rubric for assessment. Assessments Telecommunications Exam and Key Phonetic Alphabet Quiz (see Activity 1) Phonetic Alphabet Rubric Discussion Rubric Individual Work Rubric Role Play Rubric Materials Telecommunications computer-based presentation Phonetic Alphabet Handout Phonetic Alphabet Activity Handout Resources National Academy of Emergency Dispatch (NAED) Instructor Certification course Arlington Police Academy Mansfield Police Department General Orders http://www.sheriff.co.wise.tx.us/communic.htm Do an Internet search for the following: dictionary. Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, students will practice the phonetic alphabet. Allow the students to find audio recordings of police radio traffic and compare the differences they hear, such as noise in the transmission, keying up without talking, rapid speech, etc. Use the Individual Work Rubric for assessment. For enrichment, allow the students to write scenarios involving police action. Students will then take turns role playing the scenarios, with one to two students acting as officers. The officers will conduct any simulated radio traffic necessary for the successful resolution of the scenario. Use the Role Play Rubric for assessment. State Education Standards Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Career and Technical Education §130.294. Law Enforcement II (One to Two Credits). (2) The student uses telecommunication equipment. The student is expected to: (A) conduct telecommunication using mobile and handheld radio systems; (B) conduct simulated radio communications; 5 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. (C) (D) transmit and retrieve information over the mobile data terminal; and disseminate data to multiple mobilized units using the mobile data terminal. College and Career Readiness Standards Social Studies Standards V. Effective Communication A. Clear and coherent oral and written communication 1. Use appropriate oral communication techniques depending on the context or nature of the interaction. 6 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Name________________________________ Date__________________________ Telecommunications Exam Match the communication cycle term with the correct definition. A. The text or information of the communication; can be verbal or nonverbal, even in a non-visual environment 1) _____ Medium 2) _____ Sender 3) _____ Message B. Transmits a message by selecting the words or actions to convey meaning to the receiver and solicits feedback from the receiver to make sure the message was understood correctly 4) _____ Receiver 5) _____ Feedback C. How the message is conveyed; the actions or text (words written or spoken) of the message D. Translates the sender’s message by giving meaning to the actions or text of the sender E. The receiver’s understanding of the message or lack of understanding is transmitted back to the sender 6) _____ Which of the following is “an individual speaker’s accent, inflection, intonation, and speech-sound quality, which is usually judged in terms of prevailing standards of acceptability”? A. Pronunciation B. Enunciation C. Diction D. Phonetics 7) _____ Most people speak at a rate of over __________ words per minute. A. 20−30 B. 100 C. 30 D. 50 7 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 8) _____ Which of the following is not part of the communication cycle? A. Message B. Medium C. Translator D. Receiver 9) _____ Concise word choice, clear enunciation, appropriate rate of speech, and appropriate message length all describe which of the following key terms? A. Diction B. Pronunciation C. Phonetics D. Enunciation 10) _____ What is the length of air time for messages usually? A. 10 seconds B. 5 seconds C. 30 seconds D. 20 seconds 11) _____ Which of the following means “forming clear and distinct sounds into words”? A. Pronunciation B. Enunciation C. Phonetics D. Diction 12) _____ Effective communication is which of the following? A. Professional B. Clear and concise C. Timely D. All of the above E. None of the above 8 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 13) _____ Clear radio communication occurs through the use of what type of communication? A. Concise communication B. Phonetic alphabet C. Plain language D. Ten codes 14) _____ Which of the following requires standardized words or phrases with specific meaning? A. Plain language B. Phonetic alphabet C. Clear speech policy D. Ten codes 15) _____ Most departments use which type of radio communications? A. Ten codes B. Phonetic alphabet C. Clear speech policy D. Plain language 16) _____ Which of the following is not a challenge to communication? A. Weather B. Buildings C. Terrain D. Charged battery 17) _____ How long do you need to hold down the mic button before beginning your transmission? A. 2−3 seconds B. 20−30 seconds C. No time, just push and talk D. 5−10 seconds 9 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 18) _____ The handset or radio should be held how far from the mouth when transmitting? A. 5−10 inches B. 2−3 inches C. 10−20 inches D. Mouth should be directly on the handset/radio 19) _____ In order to access the Texas Law Enforcement Telecommunications System, officers must hold what type of certification? A. Radio operators license B. Texas Law Enforcement Telecommunications System C. National Law Enforcement Telecommunications System D. At least less than full access 20) _____ As soon as the desired TLETS/NLETS information has been obtained from the Mobile Data Transmission (MDT) screen, the officer may save the information for the duration of their shift. A. True B. False 21) _____ A citizen riding along with the officer is authorized to view TLETS/NLETS information. A. True B. False 22) _____ Officers must exercise care and caution when using the MDT and operating a motor vehicle. A. True B. False 23) _____ Officers shall log off from the MDT in which of the following situations? A. When transferring the MDT to another user B. At the end of the officer's shift C. When the officer is away from the vehicle for prolonged periods for non-police activities 10 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. D. All of the above E. None of the above 24) _____ All data that is transmitted over the MDT is recorded for which of the following reasons? A. Public records request B. To review the officer's work ethic C. To know which officers are dating D. To insure compliance with directives 25) _____ Codes for use and operation of MDTs are standard among all manufacturers. A. True B. False 26) _____ MDTs allow officers to do all except which of the following? A. Receive call information B. Make arrests C. Communicate with one another D. Run queries on vehicles, persons, and places 27) _____ If radio transmissions are lengthy, officers should do which of the following? A. Break after 30 seconds for 5−10 seconds B. Complete the entire transmission in one message C. Give 5 seconds of the message and break for 30 seconds before continuing D. Know what you want to say and get to the point 11 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 28) _____ Which type of communication challenge attenuates radio signals? A. Terrain B. Buildings C. Weather D. Low batteries 29) _____ Which of the following means “properly saying the sounds of a word while stressing the correct syllable(s)”? A. Enunciation B. Diction C. Pronunciation D. Phonetics 12 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Telecommunications Exam Key 1. C 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. E 6. C 7. B 8. C 9. A 10. C 11. B 12. D 13. B 14. C 15. D 16. D 17. D 18. B 19. D 20. B 21. B 22. A 23. D 24. D 25. B 26. B 27. A 28. B 29. C 13 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Phonetic Alphabet Handout A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Adam Boy Charles David Edward Frank George Henry Ida John King Lincoln Mary Nora Ocean Paul Queen Robert Sam Tom Union Victor William X-Ray Young Zebra 14 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Phonetic Alphabet Activity Handout Broadcast the following information over the radio, using simulated radio traffic and the Phonetic Alphabet Handout as needed. License Plates 4HIG204 X99KRP DHB822 MWB755 841EHO RF05WCL TRY088 1BD8231 HGEE487 Names Jane R. Smith Kristina Kamp Danny Richards Kelsey Davis Jon Williams George Thomas Elise Bowen Julio Gonzales Angelo DeWitte 15 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Name_______________________________________ Date_______________________________ Phonetic Alphabet Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Waited 5–10 seconds after keying the mic on the radio before speaking Used an appropriate rate of speech Used appropriate diction Did not hesitate between letters or numbers Used the phonetic alphabet correctly Gave an accurate transmission Finished the transmission and then waited 5 seconds before disengaging the mic Total Points (28 pts.) Comments: 16 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Name_______________________________________ Date_______________________________ Discussion Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Participates in group discussion Encourages others to join the conversation Keeps the discussion progressing to achieve goals Shares thoughts actively while offering helpful recommendations to others Gives credit to others for their ideas Respects the opinions of others Involves others by asking questions or requesting input Expresses thoughts and ideas clearly and effectively Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 17 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Name______________________________________ Date_______________________________________ Individual Work Rubric 4 pts. Excellent Objectives 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Follows directions Student completed the work as directed, following the directions given, in order and to the level of quality indicated Time management Student used time wisely and remained on task 100% of the time Organization Student kept notes and materials in a neat, legible, and organized manner. Information was readily retrieved Evidence of learning Student documented information in his or her own words and can accurately answer questions related to the information retrieved *Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 18 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. Name:____________________________________ Date:_____________________________ Role Play Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Relates to the audience Provides fluent rendition of the scenario All required content is included Acts with feeling and expression Varies intonation Presents characters appropriately Gives the scenario its full range Breaches are easily identified Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 19 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved.