SCBA Air Management and Safety
advertisement

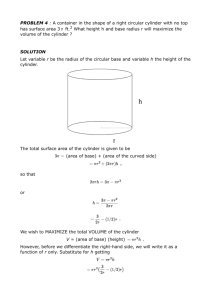
SCBA Air Management and Safety Course Firefighter I Unit II Safety and Orientation Essential Question Why are firefighters expected to thoroughly understand SCBA? TEKS §130.299(c) (10)(C) (11)(B)(D)(F) (12)(A) Prior Student Learning None Estimated Time 3 to 5 hours Rationale Firefighters work in smoky, toxic atmospheres that can be detrimental to their health. The Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) allows firefighters to perform their duties in these environments, but they must understand SCBA’s limitations, know its operational rules and requirements, and calculate its air supply continually during use. Objectives The students will be able to: 1. Identify the firefighters’ physical requirements for wearing a selfcontained breathing apparatus 2. Describe and demonstrate how to calculate the air supply duration in the cylinder 3. Describe the uses and limitations of the SCBA 4. Demonstrate the replacement of an extended cylinder on a selfcontained breathing apparatus assembly with a full cylinder 5. Document routine maintenance for the SCBA Engage Bring a SCBA to class. Allow the students to handle and examine the SCBA. Discuss as a class the importance of fully understanding a SCBA prior to use. Use the Discussion Rubric for assessment. Key Points I. SCBA Review A. Four reasons people need to wear SCBA devices 1. Oxygen falls below 18% (21% is normal) 2. Atmosphere is full of smoke 3. Toxic fumes, gasses, or materials are in the area 4. The environment is over 120 degrees Fahrenheit B. Two types of SCBA systems 1. Closed system a) The SCBA recirculates the air the wearer exhales and adds oxygen to it b) Nothing leaves the SCBA and goes into the environment c) This type of SCBA is rare in the fire service 2. Open system (two kinds) a) Demand – air is provided to the user on demand, every time he or she takes a breath b) Open – pressure in the mask is slightly above that of the normal atmosphere, keeping contaminants out C. An SCBA cylinder typically holds around 2000-2200 psi of air. A good rule of thumb is that this will last an average of 30 minutes D. NFPA requires that all SCBA devices have a personal alert safety 1 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. system (PASS) device go off if the individual wearing it stays inactive for 30 seconds E. When the pressure reaches or drops below 500 psi the person wearing it (and his or her partner) MUST evacuate the scene. This includes when a rescue is underway F. Safety checks on an SCBA: 1. Safety checks should be done daily 2. Check the cylinder pressure gauge. When full, the gauge should read approximately 2000 psi 3. Ensure that the face piece is clean and without cracks or damage. The straps must be in good working order 4. Check all of the pressure lines for damage or wear and abuse 5. Check all of the straps to ensure they are in good condition 6. Check the exhalation valve for proper functioning 7. Check all of the gauges for proper readings 8. Check the low pressure alarm to be sure it is functioning properly II. SCBA Air Management A. The low-air alarm signifies that there is 1. 25 percent of the cylinder’s air remaining 2. Up to 5 minutes of air supply 3. Insufficient time to exit from deep inside a large or complex structure B. For your own safety 1. Comply with the accountability system in use 2. Maintain your situational awareness 3. Manage your air supply C. Three basic elements to effective air management 1. Know your point of no return (beyond 50 percent of the air supply of the team member with the lowest gauge reading) 2. Know how much air you have (at all times) 3. Make a conscious decision to stay or to leave when your air is down to 50 percent D. The decision to stay or to leave is 1. A team decision that is always made by your supervisor 2. If your team has only two members, both members must leave at the same time E. To maximize your air supply, check it 1. At the beginning of your shift (make sure that the cylinder is at least 90 percent full) 2. When donning the SCBA and opening the cylinder valve 3. While working, at 5-10 minute intervals and at key points, such as when changing locations and finishing assignments 4. During egress from the hazard zone, at 2-3 minute intervals 5. When refilling or replacing a cylinder 2 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. III. SCBA Limitations A. Limitations of the wearer 1. Physical factors a) Physical condition b) Agility c) Facial features 2. Medical factors a) Neurological functioning b) Muscular/skeletal condition c) Cardiovascular training d) Respiratory functioning 3. Mental factors a) Adequate training in equipment use b) Self-confidence c) Emotional stability B. Limitations of the equipment 1. Limited visibility 2. Decreased ability to communicate 3. Increased weight 4. Decreased mobility C. Limitations of the air supply 1. Physical condition of the wearer 2. Degree of physical exertion 3. Emotional stability of the wearer 4. Condition of the apparatus 5. Cylinder pressure prior to use 6. Training and experience of the wearer IV. SCBA Safety Precautions and Special Uses A. Firefighters 1. Must be physically fit a) Breathing equipment can weigh from 25 to 35 pounds (11 kg to 16 kg) 2. Must be trained to recognize the signs and symptoms of heatrelated illnesses 3. Should closely monitor how they are feeling while wearing SCBA and rest when they become fatigued 4. Must be fit-tested annually if they are certified to wear SCBA 5. Must remember that air-supply duration varies with the following a) Size of the cylinder and the beginning pressure b) Firefighters’ conditioning c) Type of task being performed d) Level of training e) Operational environment f) Degree of firefighters’ stress 6. Should not remove their SCBA until they leave the contaminated 3 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. area 7. Must work in teams of two or more while they are in any Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health (IDLH) atmosphere a) Team members must remain in physical, voice, or visual contact b) Firefighters should check their air supply status frequently B. Special Uses 1. Operating in areas of limited visibility a) Crawling (1) Helps firefighters avoid the higher temperatures found at the ceiling (2) Helps firefighters remain below the thermal layer and increase visibility b) Crawling and probing with a tool (1) Prevents firefighters from falling through holes or down stairs or elevator shafts (2) Allows firefighters to feel for victims under beds and behind furniture c) Crouch or “duck walk” (1) Is faster than crawling (2) Is more dangerous than crawling unless firefighters can see the floor in front of them d) Using a tag-line such as a (1) Hose line (2) Rope (3) Electrical cord e) Using a wall to find an exit (door or window) V. Changing SCBA Cylinders A. SCBA cylinders need to be changed frequently during extended emergency operations B. A salvage cover should be placed on the ground to protect spare cylinders C. Empty cylinders should be segregated from the supply of cylinders ready for use D. Out-of-service cylinders should be clearly marked E. Methods for changing a cylinder 1. One-person method a) Place the SCBA unit on a firm surface b) Close the cylinder valve c) Bleed air pressure from high- and low-pressure hoses d) Disconnect the high-pressure coupling from the cylinder e) Remove the empty cylinder from the harness assembly f) Verify that the replacement cylinder is 90-100% of rated capacity g) Check the cylinder valve opening and the high-pressure hose 4 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. fitting for debris h) Place the new cylinder into the backpack i) Connect the high-pressure hose to the cylinder and then tighten the connection j) Slowly and fully open the cylinder valve and listen for an audible alarm and leaks as the system pressurizes (1) If air leaks are detected, determine if connections need to be tightened or if valves, donning switch, etc. need to be adjusted (2) SCBA with audible leaks due to malfunctions shall be removed from service, tagged, and reported to the officer (3) On some SCBA, the audible alarm does not sound when the cylinder valve is opened. You must know the operation of your particular unit 2. Two-person method a) The firefighter wearing the SCBA (1) Disconnects the regulator from the face piece or disconnects the low-pressure hose from the regulator (depending on the type of SCBA) (2) Positions the cylinder for easy access by kneeling down or bending over b) The firefighter removing the cylinder (1) Fully closes the cylinder valve (2) Releases the air pressure from the high- and low-pressure hoses (3) Disconnects the high-pressure coupling from the cylinder (4) Removes the empty cylinder from the harness assembly (5) Inspects replacement cylinder and ensures that cylinder is 90-100% of rated capacity (6) Places new cylinder into the harness assembly (7) Checks the cylinder valve opening and the high-pressure hose fitting for debris and clears any debris by quickly opening and closing the cylinder valve (8) Connects the high-pressure hose to the cylinder and handtightens (9) Slowly and completely opens the cylinder valve and listens for an audible alarm and leaks as the system pressurizes (10) On some SCBA, the audible alarm does not sound when the cylinder valve is opened c) The firefighter wearing the SCBA (1) Dons regulator and takes normal breaths (2) Checks pressure reading on remote gauge and/or indicators and reports reading Activities 1. SCBA Inspection Procedure – Have the students conduct an SCBA 5 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. inspection. During the inspection, have the students touch each component and state its name and condition. Use the SCBA Inspection Procedure Rubric as a student guide and as an assessment. (Note: This activity may be completed with the students grouped as partners while evaluating each other. Regardless of the method of assessment the components do not have to be completed in the order listed on the SCBA Inspection Procedure Rubric. The inspection should be performed with the cylinder removed from the back plate.) 2. Cylinder Replacement – Have the students demonstrate replacing a SCBA cylinder using the one- and two-person methods. Use the SCBA Cylinder Replacement–One-Person Method Checklist and the SCBA Cylinder Replacement–Two-Person Method Checklist to guide the activity and for assessment. Assessments SCBA Air Management and Safety Quiz and Key SCBA Inspection Procedure Checklist SCBA Cylinder Replacement–One-Person Method Checklist SCBA Cylinder Replacement–Two-Person Method Checklist Discussion Rubric Individual Work Rubric Presentation Rubric Materials SCBA Air Management and Safety computer-based presentation Computer with interactive white board Computer(s) with Internet access or computer-based presentation software Note-taking materials Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) SCBA Paper and pencils Resources 0135151112, Essentials of Firefighting and Fire Department Operations (5th Edition), International Fire Service Training Association (IFSTA) Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, students will create a technical illustration of the SCBA using paper and pencils. The illustration should include and label all of the SCBA components. Use the Individual Work Rubric for assessment. For enrichment, students will create a technical demonstration about either an SCBA inspection or an SCBA operational check using computer-based presentation software. Use the Presentation Rubric for assessment. 6 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. State Education Standards Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Career and Technical Education §130.299. Firefighter I (One to Two Credits). (10) The student analyzes the internal systems that sustain life in the human body and identifies the physical requirements of a self-contained breathing apparatus wearer. The student is expected to: (C) identify the firefighter's physical requirements for wearing a self-contained breathing apparatus; (11) The student demonstrates confidence in performing fire fighting skills while wearing self-contained breathing apparatus. The student is expected to: (B) describe and demonstrate how to calculate the air supply duration in the cylinder; (D) describe the uses and limitations of the self-contained breathing apparatus; (F) demonstrate the replacement of an extended cylinder on a self-contained breathing apparatus assembly with a full cylinder; (12) The student demonstrates inspection, care, and testing procedures for the self-contained breathing apparatus. The student is expected to: (A) document routine maintenance for the self-contained breathing apparatus; College and Career Readiness Standards Cross-Disciplinary Standards I. Key Cognitive Skills C. Problem solving 1. Analyze a situation to identify a problem to be solved. 2. Develop and apply multiple strategies to solve a problem. 3. Collect evidence and data systematically and directly relate to solving a problem. 7 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name ________________________________ Date ___________________ SCBA Air Management and Safety Quiz Multiple Choice: 1. _____An oxygen-deficient atmosphere contains less than which of the following percentages of oxygen? A. 15.5% B. 19.5% C. 25.5% D. 30.5% 2. _____Which of the following is not a physical factor that affects the firefighter's ability to use respiratory protection? A. Agility B. Facial features C. Physical condition D. Emotional problems 3. _____Which of the following is a medical factor that affects the firefighter's ability to use SCBA effectively? A. Cardiovascular training B. Neurological functioning C. Muscular/skeletal condition D. All of the above 4. _____Which of the following is NOT a mental factor that affects the firefighter's ability to use respiratory protection effectively? A. Agility B. Self-confidence C. Emotional stability D. Adequate training in equipment use 5. _____Which of the following is NOT an equipment limitation of SCBA? A. Decreased visibility B. Decreased weight C. Decreased mobility D. Decreased ability to communicate 6. _____Which of the following is an air-supply limitation of SCBA? A. Limited visibility B. Increased weight C. Physical condition of user D. Cylinder pressure after use 8 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. 7. _____Which of the following is a basic element to effective air management? A. Know your point of no return (beyond 50 percent of the air supply of the team member with the lowest gauge reading) B. Know how much air you have (at all times) C. Make a conscious decision to stay or to leave when your air is down to 50 percent D. All of the above 8. _____Which of the following always makes the decision to stay or leave? A. Individual B. Supervisor C. Company officer D. First-responding firefighter 9. _____Which of the following is one of the recommended points at which a firefighter should check air supply status? A. At the end of the shift B. When doffing the SCBA C. At the beginning of the shift D. When closing the cylinder valve 10. _____Which of the following constitutes the main weight of the breathing apparatus? A. Regulator B. Face piece C. Air cylinder assembly D. Harness 11. _____How often should firefighters who are certified to wear SCBA be fit-tested? A. Weekly B. Monthly C. Annually D. Biannually 12. _____Which of the following does NOT have an effect on air-supply duration? A. Level of training B. Degree of stress C. Task being performed D. End pressure of cylinder 13. _____Firefighters donning SCBA during an incident who feel they may lose consciousness should do which of the following? A. Keep searching for an exit B. Lie flat on the floor, close to a wall C. Lie flat on the floor in the center of the room D. Lean against the wall in a location near the door 9 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. 14. _____Which of the following methods of moving in areas of limited visibility allows firefighters to feel the floor as they move along? A. Rolling B. Walking C. Crawling D. Crouching 15. _____In which of the following atmospheres should firefighters always have a tag-line? A. Wet B. Hot C. Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health (IDLH) D. Limited visibility 16. _____Which of the following is a true statement about restricted openings? A. They allow space for a hose line B. They lead to an area of limited visibility C. Only highly trained firefighters may access them D. They are too small to pass through while wearing SCBA 10 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. SCBA Air Management and Safety Quiz Key 1. B 2. D 3. D 4. A 5. B 6. C 7. D 8. B 9. C 10. C 11. C 12. D 13. B 14. C 15. C 16. D 11 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name: _______________________________ Date: ________________________________ SCBA Inspection Procedure Checklist Directions: During the inspection, touch each component as you state its name and condition. Your partner or your instructor will check off the components on the list below as you complete them. The components do not have to be completed in order listed. (Note: Perform the inspection with the cylinder removed from the back plate.) 1 pt. each Performance Objectives Component 1: Cylinder and Valve Assembly Read the cylinder pressure Read the hydrostatic date Confirm/verbalize that the cylinder and valve assembly are clean and undamaged Component 2: Back plate and Harness Assembly Confirm/verbalize that the: Back plate is clean and undamaged Straps are clean, undamaged, and fully extended Regulator mount is clean and undamaged Component 3: Regulator Assembly Confirm/verbalize that the: O-ring is clean and undamaged High-pressure hose is clean and undamaged Pressure reducer is clean and undamaged PASS Device is clean and undamaged Remote gauge is clean and undamaged Auxiliary hose is clean and undamaged EBSS hose is clean and undamaged Low-pressure hose to regulator is clean and undamaged Regulator Gasket is clean and undamaged Red bypass valve moves freely and is clean and undamaged Donning switch is clean and undamaged Lock moves freely and is clean and undamaged Component 4: Face piece Assembly Confirm/verbalize that the: Regulator mount is clean and undamaged Voice Amps is clean and undamaged Face shield is clean and undamaged Nose cup is clean and undamaged Face seal is clean and undamaged Head harness is clean and undamaged Straps are fully extended Total points (25 pts. possible) 12 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name: _______________________________ Date: __________________________ SCBA Cylinder Replacement–One-Person Method Checklist Performance Objectives 10 pts. each Place the SCBA on a firm surface Close the cylinder valve Bleed the air pressure from the high- and low-pressure hoses Disconnect the high-pressure coupling from the cylinder Remove the empty cylinder from the harness assembly Verify that the replacement cylinder is 90-100% of rated capacity Check the cylinder valve opening and the high-pressure hose fitting for debris Place the new cylinder into the backpack Connect the high-pressure hose to the cylinder and hand-tighten Slowly and fully open the cylinder valve and listen for an audible alarm and/or leaks as the system pressurizes If air leaks are detected, determine if the connections need to be tightened or if the valves, donning switch, etc. need to be adjusted Total Points (110 pts. possible) Comments: 13 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name: _______________________________ Date: ____________________________ SCBA Cylinder Replacement–Two-Person Method Checklist Performance Objectives 10 pts. each Disconnect the regulator from the face piece or disconnect the lowpressure hose from the regulator Position the cylinder for easy access by kneeling down or bending over Fully close the cylinder valve Release the air pressure from the high- and low-pressure hoses Disconnect the high-pressure coupling from the cylinder Remove the empty cylinder from the harness assembly Inspect replacement cylinder and ensure that the cylinder is 90-100% of rated capacity Place the new cylinder into the harness assembly Check the cylinder valve opening and the high-pressure hose fitting for debris and clear any debris by quickly opening and closing the cylinder valve Connect the high-pressure hose to the cylinder and hand-tighten Slowly and completely open the cylinder valve and listen for an audible alarm and/or leaks as the system pressurizes Don regulator and take normal breaths Check the pressure reading on the remote gauge and/or indicators and report reading Total Points (130 pts. possible) Comments: 14 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name_______________________________________ Date_______________________________ Discussion Rubric Objectives 4 pts. Excellent 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Participates in group discussion Encourages others to join the conversation Keeps the discussion progressing to achieve goals Shares thoughts actively while offering helpful recommendations to others Gives credit to others for their ideas Respects the opinions of others Involves others by asking questions or requesting input Expresses thoughts and ideas clearly and effectively Total Points (32 pts.) Comments: 15 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name______________________________________ Date_______________________________________ Individual Work Rubric 4 pts. Excellent Objectives 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Follows directions Student completed the work as directed, following the directions given, in order and to the level of quality indicated Time management Student used time wisely and remained on task 100% of the time Organization Student kept notes and materials in a neat, legible, and organized manner. Information was readily retrieved Evidence of learning Student documented information in his or her own words and can accurately answer questions related to the information retrieved *Research/Gathering information (if relevant) Student used a variety of methods and sources to gather information. Student took notes while gathering information Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 16 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved. Name:____________________________________ Date:_____________________________ Presentation Rubric 4 pts. Excellent Objectives 3 pts. Good 2 pts. Needs Some Improvement 1 pt. Needs Much Improvement N/A Pts. Topic/Content Topic discussed completely and in-depth Includes properly cited sources (if used) Creativity/Neatness Integrates a variety of multimedia effects to create a professional presentation (transition and graphics) or appropriate visual aid used Title slide, table of contents, bibliography are included, using acceptable format Mechanics Grammar, spelling, punctuation, and capitalization are correct Image and font size are legible to the entire audience Oral Presentation Communicates with enthusiasm and eye contact Voice delivery and projection are dynamic and audible Audience Interaction Presentation holds audience’s attention and relates a clear message Clearly and effectively communicates the content throughout the presentation Total Points (20 pts.) Comments: 17 Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2013. All rights reserved.