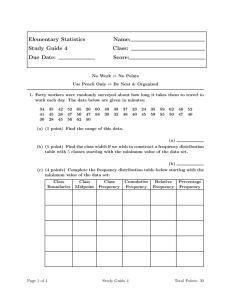
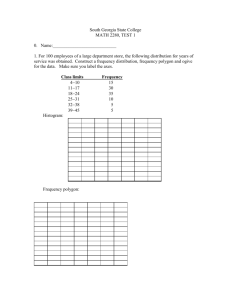
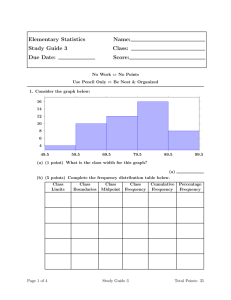
Statistics and Risk Management Describing Data Video URL:
advertisement

Statistics and Risk Management Describing Data Video URL: Intro – http://jukebox.esc13.net/untdeveloper/Videos/Introduction.mov Describing Data: http://jukebox.esc13.net/untdeveloper/Videos/Describing%20Data.mov Vocabulary List: Pie Chart: Graphical representation of data normally demonstrating the relationship in size between data groups. Histogram: Graphical representation of data normally demonstrating the relationship in size over a period of time. Scatter Chart: Graphical representation of data normally demonstrating the relationship between each score based upon 2 variables influencing the collected score. Ogive Chart: Graphical representation of data using a line to connect scores illustrating continuity and predictable outcomes. Indices: The supporting chart legends used to describe variables and measurement. Scales: A progressive classification. Descriptive Statistics: Procedures used to organize and present data in a convenient and communicable form. Inferential Statistics: Procedures employed arrive at broader conclusions or inferences about populations on the basis of samples. Qualitative Data: Statistical data collected that describes Quantitative Data: Statistical data collected that measures Data Range: The measurement between the low and high raw data score. Measure of Central Tendencies: The Mode, Median, and Mean values. Measures of Variability: The Variance and Standard Deviation values. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 1 Resources: Statistics By the Numbers Statistics By the Numbers features information about statistics and the how they are calculated. A sample math problem defines and walks through the steps for determining mean, medium, mode, range, and standard deviation. http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/statistics.html Kkan Academy: Statistics Khan Academy’s Statistics page offers a wide variety of instructional videos for various statistics lessons. Some of these video lessons include: Mean Median and Mode, Range and MidRange, Reading Pictographs, Reading Bar Graphs, Reading Line Graphs, reading Pie Graphs, and more. http://www.khanacademy.org/math/statistics The University of Sheffield (MASH) Mathematics and statistics help, including videos and problems to solve. http://www.mash.dept.shef.ac.uk/VarianceandStandardDeviation.html Ogive Use arthitecture to explain the ogive curve. http://curvebank.calstatela.edu/ogive82/ogive82.htm Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 2 Describing Data Practice Test Name:_____________________ TRUE and FALSE: 1. The measurement between the low and high raw data score is the Qualitative Data. A. True B. False 2. Indices are used to identify groups in comparison studies. A. True B. False 3. The study of collecting, organizing and analyzing data is called Statistics. A. True B. False 4. Statistics should not be used for either research and reporting. A. True B. False 5. Qualitative and Quantitative Data are two forms of data types. A. True B. False 6. The mean is the most repeated score in measures of central tendencies. A. True B. False MATCHING: A. B. C. D. E. Indices Descriptive Statistics Inferential Statistics Data Range Measures of Variability 7. __________ The measurement between the low and high raw data score. 8. __________ The supporting chart legends used to describe variables and measurement. 9. __________ Procedures used to organize and present data in a convenient and communicable form. 10. __________ The Variance and Standard Deviation Values. 11. __________ Procedures employed which arrive at broader conclusions or inferences about populations on the basis of samples. MULTIPLE CHOICE: 12. Which chart is a graphical representation of data normally demonstrating the relationship in size between data groups? B. Scatter Chart A. Pie Chart C. Histogram D. Ogive Chart 13. Which chart is a graphical representation of data normally demonstrating the relationship between each score based upon 2 variables influencing the collected score? A. Scatter Chart B. Histogram C. Pie Chart D. Ogive Chart Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 3 Describing Data Practice Test Name:_____________________ TRUE and FALSE: 14. Which chart is a graphical representation of data normally demonstrating the relationship in size over a period of time? A. Pie Chart B. Scatter Chart C. Histogram D. Ogive Chart 15. Which chart is a graphical representation of data using a line to connect scores illustrating continuity and predictable outcomes? A. Pie Chart B. Ogive Chart C. Scatter Chart D. Histogram 16. Which of the following is not a descriptive scale? A. Nominal B. Ordinal C. Interval D. Fiscal 17. The _____ is the overall group of subjects to which the research will apply. A. Sample B. Control C. Data Set D. Population 18. The _____ is a smaller, more practical, group size that represents the larger population. A. Sample B. Control C. Data Set D. Population 19. Which of the following are visual advantages of charts? A. Easier to make comparisons B. Easier to draw conclusions C. Simplifies how you see information D. All of the above rather than using words 20. This kind of charting is great for a small number of groups with large variances. A. Histogram B. Pie Chart C. Scatter Chart D. Ogive Chart Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 4 Describing Data Practice Test KEY 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. B A A B A B D A B E C A A C B D D A D B Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 5 Using a Spreadsheet for Basic Statistical Purposes Much easier, faster & more accurate than using a calculator. Spreadsheet software is great for learning how statistical formulas work. While you will probably use a program like SPSS for your career research, using spreadsheet software can give you a real appreciation on how statistical formulas work. Spreadsheet software has many build in functions for statics, but we suggest you use plain math functions while you are learning the basics. We are assuming you understand the basics of how a spreadsheet works. We assume you understand the concepts of cells, how to enter labels or data, how to enter basic formulas using relative or absolute cell addresses, and how to format the output. You will need to know how to insert and delete rows and columns. To save a lot of time you need to know how to use the Cell Handle to drag and replicate data or formulas. Creating Data Columns 1. Add a column label at the top of a column B1. 2. Type in some data in the column. Use cells B2 through B11 3. Push Enter to move down to the next cell. Summing a Column 4. Move to cell below the data you have entered. Use B12 5. Click the Formulas Menu tab. 6. Select Auto Sum 7. A box will appear surrounding the above data. 8. If you push the Enter key in the spreadsheet software with complete a =Sum(B2:B11) formula (the Letters represent the column(s), the Numbers represent the row(s).) 9. You can also type that formula in any cell you want and the program will display the sum of those cells. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 6 Computing a mean 1. Pick the cell for the mean displayed B14. 2. Type =Average( 3. Next use your mouse and select the block of cells you want included in the MEAN calculation. 4. When you are finished push the Enter key to complete the formula and display the results. 5. Computing the variation for each sample value. Creating a Deviation Column 1. Add a Column Label Deviation in cell C1. 2. In cell C2 Type the formula =B2-$B$14 and push Enter. 3. Select C2 and use the Handle located on the cell lower right-side to drag down duplicate formulas through C11. Click on a few of these cells and see if the formula duplicated OK. Creating a Squared Deviation Column 1. Add a Column Label Squared in cell D1. 2. In cell D2 Type the formula =C2*C2 and push Enter. 3. Select D2 and use the Handle located on the cells lower right-side to drag down duplicate formulas through D11. Click on a few of these cells and see if the formula duplicated OK. Creating Value Count Value 1. In cell B15 type in label SAMPLE COUNT: 2. In cell D15 type in =COUNTA(B2:B11) Creating the Total Variance Value 1. In cell B17 type in label TOTAL VARIANCE: 2. In cell D17 type in =SUM(B2:B11)/(D15-1) 3. Or In cell E17 type in =VAR.P(B2:B11) Creating the Standard Deviation 1. In cell B19 type in label TOTAL VARIANCE: 2. In cell D19 type in =SQRT(D15) 3. Or In cell E19 type in =STDEV.P(B2:B11) You can insert a row or column. Cells using relative address in their formulas should update appropriately. Cells using Absolute addresses ie: $A$14 may need manual corrections. If you want to save a note in a cell you can right click on a cell and select Insert Comment. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 7 Student Assignment 3.1a Describing Data Visually Name:_____________________ There will be times in your career, especially if you working in management where you will have to present data at a meeting. Understanding how to create and interpret charts and graphs will be essential in presenting your viewpoint. Let’s just start out by finding charts and graphs created by others. See if you can find some interesting ones that you can see what is being presented and why you think it was important enough for someone to create the chart or graph. On the Web find an example of a pie chart, a bar graph, and a histogram. Import them into a word processing document and then proceed to explain what the chart is demonstrating. In addition, describe what indices are used. Import these images into a presentation slide format and be prepared to explain to the class what the chart or graph is showing and why it interested you. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 8 Student Assignment 3.1b Describing Data Visually Name:_____________________ Using the spreadsheet provided, 3ss_DescribingDataVisually, examine the constructed charts and change the data values to see how the visual representation changes. One each of the charts describe what happens as you change the data, be specific. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 9 Student Activity 3.2a Describing Data Statistically Name: _____________________ Using the spreadsheet provided, ss_DescribingDataStatistically, examine the Statically Describing Data page and change the data values in column “B” to see how the Descriptive Results change in column “E”. To change the mean to a larger value what will you generally have to do to the data? To change the standard deviations to a smaller number what will you have to do to the data? To make the standard deviation larger what would you have to do? To make the standard deviation larger while keeping the mean unchanged what would you have to do? Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 10 Student Activity 3.2b Describing Data Statistically Name: _____________________ Your instructor posted the grades for an important exam you took. The possible range of exam points was 0 to 100 for 50 students The Mean Score was 80 with a Standard Deviation of 5 The instructor said anyone a scoring higher than +1 STDDEV would get a “B” and anyone scoring higher that +2 STDDEV would get an “A”. What would be the minimum score you would need to get to get an “A”? Explain how you figured out that score you needed. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 11 Explore Activity: Data Collection – Explore the concepts of displaying and describing data from this unit by finding a data set of interest to you. Examples of data you might use include: Survey your classmates (or teammates) with a question of interest: o How many text messages do you send in a day? o How many hours per week do you spend at a computer? o What was the cost of your last haircut? o How many songs do you have on your MP3 player? o How many pairs of shoes do you have? Find existing data about a favorite sport: o The average offensive yards per team for a particular season in the NFL o The number of runs batted in (RBI) for the team leader of each MLB team for a particular season Runs scored, free throws attempted (by player), blocks (volleyball), or some other such data for a team at your school. Other data sources: o From the Central Intelligence Agency (yes, the CIA) you can find all sorts of interesting information about the people, agriculture, infrastructure, business, etc. of nearly every country in the world (https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-worldfactbook/index.html). o Information on health issues can be found at the Center for Disease Control (http://www.cdc.gov/) or the World Health Organization (http://www.who.int/en/). Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 12 The data should be quantitative, and you should find a data set with at least 20 data points. Then produce a graph such as a histogram (or a scatterplot if you found data associated with time such as home runs by year). Also calculate the mean and the standard deviation using a spreadsheet or an on-line resource such as the Rice Virtual Lab in Statistics – select Analysis Lab where you will then be able to enter your data and produce a histogram and descriptive statistics that include the mean and standard deviation). Bonus – You might be able to find data that includes a categorical variable (gender, grade-level, sports league, country, etc.). You could then separate your data into groups based on this categorical variable and produce separate histograms (or scatterplots) and means and standard deviations for comparison (you will need more data to do this – perhaps 15-20 data points per categorical group): Compare the number of pairs of shoes owned by boys to the number of pairs of shoes owned by girls in your class. Compare the infant mortality for countries in the Americas (North and South) to infant mortality for countries in Asia. Produce a poster with your data, graphs and calculated statistics. Include a description of your data (where you found it, what it represents, why it is of interest to you, etc.). Video Links – Check out the relevant links at Khan Academy for more information and examples: http://www.khanacademy.org/#statistics Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2012. All rights reserved. 13