Lesson Plan Evaluating Company Performance
advertisement

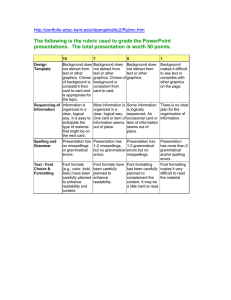
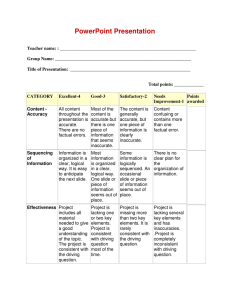
Evaluating Company Performance Financial Analysis Finance Lesson Plan Performance Objective Students will understand variables required in evaluating company performance. Specific Objectives Understand the importance of notes to financial statements. Understand that external forces can be a factor when analyzing company performance. Understand the significance of financial ratios in evaluating a company’s financial condition. Terms Annual Report– a report prepared for shareholders and investors of a company Benchmarks– comparison to a standard, such as a similar company or industry Break‐Even Analysis– the point at which there is no profit or loss Comparative Analysis– comparing ratios for different companies side‐by‐side SEC– Securities and Exchange Commission whose mission is to protect investors 10‐K– a form required by publicly‐traded companies to file with the SEC; provides a detailed summary of company performance including financial statements, risks, and other details Time When taught as written, this lesson should take approximately five to six days to teach. Preparation TEKS Correlations This lesson, as published, correlates to the following TEKS. Any changes/alterations to the activities may result in the elimination of any or all of the TEKS listed. 130.168 (c) Knowledge and Skills (3) The student demonstrates mathematics knowledge and skills required to pursue the full range of postsecondary education and career opportunities. The student is expected to: (f) analyze data when interpreting operational documents. (4) The student manages financial resources to ensure solvency. The student is expected to: (e) interpret financial statements. (5) The student calculates business ratios to evaluate company performance. The student is expected to: Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 1 (a) discuss the use of financial ratios in business finance. (6) The student analyzes a financial statement. The student is expected to: (b) describe external forces affecting a company’s value; (d) analyze a company financial situation; and (e) understand and interpret financial statement notes. Interdisciplinary Correlations English‐English I 110.31(b)(1) Reading/Vocabulary Development. Students understand new vocabulary and use it when reading and writing. 110.3(b)(11) Reading/Comprehension of informational text/procedural texts. Students understand how to glean and use information in procedural texts and documents. Math‐Algebra I 111.32(b)(1)(C) Interpret and make decisions, predictions, and critical judgments from functional relationships. Occupational Correlation (O*Net – www.onetonline.org/) Job Title: Loan Officers O*Net Number: 13-2072.00 Reported Job Titles: Commercial Loan Officer, Mortgage Loan Originator, Portfolio Manager Tasks Analyze applicants' financial status, credit, and property evaluations to determine feasibility of granting loans. Obtain and compile copies of loan applicants' credit histories, corporate financial statements, and other financial information. Approve loans within specified limits, and refer loan applications outside those limits to management for approval. Soft Skills: Complex Problem Solving, Judgment and Decision Making, Critical Thinking Accommodations for Learning Differences It is important that lessons accommodate the needs of every learner. These lessons may be modified to accommodate your students with learning differences by referring to the files found on the Special Populations page of this website. Preparation Review and familiarize yourself with the terminology and website links. Have materials and websites ready prior to the start of the lesson. References http://www.sec.gov Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 2 Century 21 Accounting: Advanced, South‐Western Publishing Contemporary Mathematics for Business and Consumers, South‐Western Publishing http://www.sba.gov http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/non‐financial‐performance‐measures‐what‐works‐and‐ what‐doesnt/ Instructional Aids Textbook or Computer Program Diagrams/Charts Lesson 1.01 Presentation Instructor Computer/Projection Unit Online Websites Introduction The main purposes of this lesson are to help students understand the following concepts: that financial information is the first step in analyzing company performance, that non‐financial data is also important to evaluating how a company is doing, and that acceptable ratios are merely guidelines and that there is no set way of guaranteeing or predicting company performance. Ask students if they know how to tell how a company is really doing. Ask students that if a company recorded a net income, would that mean that it was doing well? Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 3 Outline I. Important Considerations A. Most important statements are the Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and the Cash Flow Statement. B. Understand the products/services of the company and its industry. C. Accrual versus cash accounting 1. Accrual– revenue and expenses are recorded when they are incurred, not necessarily paid, which makes the Cash Flow Statement especially important 2. Cash– recognized when cash is received or paid II. Basic Steps for Evaluating Company Performance A. Look for recurring accounts that may have an inconsistent amount, such as, unusually high or low. B. Look for unusual items that are not present from one year to the next—for example, an amount for a capital outlay, such as a building, that was not previously an asset. C. Look for trends—for example, Ask students if they have ever made an assumption about something based on appearances. Discuss the following with the students: occasionally students may provide examples about houses or cars that are expensive. As the real estate market the last several years has shown, sometimes items that are very expensive are not necessarily paid for with cash, but instead have large debt associated with them. This can also be the case with businesses. We may like a company’s products or services and think the company is successful because it seems to have high sales, but many times the analysis of a company can prove otherwise. Ask the students what a good indicator of the future performance may be for a company. They most likely will say “the past.” This can be true. Companies look for trends over time. Multiple Intelligences Guide Existentialist Interpersonal Intrapersonal Kinesthetic/ Bodily Logical/ Mathematical Musical/Rhythmic Naturalist Verbal/Linguistic Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 4 Visual/Spatial increasing total expenses or in specific expenses. D. Compare information to that of competitors. E. Compare information to the particular industry the company is in. III. Acceptable Ratio Numbers A. Current Ratio– 2:1 B. Quick Ratio– 1:1 C. Debt to Equity and Debt to Assets– the lower the better D. Inventory Turnover– a higher ratio signals higher efficiency E. Total Assets Turnover– the higher the ratio, the higher the performance of the company F. Accounts Receivable Turnover– the higher the ratio means either the company has mainly cash sales or the accounts receivables are being managed efficiently; the lower the ratio could signify potential credit problems IV. Using Benchmarks as an Analysis Tool A. Standards by which performance can be measured B. Compare to similar businesses C. Compare to the industry Companies should also look at their competitors and see what they may be doing the same or differently than they are. Ask students, in pairs, to talk about two similar companies and decide upon things they do the same and what makes them different from each other. They should go to the Internet (or on their phones if they are allowed and they are not in a computer lab) and look for one of the ratios for each company. Each pair should volunteer a response on if that ratio was the same for both companies or which one might be more favorable. Now students, in pairs, can look for additional ratios to see if, by checking more data, the companies appear to be in more similar or more different financial situations. Multiple Intelligences Guide Existentialist Interpersonal Intrapersonal Kinesthetic/ Bodily Logical/ Mathematical Musical/Rhythmic Naturalist Verbal/Linguistic Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 5 Visual/Spatial V. Break‐Even Analysis A. The point at which there is no profit or loss B. When revenue and costs are equal C. = fixed costs/ (unit selling price‐ variable costs) D. Allows a company know when it can expect to cover its expenses VI. Difference between a 10‐K and an Annual Report A. Purpose of 10‐K is SEC filing; annual report is for stockholders B. Little graphics on a 10‐K; annual report contains graphics and pictures C. 10‐K contains more specific and detailed information including risk factors; annual report has mostly financial information VII. Annual Reports A. Available to shareholders and other investors B. Usually not prepared for privately‐held companies C. Contains several parts 1. letter to shareholders 2. usually a five‐ to ten‐year Discuss with students how, depending upon the costs a company incurs to produce a product, a similar company’s break‐even point can be higher or lower than another similar company. Ask students what can lower costs to produce products. Show students on the computer what a Form 10‐K looks like. Go to www.sec.gov Filings>Company Filings Search> Full Text (on the left)> Advanced Search Page. In Form Type, click on 10‐K, then click on Company Name, and type the company name. Click on the first link 10‐K that appears at the bottom of the screen. Show students the table of contents and click on the financial statements and the Risk Factor section as well. While students are familiar with the financial statements, they may not have seen… Multiple Intelligences Guide Existentialist Interpersonal Intrapersonal Kinesthetic/ Bodily Logical/ Mathematical Musical/Rhythmic Naturalist Verbal/Linguistic Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 6 Visual/Spatial Summary. 3. Management perspective‐ discussion of trends 4. Letter from a CPA 5. Financial statements 6. Company locations 7. Directors and officers 8. Stock information, including price history and dividends VIII. Understanding the Annual Report A. Look for trends from historical data B. Look for signs of growth for the future C. Read footnotes to financial statements IX. Notes to Financial Statements A. Clarifications or explanations of items mentioned in the financial statements B. Possible examples 1. Explanation of what is included in cash or cash equivalents 2. Explanation of how certain assets are valued 3. Clarification of which depreciation method is used for Property, Plant, and Equipment risk factors presented before. The Annual Report is another important source to use when evaluating a company’s performance. It also contains financial statements, but it has other information as well. Show students how to go directly to a company’s website, and (provided they are a publicly‐ traded company) usually there is a link for Investor Relations. There you should be able to find an Annual Report for that company. Whether students look at the financial statements from a company’s website or from the www.sec.gov 10‐K filing, look for the notes to the financial statements. These are usually explanations that simply cannot fit within the parameters of the data on the financial statements. Show students where these notes are and what some of them say. Multiple Intelligences Guide Existentialist Interpersonal Intrapersonal Kinesthetic/ Bodily Logical/ Mathematical Musical/Rhythmic Naturalist Verbal/Linguistic Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 7 Visual/Spatial X. XI. 4. Explanation of intangible assets—goodwill being one of the most common Non‐Financial Considerations A. Company market share B. Management C. Marketing strategies D. Economic condition 1. how company performs in up or down economic times 2. is company’s stock growth, cyclical, value, investments E. Social responsibility F. Customer and employee satisfaction G. Product Quality The Big Picture– to get an overall picture of the performance of a company, many aspects must be analyzed, such as: A. Comparing the company’s performance to similar companies B. Comparing the company’s performance to the industry C. Comparing the current year’s numbers to previous years’ numbers D. Ratio, horizontal, and vertical analysis E. Consider non‐financial information Much of the information used to evaluate a company relies on financial information, but there are other factors to consider as well. Ask students if they have heard any news from several years ago about the mortgage lending crisis and the foreclosure rate. While many lenders had performing mortgage loans, there were some very large corporations that had such a large amount of non‐performing loans all across the country that it negatively affected the economy, which, in turn, had an effect on almost all mortgage lenders. This is similar to how an automobile recall for one particular make and model can have a trickling effect to other car makes and models. Ask students what effects these events can have on companies. Sometimes the economy can have an effect on company data. Multiple Intelligences Guide Existentialist Interpersonal Intrapersonal Kinesthetic/ Bodily Logical/ Mathematical Musical/Rhythmic Naturalist Verbal/Linguistic Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 8 Visual/Spatial Application Guided Practice Have students get in pairs. The pairs should think of products they like or stores or restaurants they like to go to—any of these types of companies that they think must be doing very well because the students like what they have to offer. They are to locate their company financial statements on the Internet, as well as search for industry or economic information in the news that can have an effect on the business they chose. They should create a list of four factors to look at and respond to those, whether it is calculating ratios, industry ratios that may already be calculated on the Internet, or a news fact (any four factors will work). At the bottom, state whether they think the company is in good shape based on what they found. They should neatly record their information and place them on the walls around the room. Each pair will go through their list so all students can see what they chose to use for evaluation. Independent Practice Using the information from the Guided Practice activity, (individually) students will compose a list of 10 factors total after listening to and looking at what the pairs created. Summary Review Ask students the following questions on exit tickets: Question #1: What are the most common financial statements to be used when evaluating company performance? Answer #1: The Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Cash Flow Statement Question #2: Which financial statement is most important in accrual‐basis accounting? Answer #2: The Cash Flow Statements is most important in accrual accounting. Question #3: What are benchmarks? Answer #3: Benchmarks are standards to compare performance to, such as similar businesses or industry data. Question #4: What can non‐financial data tell about a company’s possible performance? Answer #4: Non‐financial measures include customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, management, and other things that cannot be measured but can be indicators of positive or negative outlooks for a company. Question #5: True or False. Financial measures are an effective way to assess a company’s performance. Answer #5: True. It is an effective way but should also be combined with non‐financial methods as well. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 9 Evaluation Informal Assessment Any and all of the following can be used as informal assessments: Exit tickets with vocabulary Pair‐share activities Class discussion and participation Formal Assessment The following can be considered a formal evaluation in order to keep students engaged during both the pre‐ test(s)s and post‐test(s): Annual Report Scavenger Hunt Assignment #1– Students will conduct Internet research for an Annual Report and create “scavenger hunt” questions that can be found in the report. They are to provide the teacher with the questions, so the teacher can make copies to distribute to the class. The teacher may assign companies or the student may select his/her own. The information can be presented in any way the student chooses. Students can create a presentation and record the information on slides. They can display their answers on flip chart paper or on a poster. They may create a typed report. The students can use any method they select. Regardless of the type of output they choose, they will present their findings to the class. Include a Quick Response Code for students to research the answers to the questions. Benchmark Analysis Assignment #2– Students can use any search engine to locate a company. They will select three of the five categories of ratios and two ratios from each category. They will also need the same ratios for the industry that the company is in to use as a benchmark. So there will be a total of 12 ratios—six for the company and six for the industry. Students should also graph the ratios to provide a visual representation of the company compared to the industry. First convert the ratios to decimals. The time periods can typically be on the x axis—decimals on the y axis. The ratios with % can be graphed with the periods on the x axis and the % on the y axis. Students should then evaluate the company performance in a short paragraph based on each of the ratio categories. This data can be placed on a word processing document, poster, or flip chart paper. Company Evaluation Research Report Assignment #3– Students are to select a company (unless the teacher assigns specific companies) and create a research paper containing the following information: a title page, table of contents, an executive summary identifying the industry, the company’s products or services, and its competitors. Mention any notable events in the economy that may have had effects on this particular business. Next should be an analysis using financial data; include at least five ratios and how they are related to or affected by the non‐financial information above. Conclude the paper with a summary of the company’s performance. Include a works cited page. Investor Presentation Assignment #4– Individually, students will prepare a presentation to investors and potential investors (the class) evaluating the performance of a company that the students select. Students are to include financial statement data (horizontal and vertical analysis), ratio analysis, Form 10‐K risk data, and economic and industry information that affects that company. The number of Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 10 slides should be appropriate to convey all information. Investors (student audience) will be allowed to ask questions at the end of the presentation. Enrichment Extension Students can interview an executive with either a small or large company. Important questions should include what he/she thinks is most important in analyzing a company’s financial situation, whether it is horizontal or trend analysis, vertical analysis, or ratio analysis. Which numbers on financial statements do they think are critical to examine? Summarize the findings in either a report or a table. Include the questions as well as the answers. Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 11 Financial Analysis Evaluating Company Performance Annual Report Scavenger Hunt Assignment #1 Student Name: ________________________________________ CATEGORY 20 15 8 1 Attractiveness Makes excellent use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. to enhance the presentation. Makes good use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. to enhance to presentation. Makes use of font, color, graphics, effects, etc. but occasionally these detract from the presentation content. Use of font, color, graphics, effects etc. but these often distract from the presentaion content. Requirements All requirements All requirements One requirement was are met and are met. not completely met. exceeded. More than one requirement was not completely met. Content Covers topic in‐ depth with details and examples. Subject knowledge is excellent. Content is minimal OR there are several factual errors. Mechanics No misspellings Three or fewer or grammatical misspellings errors. and/or mechanical errors. Oral Presentation Interesting, well‐ rehearsed with smooth delivery that holds audience attention. Maximum Points Possible: 100 Includes Includes essential essential information about the knowledge about topic but there are one the topic. Subject to two factual errors. knowledge appears to be good. Relatively interesting; rehearsed with a fairly smooth delivery that usually holds audience attention. Four misspellings and/or grammatical errors. More than four errors in spelling or grammar. Delivery not Delivery not smooth, but able to hold smooth and audience attention most audience attention of the time. lost. Student Points: _________ Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 12 Financial Analysis Evaluating Company Performance Benchmark Analysis Assignment #2 Student Name: ________________________________________ CATEGORY 20 15 8 1 Attractiveness Makes excellent use of font, color, and graphics to enhance the document. Makes good use of font, color, and graphics to enhance the document. Makes use of font, color, and graphics, but occasionally these detract from the document content. Use of font, color, and graphics, but these often distract from the document’s content. Requirements All requirements All requirements One More than one are met and are met. requirement was requirement was exceeded. not completely not completely met. met. Mechanics No misspellings Three or fewer or grammatical misspellings errors. and/or mechanical errors. Content Covers topic in‐ depth. Subject knowledge is excellent. Organization Content is well‐ Uses graph labels Content is There was no organized using to organize, but logically clear or logical graph labels. the overall organized for the organizational organization most part. structure, just appears flawed. lots of numbers. Maximum Points Possible: 100 Four misspellings and/or grammatical errors. Includes Includes essential essential knowledge about information the topic. about the topic Subject but there are knowledge one to two appears to be factual errors. good. More than four errors in spelling or grammar. Content is minimal OR there are several factual errors. Student Points: _________ Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 13 Financial Analysis Evaluating Company Performance Company Evaluation Research Report Assignment #3 Student Name: ________________________________________ CATEGORY 20 15 Quality of Information Information clearly relates to the main topic. It includes several supporting details and/or examples. Information clearly Information relates to the main clearly relates to topic. It provides one the main topic. to two supporting No details and/or details and/or examples are examples. given. Sources All sources (information and graphics) are accurately documented in the desired format. All sources (information and graphics) are accurately documented, but a few are not in the desired format. All sources Some sources are (information and not accurately graphics) are documented. accurately documented, but many are not in the desired format. Mechanics No grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors. Almost no grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors A few grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors. Paragraph Construction All paragraphs include Most paragraphs Paragraphs an introductory include an included related sentence, introductory information but explanations or sentence, were typically not details, and a explanations or constructed well. concluding sentence. details, and a concluding sentence. Paragraphing structure was not clear, and sentences were not typically related within the paragraphs. Internet Use Successfully uses suggested Internet links to find information and navigates within these sites easily without assistance. Needs assistance or supervision to use suggested Internet links and/or to navigate within these sites. Maximum Points Possible: 100 8 Usually able to use suggested Internet links to find information and navigates within these sites easily without assistance. Occasionally able to use suggested Internet links to find information. 1 Information has little or nothing to do with the main topic. Many grammatical, spelling, or punctuation errors. Student Points: _________ Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 14 Financial Analysis Evaluating Company Performance Investor Presentation Assignment #4 Student Name: ________________________________________ CATEGORY 20 15 8 Preparedness Student is completely prepared and has obviously rehearsed. Student seems pretty prepared but might have needed a couple more rehearsals. The student is Student does not somewhat seem at all prepared prepared, but it to present. is clear that rehearsal was lacking. Content Shows a full Shows a good Shows a good Does not seem to understanding of understanding of understanding of understand the topic the topic. the topic. parts of the very well. topic. Stays on Topic Stays on topic all Stays on topic Stays on topic It was hard to tell (100%) of the most (99‐90%) of some (89%‐75%) what the topic was. time. the time. of the time. Posture and Eye Contact Stands up straight and looks relaxed and confident. Establishes eye contact with everyone in the room during the presentation. Comprehension Student is able Student is able Student is able to accurately to accurately to accurately answer 90‐100% answer 75‐89% answer a few of questions of questions questions posed posed by posed by by classmates classmates about classmates about about the topic. the topic. the topic. Maximum Points Possible: 100 Stands up straight and establishes eye contact with everyone in the room during the presentation. Sometimes stands up straight and establishes eye contact. 1 Slouches and/or does not look at people during the presentation. Student is unable to accurately answer questions posed by classmates about the topic. Student Points: _________ Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2014. All rights reserved. 15