A FACT, A CONCEPT
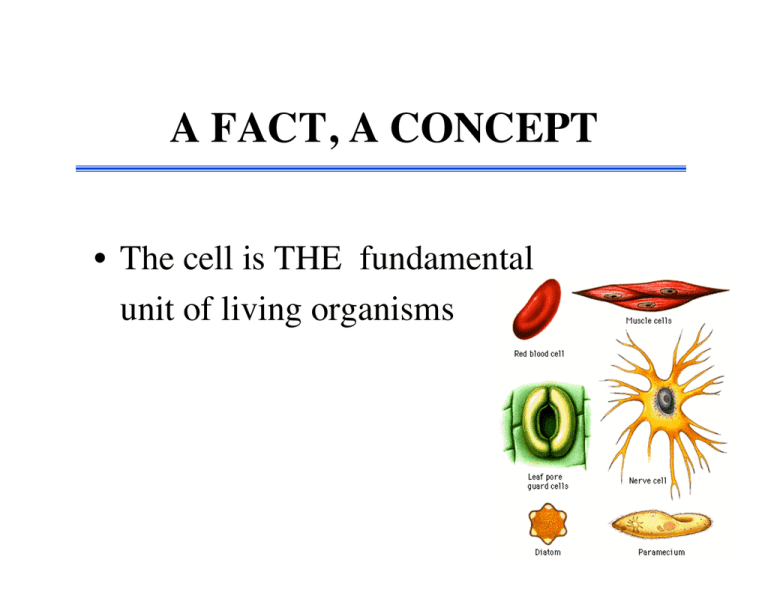
• The cell is THE fundamental unit of living organisms
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c)
1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL 60661.
All rights reserved. "WORLD BOOK illustrations by Charles
CELL THEORY HISTORY
• Robert Hooke
observed cork and
saw this: 2
IMAGINE
• Some world made up of free moving
materials
– Under some conditions, linked
materials may “survive” better than
when free and independent
3
NECESSITIES TO SURVIVE
AND PROLIFERATE
• Separation from environment
• Integrity
• Energy source
• Reproduction
NECESSITIES TO SURVIVE
AND PROLIFERATE
• Separation from environment
• Integrity
• Energy source
• Reproduction
2’ND LAW OF
THERMODYNAMICS
• All natural systems or processes move
toward disorder or randomness
(entropy)
ENERGY SOURCES
• Internal - storage problems
OR
• External - acquisition problems
ENERGY-SOURCE
PROBLEMS
• Internal – Storage
– Diffusion
– Size effects
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book illustration by John F. Eggert
ENERGY-SOURCE
PROBLEMS
• External
– Requires a permeable membrane but
this can cause leakage
– Energy needs to maintain integrity
– Surface to volume problems
– Waste
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book illustration by John F. Eggert
A SURFACE TO VOLUME
PROBLEM
• A 1 cm cube gives 6 1x1 cm surface = 6 cm2
and 1x1x1 cm volume = 1cm3 • 6:1 surface to volume SURFACE TO VOLUME
CONTINUED
• A 2 cm cube gives 6 2x2 cm surface = 24 cm2
and 2x2x2 cm volume = 8 cm3
• 24:8 surface to volume
WHY IS SURFACE TO
VOLUME IMPORTANT?
• Cell content volume increase at a faster
rate than the surface through which
materials must be brought in to support
contents
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book illustration by John F. Eggert
A FACT
• Whenever you observe a cell with
exaggerated surface area you can
assume that it has a limited surface
problem
WHY IS SURFACE TO
VOLUME IMPORTANT IN
GENERAL?
Limited surface area can constrain many
reactions
ENERGY-SOURCE
PROBLEMS
• External
– Energy needs to maintain integrity
– Surface to volume problems
– Requires a permeable membrane but
this can cause leakage
– Waste
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book illustration by John F. Eggert
NECESSITIES TO SURVIVE
AND PROLIFERATE
• Separation from environment
• Integrity
• Energy source
• Reproduction
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book illustration by John F. Eggert
REPRODUCTION
• To increase representation in the
population reproduction is essential
"It's the first self-replicating cell
on the planet that's parent is a
computer,” Craig Venter
REPRODUCTION
• …
“He has not created life, only
mimicked it,” Dr. Baltimore said.
THE CELL THEORY
• All living organisms are composed of cells
• Life-dependent chemical reactions occur
within cells
• Cells arise from other cells
• Hereditary information is passed from mother to daughter cell
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525
W. Monroe, Chicago, IL 60661. All rights reserved. "Chuck Brown, Photo Researchers
COMPARISON
PROKARYOTES
Localized Small
Always Nucleus Size Cell Wall EUKARYOTES
Distinct
Large
Sometimes
A FACT
• 1 kilogram of fertile soil may contain
more than 1 trillion individual
prokaryotes!
ENERGY USERS
• Autotrophs - do NOT require external
sources of organic materials. They obtain
energy from light or inorganic materials
• Heterotrophs - Require external sources of organic materials
for energy and building block materials. From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c)
1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book diagram by
David Cunningham
SOMETHING TO KEEP IN
MIND
• Form and function
A FACT
• All living cells are surrounded by a
plasma membrane
PLASMA MEMBRANE
COMPONENTS
• Lipid bilayer
• Cholesterol (in animals)
• Integral proteins
• Peripheral proteins
• Glycolipids
IMPORTANT FACT
• Phospholipids will spontaneously form
bi-layers when immersed in water.
MORE KITCHEN PHYSICS
• WATER TENDS TO LOWER
POTENTIAL IN 3 WAYS:
– Gravity wise
– Pressure wise – Concentration wise
TWO EXTREMES
Dilution Fresh Water Lake
Dehydration
Ocean
A FACT
• Diffusion requires random,
independent movement of particles.
A THOUGHT EXPERIMENT
• Open a perfume bottle. If more perfume
particles are inside the bottle at the outset
there should be a net flow (to or from?) the
bottle based on chance alone?
A FACT
• Water moves DOWN a concentration
gradient, the steeper the faster.
OSMOSIS
• Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
HOW TO OVERCOME
OSMOTIC TENDENCY
• IN FRESH WATER - Use a water pump to
maintain hypertonic condition
• IN SEA WATER - (1) Use salt pump to
maintain hypotonic condition or (2)
maintain isotonic condition.
3 WAYS TO GET MATERIALS
IN AND OUT OF CELLS
• Osmosis
• Carrier assisted - passive or active
• Vesicular
From The World Book (TM) Multimedia Encyclopedia (c) 1999 World Book, Inc., 525 W. Monroe, Chicago, IL
60661. All rights reserved. "World Book illustration by John F. Eggert
ANOTHER IMPORTANT
FACT
• The rate of facilitated diffusion
depends upon the number of protein
facilitators and the rate of movement
through them
2 TYPES OF VESICULAR
TRANSPORT
• Exocytosis - out of cell
• Endocytosis - into cell
36



